The p-Block Elements The p-Block Elements
... boiling points are 198.4 and 239.7 K respectively. In the solid and liquid states, it is associated through hydrogen bonds as in the case of water and that accounts for its higher melting and boiling points than expected on the basis of its molecular mass. The ammonia molecule is trigonal pyramidal ...
... boiling points are 198.4 and 239.7 K respectively. In the solid and liquid states, it is associated through hydrogen bonds as in the case of water and that accounts for its higher melting and boiling points than expected on the basis of its molecular mass. The ammonia molecule is trigonal pyramidal ...
Word Document
... importance of science literacy for a vibrant society, the need for students at all levels to be able to use scientific principles and processes meaningfully, and the critical role of the student in the learning process (constructivism). Standards and plans for action have been delineated in the docu ...
... importance of science literacy for a vibrant society, the need for students at all levels to be able to use scientific principles and processes meaningfully, and the critical role of the student in the learning process (constructivism). Standards and plans for action have been delineated in the docu ...
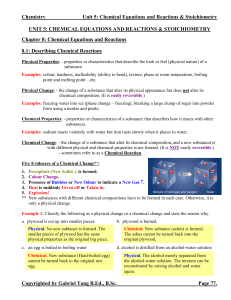
7.1 Describing Reactions
... If you examine this equation carefully, you will notice that the number of atoms on the left side does not equal the number of atoms on the right. The equation is not balanced. In order to show that mass is conserved during a reaction, a chemical equation must be balanced. You can balance a chemical ...
... If you examine this equation carefully, you will notice that the number of atoms on the left side does not equal the number of atoms on the right. The equation is not balanced. In order to show that mass is conserved during a reaction, a chemical equation must be balanced. You can balance a chemical ...
2E HARRY B. GRAY GEORGE S. HAMMONP.
... trichloride and 1 mole of chlorine, both at 1 atm pressure with the transformation occurring at the absolute temperature T. The values of AG, AH, and A$, on the other hand, are the changes in the thermodynamic functions at the reaction (pressure) conditions, that is, using the pressures of the react ...
... trichloride and 1 mole of chlorine, both at 1 atm pressure with the transformation occurring at the absolute temperature T. The values of AG, AH, and A$, on the other hand, are the changes in the thermodynamic functions at the reaction (pressure) conditions, that is, using the pressures of the react ...
C:\D\Books\Cambridge University Press\CUP Problems\Problems.wpd
... 91. Describe with necessary detail how the mass fraction wBOD is measured. 92. Define the mass fraction wCOD of an environmental water. COD =ˆ 'chemical oxygen demand'. 93. Describe with necessary detail how the mass fraction wCOD is measured. 94. The water in a sewer was analysed for salinity and b ...
... 91. Describe with necessary detail how the mass fraction wBOD is measured. 92. Define the mass fraction wCOD of an environmental water. COD =ˆ 'chemical oxygen demand'. 93. Describe with necessary detail how the mass fraction wCOD is measured. 94. The water in a sewer was analysed for salinity and b ...
chemistry
... (1) The catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway with a higher activation energy. (2) The catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. (3) The catalyst provides the same reaction pathway with a higher activation energy. (4) The catalyst provides the same rea ...
... (1) The catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway with a higher activation energy. (2) The catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. (3) The catalyst provides the same reaction pathway with a higher activation energy. (4) The catalyst provides the same rea ...
Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance in the order of C, H, and then O. The product, H2O, ...
... 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance in the order of C, H, and then O. The product, H2O, ...
Name chemistry Unit 8 worksheet 1. Why do
... 13. For each of the following pairs, choose the substance or process you would expect to react more rapidly. a. Granulated sugar or powdered sugar b. Zinc in HCl at 298 K or zinc in HCl at 410 K c. 5 g of thick platinum wire or 5 g of thin platinum wire 14. The heat of solution for silver nitrate is ...
... 13. For each of the following pairs, choose the substance or process you would expect to react more rapidly. a. Granulated sugar or powdered sugar b. Zinc in HCl at 298 K or zinc in HCl at 410 K c. 5 g of thick platinum wire or 5 g of thin platinum wire 14. The heat of solution for silver nitrate is ...
Class 3 updated Sep 30 2011
... There are two major steps in diffusion doping: predeposition and drive-in. During predeposition, impurity atoms are transported from the source onto the wafer surface and diffused into the wafer. The number of atoms that enter the wafer surface is limited by the solid solubility of the dopant in the ...
... There are two major steps in diffusion doping: predeposition and drive-in. During predeposition, impurity atoms are transported from the source onto the wafer surface and diffused into the wafer. The number of atoms that enter the wafer surface is limited by the solid solubility of the dopant in the ...
