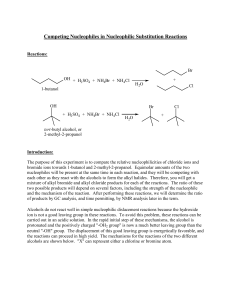
Final Review
... Balance the following chemical equations using the half-reaction method. SHOW WORK. a. As2O3 (s) + NO3- (aq) H3AsO4 (aq) + NO(g) (in acidic solution) b. CH3OH(aq) + Cr2O72CH2O(aq) + Cr3+ (aq) (in acidic solution) c. CN-(aq) + MnO4 -(aq) CNO-(aq) + MnO2 (s) (in basic solution) d. NO2-(aq) + Al(s) NH3 ...
... Balance the following chemical equations using the half-reaction method. SHOW WORK. a. As2O3 (s) + NO3- (aq) H3AsO4 (aq) + NO(g) (in acidic solution) b. CH3OH(aq) + Cr2O72CH2O(aq) + Cr3+ (aq) (in acidic solution) c. CN-(aq) + MnO4 -(aq) CNO-(aq) + MnO2 (s) (in basic solution) d. NO2-(aq) + Al(s) NH3 ...
REDOX PowerPoint - Southmoreland School District
... called a reducing agent Reduction – a species is reduced when it gains one or more electrons, and it is called an oxidizing agent Oxidation and reduction always occur together, never in isolation. If something gains electrons, something else had to lose them. ...
... called a reducing agent Reduction – a species is reduced when it gains one or more electrons, and it is called an oxidizing agent Oxidation and reduction always occur together, never in isolation. If something gains electrons, something else had to lose them. ...
KEY Final Exam Review - Iowa State University
... NO3¯ ---> NO 2) balance each half-reaction: 8H2S ---> S8 + 16H+ + 16e¯ 3e¯ + 4H+ + NO3¯ ---> NO + 2H2O 3) Make the number of electrons equal: 24H2S ---> 3S8 + 48H+ + 48e¯ <--- multiplied by a factor of 3 48e¯ + 64H+ + 16NO3¯ ---> 16NO + 32H2O <--- multiplied by a factor of 16 Note that 16 and 3 have ...
... NO3¯ ---> NO 2) balance each half-reaction: 8H2S ---> S8 + 16H+ + 16e¯ 3e¯ + 4H+ + NO3¯ ---> NO + 2H2O 3) Make the number of electrons equal: 24H2S ---> 3S8 + 48H+ + 48e¯ <--- multiplied by a factor of 3 48e¯ + 64H+ + 16NO3¯ ---> 16NO + 32H2O <--- multiplied by a factor of 16 Note that 16 and 3 have ...
CaCl2.2H2O assisted oxidation of alcohols with (NH4)2Cr2O7
... method, some of our results have compared with some of those reported in the literature19-21 (Table II). In summery, the CaCl2.2H2O was found to be an efficient reagent for the promotion of the oxidation of alcohols to their corresponding carbonyl compounds using (NH4)2Cr2O7. This new procedure is v ...
... method, some of our results have compared with some of those reported in the literature19-21 (Table II). In summery, the CaCl2.2H2O was found to be an efficient reagent for the promotion of the oxidation of alcohols to their corresponding carbonyl compounds using (NH4)2Cr2O7. This new procedure is v ...
L-13
... example, 2-decanol, were not suitable substrates for the reaction system and gave none of the desired product. However, the norborneol 2j gave allylated product 3j in 52% yield as a single isomer (entry 13). The reaction with hydroxy ester 2k gave the unsaturated ester 3k without any side products ...
... example, 2-decanol, were not suitable substrates for the reaction system and gave none of the desired product. However, the norborneol 2j gave allylated product 3j in 52% yield as a single isomer (entry 13). The reaction with hydroxy ester 2k gave the unsaturated ester 3k without any side products ...
