
5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY CATEGORY
... 4.Define osmotic pressure. How is it that measurement of osmotic pressures is more widely used for determining molar masses of macromolecules than the rise in boiling point or fall in freezing point of their solutions? 5. Calculate the amount of KCl which must be added to 1 kg of water so that its f ...
... 4.Define osmotic pressure. How is it that measurement of osmotic pressures is more widely used for determining molar masses of macromolecules than the rise in boiling point or fall in freezing point of their solutions? 5. Calculate the amount of KCl which must be added to 1 kg of water so that its f ...
Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and unwanted side-reactions. Furthermore, the timematching of the distinct reactions are ...
... played an important role to achieve high atom economy and sustainable chemistry.1-7 The major challenges in this field are compatibility between the reagents and catalysts present to prevent catalyst inhibition and unwanted side-reactions. Furthermore, the timematching of the distinct reactions are ...
Η - Knockhardy
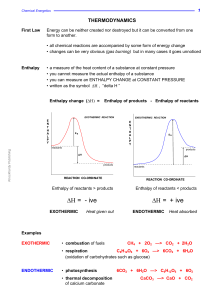
... • used for calculating changes which can’t be measured directly - Lattice Enthalpy • used for calculating ...
... • used for calculating changes which can’t be measured directly - Lattice Enthalpy • used for calculating ...
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
... 8. Even though the individual sets of equilibrium concentrations are quite different for the different situations, the equilibrium constant which depends on the ratio of the concentrations, remains the same. 9. Each set of equilibrium concentrations is called an ______________________________. 10. ...
... 8. Even though the individual sets of equilibrium concentrations are quite different for the different situations, the equilibrium constant which depends on the ratio of the concentrations, remains the same. 9. Each set of equilibrium concentrations is called an ______________________________. 10. ...
chapter_14 Equilibr
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
Reaction Rates
... reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transfe ...
... reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transfe ...
Catalytic hydrogenation
... (ketones, aldehydes) and C=N (imines) bond The catalytic hydrogenation of polar C=O and C=N bonds are key reactions in fine chemical and pharmaceutical synthesis. A very important group of catalysts operate by hydride transfer to the substrate in the outer coordination sphere of the complex. Hydroge ...
... (ketones, aldehydes) and C=N (imines) bond The catalytic hydrogenation of polar C=O and C=N bonds are key reactions in fine chemical and pharmaceutical synthesis. A very important group of catalysts operate by hydride transfer to the substrate in the outer coordination sphere of the complex. Hydroge ...
Is CO a Special Ligand in Organometallic Chemistry? Theoretical
... Carbon monoxide, CO, is a ubiquitous ligand in organometallic and coordination chemistry. In the present paper we investigate the neutral isoelectronic molecules AB ) N2, CO, BF, and SiO and their coordination in the model complexes Fe(CO)4AB and Fe(AB)5, using nonlocal density functional theory and ...
... Carbon monoxide, CO, is a ubiquitous ligand in organometallic and coordination chemistry. In the present paper we investigate the neutral isoelectronic molecules AB ) N2, CO, BF, and SiO and their coordination in the model complexes Fe(CO)4AB and Fe(AB)5, using nonlocal density functional theory and ...
First Poly(2-oxazoline)s with Pendant Amino Groups
... or catalysts that interfere with the polymerization mechanism were introduced into the polymer, not via the direct monomer route, but rather by modification of the polymer. A typical example is the reaction of poly(iodoaryl modified 2-oxazoline) with diphenyl phosphane yielding a polymer with pendan ...
... or catalysts that interfere with the polymerization mechanism were introduced into the polymer, not via the direct monomer route, but rather by modification of the polymer. A typical example is the reaction of poly(iodoaryl modified 2-oxazoline) with diphenyl phosphane yielding a polymer with pendan ...
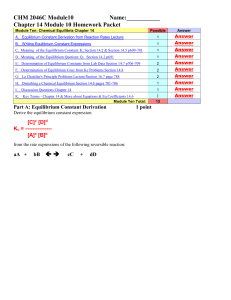
CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
... __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in __________________ equilibrium. __________________ 3. The state where the concentrations of the reactants and the products remain constant with time , it is said that ...
... __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in __________________ equilibrium. __________________ 3. The state where the concentrations of the reactants and the products remain constant with time , it is said that ...
Document
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
chap15pptlecture_chapte.ppt [Read-Only]
... two or more reactions, the equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is given by the product of the equilibrium constants of the individual reactions. ...
... two or more reactions, the equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is given by the product of the equilibrium constants of the individual reactions. ...




















![chap15pptlecture_chapte.ppt [Read-Only]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015369082_1-00cbf06a2d468a4ae1c963f5ca674e31-300x300.png)