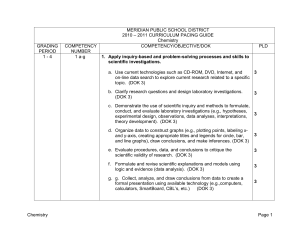
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the atomic model of matter by explaining atomic structure and chemical bonding. b. Research and explain crucial contributions and critical experiments of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, de Broglie, and Schrődinger and describe how each discovery contributed to t ...
... 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the atomic model of matter by explaining atomic structure and chemical bonding. b. Research and explain crucial contributions and critical experiments of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, de Broglie, and Schrődinger and describe how each discovery contributed to t ...
CHAPTER 21 ELECTROCHEMISTRY: CHEMICAL CHANGE AND
... a) The metal A is being oxidized to form the metal cation. To form positive ions, an atom must always lose electrons, so this half-reaction is always an oxidation. b) The metal ion B is gaining electrons to form the metal B, so it is displaced. c) The anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes ...
... a) The metal A is being oxidized to form the metal cation. To form positive ions, an atom must always lose electrons, so this half-reaction is always an oxidation. b) The metal ion B is gaining electrons to form the metal B, so it is displaced. c) The anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
... moles; mass; and volume. • Mass and atoms are conserved in every chemical reaction. 12.2 Chemical Calculations • In chemical calculations, mole ratios are used to convert between moles of reactant and moles of product, between moles of reactants, or between moles of products. ...
... moles; mass; and volume. • Mass and atoms are conserved in every chemical reaction. 12.2 Chemical Calculations • In chemical calculations, mole ratios are used to convert between moles of reactant and moles of product, between moles of reactants, or between moles of products. ...
Ch 9 Pkt - mvhs
... 26. How many g of water vapor can be generated from the combustion of 18.74 g of ethanol? C2H3O2(g) + O2 (g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) (unbalanced) 27. How many grams of sodium hydroxide are required to form 51.63 g of lead hydroxide? Pb(NO3)2(aq + NaOH(aq) Pb(OH)2(s) + NaNO3(aq) (unbalanced) 28. How many ...
... 26. How many g of water vapor can be generated from the combustion of 18.74 g of ethanol? C2H3O2(g) + O2 (g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) (unbalanced) 27. How many grams of sodium hydroxide are required to form 51.63 g of lead hydroxide? Pb(NO3)2(aq + NaOH(aq) Pb(OH)2(s) + NaNO3(aq) (unbalanced) 28. How many ...
New Materials from Metal Vapour Chemistry
... Another interesting example of cluster growth in the liquid phase that has recently found application in the fabrication of fuel cell electrodes involves the interaction of e.g. Ag, Pd and Pt atoms with ether and aromatic solvents, liquid oligoand poly-ethers and olefins, in the presence of various ...
... Another interesting example of cluster growth in the liquid phase that has recently found application in the fabrication of fuel cell electrodes involves the interaction of e.g. Ag, Pd and Pt atoms with ether and aromatic solvents, liquid oligoand poly-ethers and olefins, in the presence of various ...
Charging of Oil-Water Interfaces Due to Spontaneous Adsorption of
... coalescence of the emulsion droplets. In order to increase the reliability of the data, two alternative procedures for emulsion preparation were used. The first procedure was close to the standard method for preparation of surfactant containing emulsions. The purified and presaturated liquid phases ...
... coalescence of the emulsion droplets. In order to increase the reliability of the data, two alternative procedures for emulsion preparation were used. The first procedure was close to the standard method for preparation of surfactant containing emulsions. The purified and presaturated liquid phases ...
Stoichiometry, Lab Basics, Reactions
... ____ 16. When 70.0 mL of 3.00 M Na2CO3 is added to 30.0 mL of 1.00 M NaHCO3, the resulting concentration of Na+ is: A) 2.00 M B) 2.40 M C) 4.00 M D) 4.50 M E) 7.00 M ____ 17. A student wishes to prepare 2.00 L of 0.100 M KIO3 (MM 214). The proper procedure is to: A) weigh out 42.8 grams of KIO3 and ...
... ____ 16. When 70.0 mL of 3.00 M Na2CO3 is added to 30.0 mL of 1.00 M NaHCO3, the resulting concentration of Na+ is: A) 2.00 M B) 2.40 M C) 4.00 M D) 4.50 M E) 7.00 M ____ 17. A student wishes to prepare 2.00 L of 0.100 M KIO3 (MM 214). The proper procedure is to: A) weigh out 42.8 grams of KIO3 and ...
Chapter 18 - Louisiana Tech University
... temperature and pressure because of increased positional probabilities available for H2O. The additional positional probabilities comes from the extra rotations and vibrations H2O molecule can adopt because of more atoms in the molecule compared to simple H2 molecule. Measuring Dispersal or Disorder ...
... temperature and pressure because of increased positional probabilities available for H2O. The additional positional probabilities comes from the extra rotations and vibrations H2O molecule can adopt because of more atoms in the molecule compared to simple H2 molecule. Measuring Dispersal or Disorder ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.