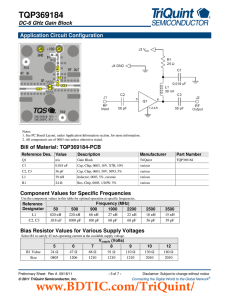
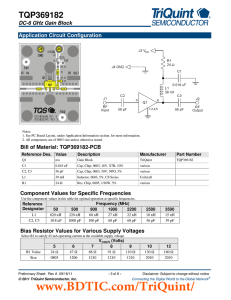
Experiment V: The AC Circuit, Impedance, and Applications to High
... (approaching infinity), the same circuit will have nearly zero resistance, and will be have like a short circuit. Conversely, we see that an inductor will behave like a short circuit for a DC current, and an open circuit as the frequency approaches infinity. So, what is all of this good for? We can ...
... (approaching infinity), the same circuit will have nearly zero resistance, and will be have like a short circuit. Conversely, we see that an inductor will behave like a short circuit for a DC current, and an open circuit as the frequency approaches infinity. So, what is all of this good for? We can ...
OP97
... The input pins of the OP97 are protected against large differential voltage by back-to-back diodes. Current-limiting resistors are not used to maintain low noise performance. If differential voltages above ±1 V are expected at the inputs, series resistors must be used to limit the current flow to a ...
... The input pins of the OP97 are protected against large differential voltage by back-to-back diodes. Current-limiting resistors are not used to maintain low noise performance. If differential voltages above ±1 V are expected at the inputs, series resistors must be used to limit the current flow to a ...
Xmedia_ELab1_FadingLED
... •Diode Test –Diodes only allow current to flow in one direction only, they have a positive (+) lead (i.e. anode) and a negative (-) lead (i.e. cathode) –LEDs are diodes that emit light –You can test the polarity of a diode using a multimeter set to "diode test" mode –Connect the black lead to (-) an ...
... •Diode Test –Diodes only allow current to flow in one direction only, they have a positive (+) lead (i.e. anode) and a negative (-) lead (i.e. cathode) –LEDs are diodes that emit light –You can test the polarity of a diode using a multimeter set to "diode test" mode –Connect the black lead to (-) an ...
G. Pascovici, IKP-Cologne, FEE Meeting, Saclay, 04 Dec - CEA-Irfu
... • solution only for small number of channels, • distribution of infrastructure signals (PS, adj.) ...
... • solution only for small number of channels, • distribution of infrastructure signals (PS, adj.) ...
Word - ITU
... programme with a considerable proportion of high audio-frequencies, which occur most frequently. However, the dynamic range of this type of programme is too wide and does not fulfil, therefore, the second requirement mentioned above. A signal which is appropriate for this purpose is a standardized c ...
... programme with a considerable proportion of high audio-frequencies, which occur most frequently. However, the dynamic range of this type of programme is too wide and does not fulfil, therefore, the second requirement mentioned above. A signal which is appropriate for this purpose is a standardized c ...
LECT7V23
... (note: Generally speaking, VOL is a function of fanout. In this case, for our model of saturation, the output voltage does not change with fanout. This is a special case. In general, we will have a noise margin which changes with fanout.) Now, we look at the high state case: When the output is high, ...
... (note: Generally speaking, VOL is a function of fanout. In this case, for our model of saturation, the output voltage does not change with fanout. This is a special case. In general, we will have a noise margin which changes with fanout.) Now, we look at the high state case: When the output is high, ...
Audio Frequency Amplifier Andradige Silva ENEE417 Introduction
... lab. The PSPICE simulation results heavily depended on the model of the speaker. The simulations done with the speaker model better correlated with the actual data. As seen in figure 12 the amplifier worked with constant gain up to 50 kHz, which was sufficient for our project. The final circuit is i ...
... lab. The PSPICE simulation results heavily depended on the model of the speaker. The simulations done with the speaker model better correlated with the actual data. As seen in figure 12 the amplifier worked with constant gain up to 50 kHz, which was sufficient for our project. The final circuit is i ...
