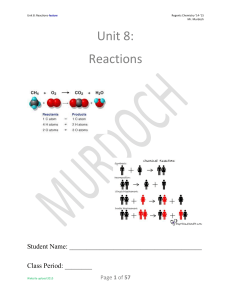
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Q - Write simplest formulas for propene (C3H6), C2H2, glucose (C6H12O6), octane (C8H14) Q - Identify these as simplest formula, molecular formula, or both H2O, C4H10, CH, NaCl A - CH2 CH CH2O C 4H 7 A - H2O is both simplest and molecular C4H10 is molecular (C2H5 would be simplest) CH is simplest (no ...
... Q - Write simplest formulas for propene (C3H6), C2H2, glucose (C6H12O6), octane (C8H14) Q - Identify these as simplest formula, molecular formula, or both H2O, C4H10, CH, NaCl A - CH2 CH CH2O C 4H 7 A - H2O is both simplest and molecular C4H10 is molecular (C2H5 would be simplest) CH is simplest (no ...
Thermochemistry and calorimetry
... The most common types of calorimeters contain a known quantity of water which absorbs the heat released by the reaction. Because the specific heat capacity of water (4.184 J g–1 K–1) is known to high precision, a measurement of its temperature rise due to the reaction enables one to calculate the qu ...
... The most common types of calorimeters contain a known quantity of water which absorbs the heat released by the reaction. Because the specific heat capacity of water (4.184 J g–1 K–1) is known to high precision, a measurement of its temperature rise due to the reaction enables one to calculate the qu ...
Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
... graphitic sheets rolled into closed concentric tubes (with 50 nm o.d. and microns in length), each separated by van der Waals forces to have a gap of 3.4 Å. Carbon nanotubes have been known to promote electron-transfer reactions of cytochrome c,[2] NADH,[1,6] catecholamine neurotransmitters,[3] and ...
... graphitic sheets rolled into closed concentric tubes (with 50 nm o.d. and microns in length), each separated by van der Waals forces to have a gap of 3.4 Å. Carbon nanotubes have been known to promote electron-transfer reactions of cytochrome c,[2] NADH,[1,6] catecholamine neurotransmitters,[3] and ...
mark scheme - A-Level Chemistry
... HCl would form a (white) precipitate / (white) solid (with silver nitrate and this would interfere with the test) It is not sufficient simply to state either that it will interfere or simply that the ions / compounds react to form AgCl ...
... HCl would form a (white) precipitate / (white) solid (with silver nitrate and this would interfere with the test) It is not sufficient simply to state either that it will interfere or simply that the ions / compounds react to form AgCl ...
Slide 1
... through a bed of shredded scrap iron, resulting in the copper ions being plated out as solid Cu on the iron surface. • For the process to be efficient, the surface of the scrap iron must be large. ...
... through a bed of shredded scrap iron, resulting in the copper ions being plated out as solid Cu on the iron surface. • For the process to be efficient, the surface of the scrap iron must be large. ...
honors chemistry harvard-westlake second semester final exam
... -you should be able to distinguish among common strong/weak acids and bases -you should know how a buffer solution is prepared and how it functions (not to mention why) Unit 13 -you should be able to calculate E o for an electrochemical cell and correctly interpret a diagram for a galvanic cell (flo ...
... -you should be able to distinguish among common strong/weak acids and bases -you should know how a buffer solution is prepared and how it functions (not to mention why) Unit 13 -you should be able to calculate E o for an electrochemical cell and correctly interpret a diagram for a galvanic cell (flo ...
Unit 8: Reactions
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
... 3. Double Replacement: A solution reaction in which the positive ion of one compound combines with the negative ion of the other compound to form a precipitate, and the other ions remain dissolved in solution. 4. Law of Conservation of Charge: Charge may not be created or destroyed by physical or ch ...
General Sciences Sample First Exercise Propanoic Acid Solution
... A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1) which is liberated from one liter of hydrogen peroxi ...
... A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1) which is liberated from one liter of hydrogen peroxi ...
The aim of this exercise is to study the acid... prepare a buffer solution. General Sciences Sample
... A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1) which is liberated from one liter of hydrogen peroxi ...
... A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1) which is liberated from one liter of hydrogen peroxi ...
Chemical Equilibrium Stress? What stress? 1
... The concentration of a pure liquid cannot change, it is fixed and equal to the liquid’s K = [H2]2 [O2] density. [H2O]2 We know that K remains constant for all combinations of reactant and product K[H2O]2 = [H2]2 [O2] = K concentrations at equilibrium. Therefore, since K is constant and the con ...
... The concentration of a pure liquid cannot change, it is fixed and equal to the liquid’s K = [H2]2 [O2] density. [H2O]2 We know that K remains constant for all combinations of reactant and product K[H2O]2 = [H2]2 [O2] = K concentrations at equilibrium. Therefore, since K is constant and the con ...
Stoichiometry
... • A 2.00 g sample of ammonia is mixed with 4.00 g of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant and how much excess reactant remains after the reaction has stopped? • First, we need to create a balanced equation for the reaction: 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g)4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) • Next we can use stoichiometry to ca ...
... • A 2.00 g sample of ammonia is mixed with 4.00 g of oxygen. Which is the limiting reactant and how much excess reactant remains after the reaction has stopped? • First, we need to create a balanced equation for the reaction: 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g)4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) • Next we can use stoichiometry to ca ...
