UHM-A-634-2015-2-eye
... remaining in your film will darken with time if exposed to light. To prevent this, film is “fixed” or has the undeveloped silver halide crystals removed from the film. Sodium Thiosulfate, usually referred to as “Hypo” is one of the most common fixing agents though others are used depending on the sp ...
... remaining in your film will darken with time if exposed to light. To prevent this, film is “fixed” or has the undeveloped silver halide crystals removed from the film. Sodium Thiosulfate, usually referred to as “Hypo” is one of the most common fixing agents though others are used depending on the sp ...
eye-and-photography-2013
... remaining in your film will darken with time if exposed to light. To prevent this, film is “fixed” or has the undeveloped silver halide crystals removed from the film. Sodium Thiosulfate, usually referred to as “Hypo” is one of the most common fixing agents though others are used depending on the sp ...
... remaining in your film will darken with time if exposed to light. To prevent this, film is “fixed” or has the undeveloped silver halide crystals removed from the film. Sodium Thiosulfate, usually referred to as “Hypo” is one of the most common fixing agents though others are used depending on the sp ...
Part I Power generation in fuel cells
... The ferrate ion, FeO42-, which contains iron in its highest known oxidation state, can be prepared by reacting solid iron(III) oxide at 60oC, with concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide through which chlorine is passing. The reaction mixture gradually turns deep purple and is filtered hot through a s ...
... The ferrate ion, FeO42-, which contains iron in its highest known oxidation state, can be prepared by reacting solid iron(III) oxide at 60oC, with concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide through which chlorine is passing. The reaction mixture gradually turns deep purple and is filtered hot through a s ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued th ...
... aims of alchemy that emerged with time were the quest for the elixir of life (the drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued th ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
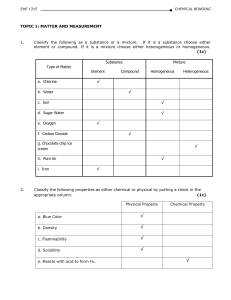
... variety of matter is recognized is called a property. A characteristic that depends upon the amount of matter in the sample is called an extensive property. A characteristic that does not depend upon the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without ...
... variety of matter is recognized is called a property. A characteristic that depends upon the amount of matter in the sample is called an extensive property. A characteristic that does not depend upon the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without ...
ECE final exam_fall 2013
... There are 12 numbered pages in this exam. Check to see they are all here before you begin the exam. Return all these papers when you are finished. A separate packet has a page of equations, a periodic table, and a phase diagram. Make sure that you have both packets. Use a pen with blue or black ink ...
... There are 12 numbered pages in this exam. Check to see they are all here before you begin the exam. Return all these papers when you are finished. A separate packet has a page of equations, a periodic table, and a phase diagram. Make sure that you have both packets. Use a pen with blue or black ink ...
Fall 2013 Final practice questions w/o solution
... B) The potassium ion has the least amount of shielding, so Zeff is greatest for it. C) Zeff increases with the number of protons. D) The amount of shielding is equal, but the nucleus of sulfur is least positive resulting in smallest Zeff. E) The radii trend above is not correct. ...
... B) The potassium ion has the least amount of shielding, so Zeff is greatest for it. C) Zeff increases with the number of protons. D) The amount of shielding is equal, but the nucleus of sulfur is least positive resulting in smallest Zeff. E) The radii trend above is not correct. ...
Chapter 13: Water and the Lithosphere Preview
... highly soluble because the positive and negative ions differ in charge, but calcium carbonate is sparingly soluble because both the cation and anion are doubly charged and therefore have a large lattice energy. Magnesium carbonate is more soluble than calcium carbonate, while sodium silicates are ...
... highly soluble because the positive and negative ions differ in charge, but calcium carbonate is sparingly soluble because both the cation and anion are doubly charged and therefore have a large lattice energy. Magnesium carbonate is more soluble than calcium carbonate, while sodium silicates are ...
COMPLEXES WITH BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE LIGANDS
... The ligand 3 might act polydentately due to the presence of exocyclic nitrogen, chlorine, and oxygen atoms, together with the endocyclic nitrogens. To establish the basicity order of the different donor atoms of 3, the HYPERCHEM program has been used for electronic density calculations. As seen from ...
... The ligand 3 might act polydentately due to the presence of exocyclic nitrogen, chlorine, and oxygen atoms, together with the endocyclic nitrogens. To establish the basicity order of the different donor atoms of 3, the HYPERCHEM program has been used for electronic density calculations. As seen from ...
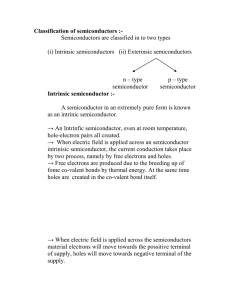
Classification of semiconductors :-
... → When electric field is applied across the semiconductors material electrons will move towards the possitive terminal of supply, holes will move towards negative terminal of the ...
... → When electric field is applied across the semiconductors material electrons will move towards the possitive terminal of supply, holes will move towards negative terminal of the ...
Spring 2014
... (8 pts) If it takes 4.184 J of energy to raise the temperature of exactly one gram of water one degree Celcius, how many photons from this LED are needed to raise the temperature of 250 g of water (about one cup) one degree Celcius? ...
