Electronics - Kelso High School
... 7. Carry out calculations involving voltages and resistances in a voltage divider. 8. State that the time taken to charge a capacitor depends on 2 things: resistance of the circuit; the value of the capacitor. 9. Choose the most appropriate input device for a given application. ...
... 7. Carry out calculations involving voltages and resistances in a voltage divider. 8. State that the time taken to charge a capacitor depends on 2 things: resistance of the circuit; the value of the capacitor. 9. Choose the most appropriate input device for a given application. ...
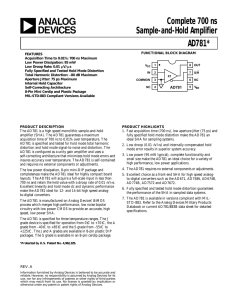
a Complete 700 ns Sample-and-Hold Amplifier AD781*
... *Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. ...
... *Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. ...
Radio astronomy receiver overview
... convenient in that ampli er gains in dB can be added to input signal levels to get output levels. The conversion to dBm is 10 log(PA ) + 30, where 30 comes from the change from Watts to milliWatts. At the output of the rst ampli er, point B, we have ?99:6 + 38 = ?61:6 dBm/MHz. At 50 MHZ the loss in ...
... convenient in that ampli er gains in dB can be added to input signal levels to get output levels. The conversion to dBm is 10 log(PA ) + 30, where 30 comes from the change from Watts to milliWatts. At the output of the rst ampli er, point B, we have ?99:6 + 38 = ?61:6 dBm/MHz. At 50 MHZ the loss in ...
Inverting amplifier
... Inverting amplifier gain • One of the main features of the inverting amplifier circuit is the overall gain that it produces. • This is quite easy to calculate. The voltage gain is actually the output voltage (Vout) divided by the input voltage (Vin), i.e. • it is the number of times the output volt ...
... Inverting amplifier gain • One of the main features of the inverting amplifier circuit is the overall gain that it produces. • This is quite easy to calculate. The voltage gain is actually the output voltage (Vout) divided by the input voltage (Vin), i.e. • it is the number of times the output volt ...
Questions
... b) A forward bias pn junction diode has the current ID = 3.5 mA. Consider that diode is operating at room temperature (300°K). If the reverse saturation current, IS = 1.5×10-11 mA and n = 1, determine the diode voltage VD. (6 marks) c) A diode circuit and its load line are as shown in Fig. 2(c). ...
... b) A forward bias pn junction diode has the current ID = 3.5 mA. Consider that diode is operating at room temperature (300°K). If the reverse saturation current, IS = 1.5×10-11 mA and n = 1, determine the diode voltage VD. (6 marks) c) A diode circuit and its load line are as shown in Fig. 2(c). ...
Measurements (final)
... In a clear day, a 10 inch by 8 inch solar panel can generate a voltage potential of 20 volts at the output. If a 40 Ohms resistance is connected to it, what is the electric current flowing through the circuit? ...
... In a clear day, a 10 inch by 8 inch solar panel can generate a voltage potential of 20 volts at the output. If a 40 Ohms resistance is connected to it, what is the electric current flowing through the circuit? ...
PRECISE ANALOG CURRENT DRIVER FOR MICRO-MECHANICAL
... The possibility of a sensorless actuator makes the SM A eligible for a new way of actuation. This implies that the main feature of a SM A current driver is the high precision in the measuring of the electrical characteristics of the wire. M oreover, to avoid any noise, the control frequency must be ...
... The possibility of a sensorless actuator makes the SM A eligible for a new way of actuation. This implies that the main feature of a SM A current driver is the high precision in the measuring of the electrical characteristics of the wire. M oreover, to avoid any noise, the control frequency must be ...
LF347 - Slot Tech Forum
... LF147 is a high-grade device. It is specified to be able to run at higher supply voltages, consume less power, lower noise, and generally improved characteristics over the LF347 devices. The chip is tested in the die form (before it goes into a case). Those with superior characteristics are put in c ...
... LF147 is a high-grade device. It is specified to be able to run at higher supply voltages, consume less power, lower noise, and generally improved characteristics over the LF347 devices. The chip is tested in the die form (before it goes into a case). Those with superior characteristics are put in c ...
DATASHEET SEARCH SITE | WWW.ALLDATASHEET.COM
... There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for printed-circuits with high populat ...
... There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for printed-circuits with high populat ...
MS Word - Sonoma State University
... Problem 2 (15 points) Design a MOS differential amplifier to operate from power supply voltages of VDD = 1 V and VSS = -1 V, and dissipate at most 1 mW of power P at its quiescent state (i.e., no applied input signal). Find the value of VOV so that a value for the differential input voltage, namely ...
... Problem 2 (15 points) Design a MOS differential amplifier to operate from power supply voltages of VDD = 1 V and VSS = -1 V, and dissipate at most 1 mW of power P at its quiescent state (i.e., no applied input signal). Find the value of VOV so that a value for the differential input voltage, namely ...
AC Series Circuit: Power and Resonance
... for the LRC circuit board last week. Assume the source voltage is 5.0 V. Hint: You should use frequency values which are grouped near resonance as well as some which are more widely spaced when away from the resonance frequency. Apparatus: The same RLC circuit board used last week, audio frequency ...
... for the LRC circuit board last week. Assume the source voltage is 5.0 V. Hint: You should use frequency values which are grouped near resonance as well as some which are more widely spaced when away from the resonance frequency. Apparatus: The same RLC circuit board used last week, audio frequency ...
EGM 180 Take Home Quiz 1
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
Ans: Analogue Electronics
... Fixed bias circuits get their bias voltages from independently designed reference voltage sources (or even something as simple as a voltage divider). Often is the case that the bias may be left for the end-user to give some control over the operation point of the circuit. Self Bias Circuit: Self bia ...
... Fixed bias circuits get their bias voltages from independently designed reference voltage sources (or even something as simple as a voltage divider). Often is the case that the bias may be left for the end-user to give some control over the operation point of the circuit. Self Bias Circuit: Self bia ...
ZODIAC DATA SYSTEMS
... The shown values were measured using an appropriately designed test system including the HEIM DATaRec® 4 power supplies under nominal conditions of temperature, voltage, etc.. ...
... The shown values were measured using an appropriately designed test system including the HEIM DATaRec® 4 power supplies under nominal conditions of temperature, voltage, etc.. ...
Valve RF amplifier

A valve RF amplifier (UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs.