Thermochemistry 2 Matching Match each item with the correct
... Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
... Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
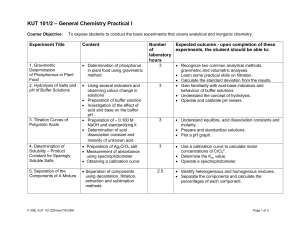
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Differentiate the primary and secondary standards. • Differentiate the equivalence and end-points. • Choose suitable indicators for acid-base titration. • Determine the amount of acid in an unknown. • Know a quantitative technique of volumetric analysis. • Understand the definition of BOD (Biochem ...
... • Differentiate the primary and secondary standards. • Differentiate the equivalence and end-points. • Choose suitable indicators for acid-base titration. • Determine the amount of acid in an unknown. • Know a quantitative technique of volumetric analysis. • Understand the definition of BOD (Biochem ...
+ H 2 (g) - WordPress.com
... (usually 25°C). These standard conditions are indicated with a degree sign (°). When reactants in their standard states yield products in their standard states, the enthalpy of reaction is called the standard enthalpy of reaction, DH°. (DH° is read “delta H zero.”) ...
... (usually 25°C). These standard conditions are indicated with a degree sign (°). When reactants in their standard states yield products in their standard states, the enthalpy of reaction is called the standard enthalpy of reaction, DH°. (DH° is read “delta H zero.”) ...
Chapter 6A Chemical Reactions CHAPTER OUTLINE
... q The physical state of the substances are indicated by the symbols (s), (l), (g), (aq). Δ 2 Al (s) + Fe2O3 (s) → 2 Fe (l) + Al2O3 (s) solid ...
... q The physical state of the substances are indicated by the symbols (s), (l), (g), (aq). Δ 2 Al (s) + Fe2O3 (s) → 2 Fe (l) + Al2O3 (s) solid ...
class-11thermodynamics
... Types of Thermodynamic Process (i) Isothermal process :-A process which is carried out at constant temperature. (ii) Adiabatic process:-A process which is carried out in such a way that no heat flows from the system to surroundings and vice versa. (iii) Isochoric process :-A process which is carrie ...
... Types of Thermodynamic Process (i) Isothermal process :-A process which is carried out at constant temperature. (ii) Adiabatic process:-A process which is carried out in such a way that no heat flows from the system to surroundings and vice versa. (iii) Isochoric process :-A process which is carrie ...
CP Chemistry Midterm Study Guide
... 20. What is the solution concentration of 25 g of NaCl mixed in 50 g of H2O? 21. How many grams of MgCl2 are in 500 mL of a 3.2 M solution? 22. How many atoms of sulfur do you have if you have 4 moles? 23. Convert 500 grams of magnesium to moles. 24. If we have 6.02x1023 molecules of oxygen, how man ...
... 20. What is the solution concentration of 25 g of NaCl mixed in 50 g of H2O? 21. How many grams of MgCl2 are in 500 mL of a 3.2 M solution? 22. How many atoms of sulfur do you have if you have 4 moles? 23. Convert 500 grams of magnesium to moles. 24. If we have 6.02x1023 molecules of oxygen, how man ...
Audit Schedule
... and Kelvin. 5. To apply the rules for significant figures. 6. To distinguish between precision and accuracy. Study Hints: 1. In the textbook, the problems are worked with a calculator and the answer is rounded to the correct number of significant figures only at the end of the problem. Rounding off ...
... and Kelvin. 5. To apply the rules for significant figures. 6. To distinguish between precision and accuracy. Study Hints: 1. In the textbook, the problems are worked with a calculator and the answer is rounded to the correct number of significant figures only at the end of the problem. Rounding off ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... 8.1 Dynamic equilibrium 8.1.1 Outline the characteristics of a system in a state of equilibrium. Many chemical reactions are reversible and never go to completion. Equilibrium can be approached from both directions. For a system in equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the ...
... 8.1 Dynamic equilibrium 8.1.1 Outline the characteristics of a system in a state of equilibrium. Many chemical reactions are reversible and never go to completion. Equilibrium can be approached from both directions. For a system in equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the ...
Thermochemistry
... The state of any system is described by properties such as pressure, volume, temperature, density, composition, and so forth. Some, or all, of these properties will change as the state of the system changes. For example, if 1.00 L of gas is warmed from 25oC to 100oC at a constant pressure, the volum ...
... The state of any system is described by properties such as pressure, volume, temperature, density, composition, and so forth. Some, or all, of these properties will change as the state of the system changes. For example, if 1.00 L of gas is warmed from 25oC to 100oC at a constant pressure, the volum ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... 2. The relative masses of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction can be determined from the reaction’s coefficients. ...
... 2. The relative masses of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction can be determined from the reaction’s coefficients. ...
File
... • If a chemical equation is reversed, then the sign of ΔrH changes. • If the coefficients of a chemical equation are altered by multiplying or dividing by a constant factor, then the ΔrH is altered by the same factor. ...
... • If a chemical equation is reversed, then the sign of ΔrH changes. • If the coefficients of a chemical equation are altered by multiplying or dividing by a constant factor, then the ΔrH is altered by the same factor. ...
ME 215
... A closed tank contains compressed air and oil (SGoil 0.90) as is shown in Fig. A U-tube manometer using mercury (SGHg = 13.6) is connected to the tank as shown. For column heights h1=15 cm, h2=7 cm, and h3=10 cm, determine the pressure reading of the gage. The pressure at level (1) is equal to the p ...
... A closed tank contains compressed air and oil (SGoil 0.90) as is shown in Fig. A U-tube manometer using mercury (SGHg = 13.6) is connected to the tank as shown. For column heights h1=15 cm, h2=7 cm, and h3=10 cm, determine the pressure reading of the gage. The pressure at level (1) is equal to the p ...
Chapter 8
... 1. Some oxy-acids, when heated, decompose to form water and the nonmetal oxide. Example: Sulfuric acid is heated Example: Nitric acid is heated 2. Some metallic hydroxides (bases), when heated, decompose to form the metal oxide and water. Example: Sodium hydroxide is heated Example: Calcium hydroxid ...
... 1. Some oxy-acids, when heated, decompose to form water and the nonmetal oxide. Example: Sulfuric acid is heated Example: Nitric acid is heated 2. Some metallic hydroxides (bases), when heated, decompose to form the metal oxide and water. Example: Sodium hydroxide is heated Example: Calcium hydroxid ...
Honors Chapter 11 Reactions
... numbers in front of formula distributes to numbers of atoms in formula specifies the relative number of moles and molecules involved in the reaction used to balance the equation ...
... numbers in front of formula distributes to numbers of atoms in formula specifies the relative number of moles and molecules involved in the reaction used to balance the equation ...
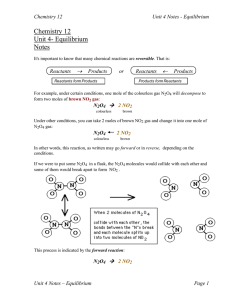
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.