Chapter 7 - HCC Learning Web
... attractions between valence electrons and the nucleus • Electrons are both attracted to the nucleus and repelled by other electrons ...
... attractions between valence electrons and the nucleus • Electrons are both attracted to the nucleus and repelled by other electrons ...
Module 3 Questions
... Note that at both the melting point (m.p.) and boiling point (b.p.), a certain amount of energy can be added to the system without a corresponding increase in temperature. ...
... Note that at both the melting point (m.p.) and boiling point (b.p.), a certain amount of energy can be added to the system without a corresponding increase in temperature. ...
chemical reaction
... the oxidation state(O.S) of an atom in the pure (uncombined) element is 0. The total (sum) of the oxidation state of all the atoms in a molecule or formula unit is 0. For an ion total of the oxidation state is equal to the charge on the ion. In their compounds the alkali metals (1a groups Li, Na, K, ...
... the oxidation state(O.S) of an atom in the pure (uncombined) element is 0. The total (sum) of the oxidation state of all the atoms in a molecule or formula unit is 0. For an ion total of the oxidation state is equal to the charge on the ion. In their compounds the alkali metals (1a groups Li, Na, K, ...
REAKSI SENYAWA KOMPLEKS
... time of disappearance of half the initial compound) of one minute or less as the criterion for lability. ...
... time of disappearance of half the initial compound) of one minute or less as the criterion for lability. ...
Rate of Reaction
... Rate of Reaction Rates of reactions are usually expressed in units of moles per liter per unit time. If we know the chemical equation for a reaction, its rate can be determined by following the change in concentration of any product or reactant that can be detected quantitatively. r = ∆ concentratio ...
... Rate of Reaction Rates of reactions are usually expressed in units of moles per liter per unit time. If we know the chemical equation for a reaction, its rate can be determined by following the change in concentration of any product or reactant that can be detected quantitatively. r = ∆ concentratio ...
File
... • This is because its anion is much more stable than that of ethanol • This enables it to lose a hydrogen ion ...
... • This is because its anion is much more stable than that of ethanol • This enables it to lose a hydrogen ion ...
exam review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2 NOCl(g) ↔ 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) using the following information. In one experiment 2.00 mol of NOCl is placed in a 1.00 -L flask, and the concentration of NO after equilibrium is achieved is 0.66 mol/L. 18. For the gas phase reaction H2(g) + I2(g) 2 HI(g) Kc = 50.3 at 731 K. 0.100 mol of HI is introd ...
... 2 NOCl(g) ↔ 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) using the following information. In one experiment 2.00 mol of NOCl is placed in a 1.00 -L flask, and the concentration of NO after equilibrium is achieved is 0.66 mol/L. 18. For the gas phase reaction H2(g) + I2(g) 2 HI(g) Kc = 50.3 at 731 K. 0.100 mol of HI is introd ...
Test 8 Review
... Reaction rates. The speed of chemical reactions depends on several factors: [1] Nature of reactants. Chemical reactions occur by breaking and rearranging existing bonds. The fewer electrons that need to be rearranged, the faster the reaction is. As a result, reactions between ionic substances in aqu ...
... Reaction rates. The speed of chemical reactions depends on several factors: [1] Nature of reactants. Chemical reactions occur by breaking and rearranging existing bonds. The fewer electrons that need to be rearranged, the faster the reaction is. As a result, reactions between ionic substances in aqu ...
Chapter 4: Chemical Reaction Dynamics
... (early or late barrier). From an inspection of the favourable reaction trajectories, it can be seen that: For an early barrier, translational excitation (high kinetic energies) of the reactants promotes the reaction and leads to vibrationally excited products. Vibrational excitation hinders the reac ...
... (early or late barrier). From an inspection of the favourable reaction trajectories, it can be seen that: For an early barrier, translational excitation (high kinetic energies) of the reactants promotes the reaction and leads to vibrationally excited products. Vibrational excitation hinders the reac ...