J210 MMBFJ210 MMBFJ211 J211
... N-Channel RF Amplifier This device is designed for HF/VHF mixer/amplifier and applications where Process 50 is not adequate. Sufficient gain and low noise for sensitive receivers. Sourced from Process 90. ...
... N-Channel RF Amplifier This device is designed for HF/VHF mixer/amplifier and applications where Process 50 is not adequate. Sufficient gain and low noise for sensitive receivers. Sourced from Process 90. ...
SG3524 SMPS control circuit
... shutdown terminal: i.e., the output will be off with Pin 4 open and on when it is grounded. Finally, foldback current limiting can be provided with the network of Figure 10. This circuit can reduce the short-circuit current (ISC) to approximately one-third the maximum available output current (IMAX) ...
... shutdown terminal: i.e., the output will be off with Pin 4 open and on when it is grounded. Finally, foldback current limiting can be provided with the network of Figure 10. This circuit can reduce the short-circuit current (ISC) to approximately one-third the maximum available output current (IMAX) ...
Lecture 22: Class C Power Amplifiers
... amplifiers with directly-coupled resistive loads. To greatly reduce the power dissipated in the transistor, we will try operating Q outside of the active region! We could greatly increase the efficiency of such an amplifier if we incorporated the following characteristics: 1. To eliminate power diss ...
... amplifiers with directly-coupled resistive loads. To greatly reduce the power dissipated in the transistor, we will try operating Q outside of the active region! We could greatly increase the efficiency of such an amplifier if we incorporated the following characteristics: 1. To eliminate power diss ...
Source Transformation
... source in series with a resistor to a current source in parallel with resistor. ...
... source in series with a resistor to a current source in parallel with resistor. ...
Test Procedure for the NCP1013LED Evaluation Board Introduction:
... nominal. It is power limited if the power exceeds 5W. A typical transfer function of the output voltage‐ current characteristic is illustrated below. ...
... nominal. It is power limited if the power exceeds 5W. A typical transfer function of the output voltage‐ current characteristic is illustrated below. ...
MAX4100/MAX4101 500MHz, Low-Power Op
... and a 0.1dB gain flatness of 65MHz. It offers differential gain and phase errors of 0.06%/0.04°, respectively. The MAX4101 features a -3dB bandwidth of 200MHz, a 0.1dB bandwidth of 50MHz, and 0.07%/0.04° differential gain and phase. Available in small 8-pin SO and µMAX packages, these ICs are ideall ...
... and a 0.1dB gain flatness of 65MHz. It offers differential gain and phase errors of 0.06%/0.04°, respectively. The MAX4101 features a -3dB bandwidth of 200MHz, a 0.1dB bandwidth of 50MHz, and 0.07%/0.04° differential gain and phase. Available in small 8-pin SO and µMAX packages, these ICs are ideall ...
AD8614 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... the output directly to ground or to a supply rail can destroy the device. The typical maximum safe output current is 70 mA. In applications where some output current protection is needed, but not at the expense of reduced output voltage headroom, a low value resistor in series with the output can be ...
... the output directly to ground or to a supply rail can destroy the device. The typical maximum safe output current is 70 mA. In applications where some output current protection is needed, but not at the expense of reduced output voltage headroom, a low value resistor in series with the output can be ...
EX: a) Find a symbolic expression for v3 in the circuit below using
... a) Find a symbolic expression for v3 in the circuit below using not more than symbolic component names is, R1, R2, α = 32 (in the dependent voltage source), and β = 4 (in the dependent current source). b) Find the numerical value of v3 in the circuit below. ...
... a) Find a symbolic expression for v3 in the circuit below using not more than symbolic component names is, R1, R2, α = 32 (in the dependent voltage source), and β = 4 (in the dependent current source). b) Find the numerical value of v3 in the circuit below. ...
Valve RF amplifier

A valve RF amplifier (UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs.