Thomson`s Experiment
... How Rutherford Explained It To explain the results of the experiment, Rutherford’s team proposed a new model of the atom: Because most of the particles passed through the foil, they concluded that the atom is nearly all empty space. ...
... How Rutherford Explained It To explain the results of the experiment, Rutherford’s team proposed a new model of the atom: Because most of the particles passed through the foil, they concluded that the atom is nearly all empty space. ...
Honors Chemistry Name_______________________________
... 15. Assume the following three isotopes of element Q exist: 258.63 amu, which of its isotopes is most abundant? A. 248Q B. 252Q C. 259Q 16. The symbol “Si” is used to represent the element _____. A. silver B. silicon C. sodium ...
... 15. Assume the following three isotopes of element Q exist: 258.63 amu, which of its isotopes is most abundant? A. 248Q B. 252Q C. 259Q 16. The symbol “Si” is used to represent the element _____. A. silver B. silicon C. sodium ...
Father of the Periodic Table.
... by this scientist to explain the existence of electrons. Show Answer ...
... by this scientist to explain the existence of electrons. Show Answer ...
CHEMISTRY Periodic Table of the Elements
... What does the phenolphthalein indicate? What does this mean? Based on part B, what other substance do you think was produced? Why? Rate these 3 metals in order of their reactivity with the water. Write full electron configurations for Li, Na and K. How many electrons do each of them have in their ou ...
... What does the phenolphthalein indicate? What does this mean? Based on part B, what other substance do you think was produced? Why? Rate these 3 metals in order of their reactivity with the water. Write full electron configurations for Li, Na and K. How many electrons do each of them have in their ou ...
Redox Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
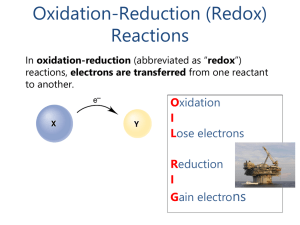
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
Unit 3-The Atom Chapter Packet
... _____________________________3. proposed the first atomic model that accounted for the electrical nature of the atom _____________________________4. measured the size of the charge on an electron _____________________________5. suggested that alpha particles might be rebounding at an angle approachi ...
... _____________________________3. proposed the first atomic model that accounted for the electrical nature of the atom _____________________________4. measured the size of the charge on an electron _____________________________5. suggested that alpha particles might be rebounding at an angle approachi ...
Group 1: The Alkali Metals
... Properties and Facts about Alkali Metals Alkali metals are known for being some of the most reactive metals. This is due in part to their larger atomic radii and low ionization energies. They tend to donate their electrons in reactions and often have an oxidation state of +1. These metals are charac ...
... Properties and Facts about Alkali Metals Alkali metals are known for being some of the most reactive metals. This is due in part to their larger atomic radii and low ionization energies. They tend to donate their electrons in reactions and often have an oxidation state of +1. These metals are charac ...
Chapter 3-3—Parts of the Atom - Phoenix Union High School District
... Atoms have a center or core called a nucleus The nucleus contains 2 subatomic particles: Proton that has a positive charge Neutron that has a NEUTRAL charge Protons and neutrons together are called nucleons because they are in the nucleus The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of very tiny particle ...
... Atoms have a center or core called a nucleus The nucleus contains 2 subatomic particles: Proton that has a positive charge Neutron that has a NEUTRAL charge Protons and neutrons together are called nucleons because they are in the nucleus The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of very tiny particle ...
Hands-On Chemistry Unit
... atom: the smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element element: the simplest type of pure substance; a substance consisting entirely of atoms having identical chemical properties solid: matter with a definite shape and volume liquid: matter with no definite shape but with ...
... atom: the smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element element: the simplest type of pure substance; a substance consisting entirely of atoms having identical chemical properties solid: matter with a definite shape and volume liquid: matter with no definite shape but with ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
Ch6-Energy in Chemical Reactions-Chemical Reactions
... need a conversion factor to convert grams to atoms or molecules. Mole is the connection or the conversion factor between atoms and grams. Mole is just a large number 6.022 x 1023 for counting atoms like dozen -12 for counting to make counting of eggs easier. Since atoms are so small, we need large n ...
... need a conversion factor to convert grams to atoms or molecules. Mole is the connection or the conversion factor between atoms and grams. Mole is just a large number 6.022 x 1023 for counting atoms like dozen -12 for counting to make counting of eggs easier. Since atoms are so small, we need large n ...
Honors Chemistry
... different kinds of emissions alpha, a, particles with a mass 4x H atom and + charge beta, b, particles with a mass ~1/2000th H atom and – ...
... different kinds of emissions alpha, a, particles with a mass 4x H atom and + charge beta, b, particles with a mass ~1/2000th H atom and – ...
