Transformer - Electrical engineering
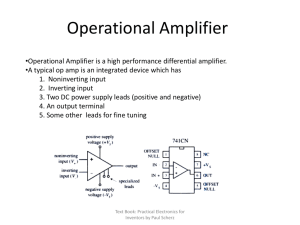
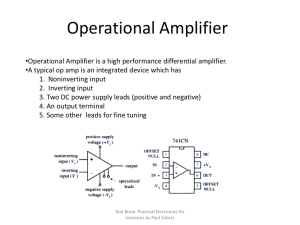
... •A typical op amp is an integrated device which has 1. Noninverting input 2. Inverting input 3. Two DC power supply leads (positive and negative) 4. An output terminal 5. Some other leads for fine tuning ...
... •A typical op amp is an integrated device which has 1. Noninverting input 2. Inverting input 3. Two DC power supply leads (positive and negative) 4. An output terminal 5. Some other leads for fine tuning ...
Transformer
... •A typical op amp is an integrated device which has 1. Noninverting input 2. Inverting input 3. Two DC power supply leads (positive and negative) 4. An output terminal 5. Some other leads for fine tuning ...
... •A typical op amp is an integrated device which has 1. Noninverting input 2. Inverting input 3. Two DC power supply leads (positive and negative) 4. An output terminal 5. Some other leads for fine tuning ...
Current and voltage
... Are voltage and current amplifiers separate devices, and if so, what are the differences between them? ...
... Are voltage and current amplifiers separate devices, and if so, what are the differences between them? ...
EE 101 Lab 2 Ohm`s and Kirchhoff`s Circuit Laws
... Please Circle One: Monday Lecture Tuesday Lecture ...
... Please Circle One: Monday Lecture Tuesday Lecture ...
7400
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N14A ...
DM74LS38 Quad 2-Input NAND Buffer with Open
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
Lecture 5
... The lay out of the circuit is very similar to that of the inverting amplifier or the integrator except that, in place of the feedback resistor R2 (of the inverter) or the capacitor C (of the integrator), we have a new component labelled D. In principle, and assuming the op amp to be ideal, in order ...
... The lay out of the circuit is very similar to that of the inverting amplifier or the integrator except that, in place of the feedback resistor R2 (of the inverter) or the capacitor C (of the integrator), we have a new component labelled D. In principle, and assuming the op amp to be ideal, in order ...
Where Can You Go after ELEC 312 ?
... IF2_VCO: It is a voltage controlled oscillator with a tuning range between 40MHz to 120MHz (partly covered in ELEC 312) Limiter Amplifier: A linear amplifier, receiving input from IF2_Mixer via a band-pass filter at 450 kHz. The gain is high ~90 dB (cascaded basic amplifiers chain with feedback and ...
... IF2_VCO: It is a voltage controlled oscillator with a tuning range between 40MHz to 120MHz (partly covered in ELEC 312) Limiter Amplifier: A linear amplifier, receiving input from IF2_Mixer via a band-pass filter at 450 kHz. The gain is high ~90 dB (cascaded basic amplifiers chain with feedback and ...
Example
... % wave forms that you generated wave_rec=sum(a); %the rectangular wave is form by summing these waves; plot(t,wave_rec); xlabel('t'); ylabel('wave forms'); hold on; plot(t,a(1,:),'r'); %the first sine wave (shown as red); plot(t,a(2,:),'g'); %the second sine wave (shown as green); ...
... % wave forms that you generated wave_rec=sum(a); %the rectangular wave is form by summing these waves; plot(t,wave_rec); xlabel('t'); ylabel('wave forms'); hold on; plot(t,a(1,:),'r'); %the first sine wave (shown as red); plot(t,a(2,:),'g'); %the second sine wave (shown as green); ...
File lm3875t | allcomponents.ru
... Over-Voltage Protection: The LM3875 contains overvoltage protection circuitry that limits the output current to approximately 4Apeak while also providing voltage clamping, though not through internal clamping diodes. The clamping effect is quite the same, however, the output transistors are designed ...
... Over-Voltage Protection: The LM3875 contains overvoltage protection circuitry that limits the output current to approximately 4Apeak while also providing voltage clamping, though not through internal clamping diodes. The clamping effect is quite the same, however, the output transistors are designed ...
Take another look at the Noise Bridge
... A practical design of the bridge circuit. The practical circuit of this noise bridge is shown in Figure 3. It can be seen there are the two parts described above, and a third part, a modulator. The noise source uses a reversed biased base emitter junction Q3 to generate a low level noise signal, whi ...
... A practical design of the bridge circuit. The practical circuit of this noise bridge is shown in Figure 3. It can be seen there are the two parts described above, and a third part, a modulator. The noise source uses a reversed biased base emitter junction Q3 to generate a low level noise signal, whi ...
G An Examination of Recovery Time of an Integrated Limiter/LNA
... with a lower incident power level. In this plot, the power tone F2 is no longer detectable. The small-signal tone F1 is still clipping, but not as much as in Figure 4. Under these conditions, the 10–90% rise time is < 5 ns. When this testing was conducted several test “issues” were noted and are lis ...
... with a lower incident power level. In this plot, the power tone F2 is no longer detectable. The small-signal tone F1 is still clipping, but not as much as in Figure 4. Under these conditions, the 10–90% rise time is < 5 ns. When this testing was conducted several test “issues” were noted and are lis ...
Noise - UniMAP Portal
... electronic devices are constantly producing noise voltage Vn(t). • Since it is dependent on temperature, it is also referred to as thermal noise. ...
... electronic devices are constantly producing noise voltage Vn(t). • Since it is dependent on temperature, it is also referred to as thermal noise. ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
INA111 High Speed FET-Input INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
... NOTE: (1) Temperature coefficient of the “50kΩ” term in the gain equation. The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of suc ...
... NOTE: (1) Temperature coefficient of the “50kΩ” term in the gain equation. The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of suc ...
AN-778 APPLICATION NOTE
... APPLICATION CIRCUIT FOR PRUP PIN The application circuit for the PRUP pin is shown in Figure 1. This circuit is used to condition the control signal for PRUP such that the device starts in the correct state. As described in the AD607 and AD61009 data sheets, there are instances when an improperly co ...
... APPLICATION CIRCUIT FOR PRUP PIN The application circuit for the PRUP pin is shown in Figure 1. This circuit is used to condition the control signal for PRUP such that the device starts in the correct state. As described in the AD607 and AD61009 data sheets, there are instances when an improperly co ...
Relative material
... tunable voltage between the bases of the Darlingtons X1 and X2. The purpose of this voltage is to bias the bases of the two Darlingtons, keeping them in a “slightly” ON state - a quiescent current of about 20 mA is desirable. Tuning is obtained through the use of potentiometer XRV1. The quiescent cu ...
... tunable voltage between the bases of the Darlingtons X1 and X2. The purpose of this voltage is to bias the bases of the two Darlingtons, keeping them in a “slightly” ON state - a quiescent current of about 20 mA is desirable. Tuning is obtained through the use of potentiometer XRV1. The quiescent cu ...
Valve RF amplifier

A valve RF amplifier (UK and Aus.) or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers during the 1960s and 1970s, initially for receivers and low power stages of transmitters, transmitter output stages switching to transistors somewhat later. Specially constructed valves are still in use for very high power transmitters, although rarely in new designs.