Organometallic Chemistry
... vitamin, cyanocobalamin (R = CN), does not occur in nature, but is used in many pharmaceuticals, supplements and as food additive, due to its stability and lower cost. In the body it is converted to the physiological forms, methylcobalamin (R = CH3) and adenosylcobalamin, leaving behind the cyanide. ...
... vitamin, cyanocobalamin (R = CN), does not occur in nature, but is used in many pharmaceuticals, supplements and as food additive, due to its stability and lower cost. In the body it is converted to the physiological forms, methylcobalamin (R = CH3) and adenosylcobalamin, leaving behind the cyanide. ...
Document
... given per mole. To find the total energy change, you must multiple by the number of moles (according to the balanced ...
... given per mole. To find the total energy change, you must multiple by the number of moles (according to the balanced ...
Unit 8: Reactions - Mark Rosengarten
... The substances that are reacted together, designated as the left side of a chemical equation. A chemical change where reactants are turned into products. A reaction in which one element is oxidized and another element is reduced. The gain of electron(s), causing the oxidation number of a species to ...
... The substances that are reacted together, designated as the left side of a chemical equation. A chemical change where reactants are turned into products. A reaction in which one element is oxidized and another element is reduced. The gain of electron(s), causing the oxidation number of a species to ...
Notes Set 1
... The table you have in front of you is a much more complete list than the one you made in the lab. It will be provided for you on the final exam. It is important that you know how to use this table. As you can see, there are several reactions that simply involve the transfer of electrons from an ion ...
... The table you have in front of you is a much more complete list than the one you made in the lab. It will be provided for you on the final exam. It is important that you know how to use this table. As you can see, there are several reactions that simply involve the transfer of electrons from an ion ...
Spring 2013 Semester Exam Study Guide (Bonding, Nomenclature
... ____ 95. A chemical equation is balanced when the a. coefficients of the reactants equal the coefficients of the products. b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the sub ...
... ____ 95. A chemical equation is balanced when the a. coefficients of the reactants equal the coefficients of the products. b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the sub ...
Scheme A Topic Checklist Atomic Structure 1.1
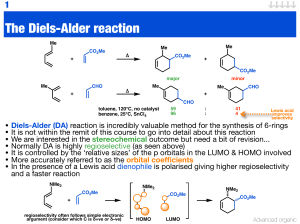
... different levels in a fractionating column because of the temperature gradient understand that cracking involves the breaking of C–C bonds in alkanes know that thermal cracking takes place at high pressure and high temperature and produces a high percentage of alkenes (mechanism not required) know t ...
... different levels in a fractionating column because of the temperature gradient understand that cracking involves the breaking of C–C bonds in alkanes know that thermal cracking takes place at high pressure and high temperature and produces a high percentage of alkenes (mechanism not required) know t ...
Lecture 4
... c. The oxidation number of fluorine is –1 in all compounds. The other halogens have an oxidation number of –1 in most binary compounds. When combined with oxygen, as in oxyanions, they have positive oxidation states. 4. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is zero. The ...
... c. The oxidation number of fluorine is –1 in all compounds. The other halogens have an oxidation number of –1 in most binary compounds. When combined with oxygen, as in oxyanions, they have positive oxidation states. 4. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is zero. The ...
Chemical Industry
... © OCR 2016 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work. OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: n/a Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resou ...
... © OCR 2016 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work. OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: n/a Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resou ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...
... The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if neutral, or equal to the charge if an ion. The oxidat ...








![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)