... (8 pts) If it takes 4.184 J of energy to raise the temperature of exactly one gram of water one degree Celcius, how many photons from this LED are needed to raise the temperature of 250 g of water (about one cup) one degree Celcius? ...
George Facer`s A level Chemistry
... 16 Exam technique and laboratory chemistry Exam technique Laboratory tests Organic techniques Enthalpy change measurements Titration techniques Evaluation of error ...
... 16 Exam technique and laboratory chemistry Exam technique Laboratory tests Organic techniques Enthalpy change measurements Titration techniques Evaluation of error ...
elements of chemistry unit
... Rule 1. As shown earlier, the oxidation number of atoms in a pure element is defined as zero: C(0) Fe(0) H2(0) Rule 2. A single atom is assigned an oxidation number equal to its electrical charge. For metals, electrical charges are assigned to the metal’s number of valence electrons. Examples are Na ...
... Rule 1. As shown earlier, the oxidation number of atoms in a pure element is defined as zero: C(0) Fe(0) H2(0) Rule 2. A single atom is assigned an oxidation number equal to its electrical charge. For metals, electrical charges are assigned to the metal’s number of valence electrons. Examples are Na ...
Basic Agricultural Chemistry - Macmillan Education South Africa
... (such as helium) consist of molecules of single atoms (He). An atom of hydrogen is H, while a molecule of hydrogen is H2. An atom of helium is He and it is also a molecule of helium. ...
... (such as helium) consist of molecules of single atoms (He). An atom of hydrogen is H, while a molecule of hydrogen is H2. An atom of helium is He and it is also a molecule of helium. ...
Transition Metal Coordination Chemistry a subset of the lecture notes
... Now, How about those colors and the magnetism? Where are the electrons? Show me the electrons!! Color: Electronic transitions due to energy levels whose gaps are in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Magnetism: partially filled orbitals, unpaired electrons. high spin: maximum no. of ...
... Now, How about those colors and the magnetism? Where are the electrons? Show me the electrons!! Color: Electronic transitions due to energy levels whose gaps are in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Magnetism: partially filled orbitals, unpaired electrons. high spin: maximum no. of ...
physical setting chemistry
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
Properties of Ionic Compounds
... For sodium chloride, the lowest wholenumber ratio of the ions is 1:1 (one Na+ ion to each Cℓ– ion). • The formula unit for sodium chloride is NaCℓ. • Although ionic charges are used to derive the correct formula, they are not shown when you write the formula unit of the compound. ...
... For sodium chloride, the lowest wholenumber ratio of the ions is 1:1 (one Na+ ion to each Cℓ– ion). • The formula unit for sodium chloride is NaCℓ. • Although ionic charges are used to derive the correct formula, they are not shown when you write the formula unit of the compound. ...
REDOX PowerPoint - Southmoreland School District
... called a reducing agent Reduction – a species is reduced when it gains one or more electrons, and it is called an oxidizing agent Oxidation and reduction always occur together, never in isolation. If something gains electrons, something else had to lose them. ...
... called a reducing agent Reduction – a species is reduced when it gains one or more electrons, and it is called an oxidizing agent Oxidation and reduction always occur together, never in isolation. If something gains electrons, something else had to lose them. ...
Some Consumer Chemistry
... Toothpastes contain one or more of the following: • Detergent - to remove grease/oil (sodium lauryl sulfate) • Basic compound – to neutralize acid formed by bacteria (CaCO3 or baking soda and ammonia) • Abrasive – to remove material deposited on the mineral tooth surface (silicates…like sand) • Colo ...
... Toothpastes contain one or more of the following: • Detergent - to remove grease/oil (sodium lauryl sulfate) • Basic compound – to neutralize acid formed by bacteria (CaCO3 or baking soda and ammonia) • Abrasive – to remove material deposited on the mineral tooth surface (silicates…like sand) • Colo ...
Various Types of RXNS
... 5. small chunks of solid sodium are added to water --describe a test to confirm the gaseous product in your reaction 6. hydrobromic acid is added to a solution of potassium hydrogen carbonate --when a gas produced by the reaction is bubbled through limewater, what visible change is expected? 7. aque ...
... 5. small chunks of solid sodium are added to water --describe a test to confirm the gaseous product in your reaction 6. hydrobromic acid is added to a solution of potassium hydrogen carbonate --when a gas produced by the reaction is bubbled through limewater, what visible change is expected? 7. aque ...
Number of Electron Pairs Allowed Sigmatropic Rearrangement
... 1. The number of MO’s equals the number of AO’s combining to form them. 2. The energies of the MO’s are symmetrically placed about the energy of an isolated p orbital (arbitrarily taken as zero energy). 3. The energy of an MO increases as the number of nodes increases. 4. Nodes are symmetrically pla ...
... 1. The number of MO’s equals the number of AO’s combining to form them. 2. The energies of the MO’s are symmetrically placed about the energy of an isolated p orbital (arbitrarily taken as zero energy). 3. The energy of an MO increases as the number of nodes increases. 4. Nodes are symmetrically pla ...
Document
... Check for Understanding Aqueous potassium nitrate and a precipitate of barium chromate are formed when aqueous solutions of barium nitrate and potassium chromate are mixed. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) ...
... Check for Understanding Aqueous potassium nitrate and a precipitate of barium chromate are formed when aqueous solutions of barium nitrate and potassium chromate are mixed. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) ...
Unit 2 Assignments Answers
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...