Activating Nonreducible Oxides via Doping
... methodology and therefore require a finite conductivity of the sample. Because most nonreducible oxides are insulators even in the doped state, we have mimicked their properties by growing oxide films on metal single crystals. We have focused on the thickness range of 10−50 ML, thick enough to suppres ...
... methodology and therefore require a finite conductivity of the sample. Because most nonreducible oxides are insulators even in the doped state, we have mimicked their properties by growing oxide films on metal single crystals. We have focused on the thickness range of 10−50 ML, thick enough to suppres ...
Belarus, National Final, 2008 (PDF 405K).
... brush or with the hand, and let dry: then place it in the furnace... Fire slowly at first for the space of an hour, then increase the fire until you see the minium flow like wax, then permit the furnace to cool, open it and take out the well-glazed ...
... brush or with the hand, and let dry: then place it in the furnace... Fire slowly at first for the space of an hour, then increase the fire until you see the minium flow like wax, then permit the furnace to cool, open it and take out the well-glazed ...
Membrane Processes_part 1
... This process depends on the presence of an electrical filed across the selectively permeable membrane. The driving force is an electromotive force (electrical potential) When electromotive force is applied across the permeable membrane: – An increased rate of ion transfer will occur – This results i ...
... This process depends on the presence of an electrical filed across the selectively permeable membrane. The driving force is an electromotive force (electrical potential) When electromotive force is applied across the permeable membrane: – An increased rate of ion transfer will occur – This results i ...
New Advances in Catalytic Systems for Conversion of CH4 and CO2
... are much more active than the raw material, they are consumed before recovery, making products separation and by-products recovery very difficult. Furthermore, the greenhouse effect on global environment is going from bad to worse due to the extra discharge of CO2 , so that direct conversion of CO2 ...
... are much more active than the raw material, they are consumed before recovery, making products separation and by-products recovery very difficult. Furthermore, the greenhouse effect on global environment is going from bad to worse due to the extra discharge of CO2 , so that direct conversion of CO2 ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... If everything in the reaction went according to plan, and all of the reactant(s) reacted, this is how much product should be made. This is NOT the same as the actual yield- amount that is produced based on an experiment Error occurs, so actual yield is less than the ...
... If everything in the reaction went according to plan, and all of the reactant(s) reacted, this is how much product should be made. This is NOT the same as the actual yield- amount that is produced based on an experiment Error occurs, so actual yield is less than the ...
Student Review Packet
... NOTE: Graph should have “pH” as the vertical axis and “added base” as the horizontal axis. The graph should be in a “double S” shape. The middle of the lower part of the “first S” indicates the point of maximum buffering of the first buffering zone where [H2A] / [HA-] = 1. The middle of the “first S ...
... NOTE: Graph should have “pH” as the vertical axis and “added base” as the horizontal axis. The graph should be in a “double S” shape. The middle of the lower part of the “first S” indicates the point of maximum buffering of the first buffering zone where [H2A] / [HA-] = 1. The middle of the “first S ...
Microbial Electrolytic Carbon Capture for Carbon
... The MECC reactors were operated in continuous-flow mode using both AW and PW. Despite a similar COD provided in both reactors, the maximum current generated from PW reached to 130 A/m3, which was 58% higher than the peak current from AW (Figure 2). This should be mainly due to the more than doubled c ...
... The MECC reactors were operated in continuous-flow mode using both AW and PW. Despite a similar COD provided in both reactors, the maximum current generated from PW reached to 130 A/m3, which was 58% higher than the peak current from AW (Figure 2). This should be mainly due to the more than doubled c ...
Unit - 7.pmd
... boiling points are 198.4 and 239.7 K respectively. In the solid and liquid states, it is associated through hydrogen bonds as in the case of water and that accounts for its higher melting and boiling points than expected on the basis of its molecular mass. The ammonia molecule is trigonal pyramidal ...
... boiling points are 198.4 and 239.7 K respectively. In the solid and liquid states, it is associated through hydrogen bonds as in the case of water and that accounts for its higher melting and boiling points than expected on the basis of its molecular mass. The ammonia molecule is trigonal pyramidal ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... (a) Explain how a sodium atom changes into a sodium ion. (2 marks) (b) Explain how a chlorine atom changes into a chloride ion. (2 marks) Rubidium (Rb) is in the same group of the periodic table as sodium. Rubidium reacts with chlorine to make rubidium chloride. (c) Predict the formula of rubidium c ...
... (a) Explain how a sodium atom changes into a sodium ion. (2 marks) (b) Explain how a chlorine atom changes into a chloride ion. (2 marks) Rubidium (Rb) is in the same group of the periodic table as sodium. Rubidium reacts with chlorine to make rubidium chloride. (c) Predict the formula of rubidium c ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that measures rates of chemical reactions, studies the factors that influence them, designs and prepares new catalysts, and interprets the results at the molecular level. The independent variable of chemical kinetics, from the chemical reaction starting m ...
... Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that measures rates of chemical reactions, studies the factors that influence them, designs and prepares new catalysts, and interprets the results at the molecular level. The independent variable of chemical kinetics, from the chemical reaction starting m ...
Word Document
... importance of science literacy for a vibrant society, the need for students at all levels to be able to use scientific principles and processes meaningfully, and the critical role of the student in the learning process (constructivism). Standards and plans for action have been delineated in the docu ...
... importance of science literacy for a vibrant society, the need for students at all levels to be able to use scientific principles and processes meaningfully, and the critical role of the student in the learning process (constructivism). Standards and plans for action have been delineated in the docu ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.