Mass Number, A
... particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical (all hydrogen atoms are identical). 3. The atoms of an element are different than the atoms of another element (hydrogen is different than helium). 4. Atoms of one element can combine with the atoms of another element to make c ...
... particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical (all hydrogen atoms are identical). 3. The atoms of an element are different than the atoms of another element (hydrogen is different than helium). 4. Atoms of one element can combine with the atoms of another element to make c ...
Honors Chemistry
... different kinds of emissions alpha, a, particles with a mass 4x H atom and + charge beta, b, particles with a mass ~1/2000th H atom and – ...
... different kinds of emissions alpha, a, particles with a mass 4x H atom and + charge beta, b, particles with a mass ~1/2000th H atom and – ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In Al2O3, the ions are Al+3 and O2–, so oxidation #’s: Al = +3 and O = -2 3. In a compound or polyatomic ion, – Group I elements are always +1. – Group II elements are always +2. – Fluorine is always -1. – Oxygen is usua ...
... Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In Al2O3, the ions are Al+3 and O2–, so oxidation #’s: Al = +3 and O = -2 3. In a compound or polyatomic ion, – Group I elements are always +1. – Group II elements are always +2. – Fluorine is always -1. – Oxygen is usua ...
Utah - Wavefunction, Inc.
... → Lab 89 "The Alkali Metals" → Lab 90 "The Alkaline Earth Metals" → Lab 91 "The Elements of the Boron Group" → Lab 92 "The Elements of the Carbon Group" → Lab 93 "The Elements of the Nitrogen Group" → Lab 94 "The Elements of the Oxygen Group" → Lab 95 "The Halogens" → ...
... → Lab 89 "The Alkali Metals" → Lab 90 "The Alkaline Earth Metals" → Lab 91 "The Elements of the Boron Group" → Lab 92 "The Elements of the Carbon Group" → Lab 93 "The Elements of the Nitrogen Group" → Lab 94 "The Elements of the Oxygen Group" → Lab 95 "The Halogens" → ...
Key Concept Summary - Bellingham High School
... Metalloid (semimetal): is an element having both metallic and nonmetallic properties. Or into three groups Main group elements are those in groups 1, 2 and 13-18. when form ions, group 1, 2 lose the same # e as their group #; group 13 lose group #-10; group 14-18 gain 18-group #. Transition elements ...
... Metalloid (semimetal): is an element having both metallic and nonmetallic properties. Or into three groups Main group elements are those in groups 1, 2 and 13-18. when form ions, group 1, 2 lose the same # e as their group #; group 13 lose group #-10; group 14-18 gain 18-group #. Transition elements ...
Document
... • Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill from the lowest possible energy to the highest energy. • Hund’s Rule In orbitals of EQUAL ENERGY (p, d, and f), place one electron in each orbital before making any pairs. All single electrons must spin the same way • Pauli Exclusion Principle says that ...
... • Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill from the lowest possible energy to the highest energy. • Hund’s Rule In orbitals of EQUAL ENERGY (p, d, and f), place one electron in each orbital before making any pairs. All single electrons must spin the same way • Pauli Exclusion Principle says that ...
Chapter 7: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... integer whose value must be between - l and + l. mℓ specifies the direction of the orbital. Think of a specific orbital (or specific wave function ψ) as the house for an electron. The house is characterized by an address (three quantum numbers: n, ℓ and mℓ). n defines the city (shell) where ...
... integer whose value must be between - l and + l. mℓ specifies the direction of the orbital. Think of a specific orbital (or specific wave function ψ) as the house for an electron. The house is characterized by an address (three quantum numbers: n, ℓ and mℓ). n defines the city (shell) where ...
2.1 Imaging and Moving Individual Atoms
... pitchblende produced a current 300 times stronger than that produced by pure uranium. They tested and recalibrated their instruments, and yet they still found the same puzzling results. The Curies reasoned that a very active unknown substance in addition to the uranium must exist within the pitchbl ...
... pitchblende produced a current 300 times stronger than that produced by pure uranium. They tested and recalibrated their instruments, and yet they still found the same puzzling results. The Curies reasoned that a very active unknown substance in addition to the uranium must exist within the pitchbl ...
Chemistry Academic v. 2016
... Compare an element’s relativity to that of other elements. Describe chemical reactions in terms of atomic rearrangement and /or electron configuration. Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arrangement of elements on the periodic table. Compare and/or predict the properties ( ...
... Compare an element’s relativity to that of other elements. Describe chemical reactions in terms of atomic rearrangement and /or electron configuration. Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arrangement of elements on the periodic table. Compare and/or predict the properties ( ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table PPT
... Quantum mechanics electrons can only exist in specified energy states ...
... Quantum mechanics electrons can only exist in specified energy states ...