![1 Solutions 4a (Chapter 4 problems) Chem151 [Kua]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002731518_1-574ec10e88e667508364281b6325aeef-300x300.png)
1 Solutions 4a (Chapter 4 problems) Chem151 [Kua]
... potassium and most of chloride are soluble. Al(OH)3 is not soluble by the guidelines and is thus insoluble by guideline 3: Al3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq)→ Al(OH)3(s); spectator ions: K+, Cl-. ...
... potassium and most of chloride are soluble. Al(OH)3 is not soluble by the guidelines and is thus insoluble by guideline 3: Al3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq)→ Al(OH)3(s); spectator ions: K+, Cl-. ...
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 17-Jul
... Ethanol has the formula C2H5OH and is used as a fuel (e.g. for cars in Brazil). It burns in the following reaction for which the enthalpy change is -1015 kJ/mol. C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(g) Calculate the C-C bond enthalpy in ethanol given the following bond enthalpies and enthalpy of v ...
... Ethanol has the formula C2H5OH and is used as a fuel (e.g. for cars in Brazil). It burns in the following reaction for which the enthalpy change is -1015 kJ/mol. C2H5OH(l) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(g) Calculate the C-C bond enthalpy in ethanol given the following bond enthalpies and enthalpy of v ...
ADSORPTION OF MOLECULES OF BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE AT
... bands in the SNIFTIRS s p e c t m indicates that the DMPC bilayer displays a tail-to-tail configuration with the polar heads t m e d towards the electrode surface. The peak positions of h t h CH2 stretching and C=O stretching bands show Little variation with the electrode potentials although their i ...
... bands in the SNIFTIRS s p e c t m indicates that the DMPC bilayer displays a tail-to-tail configuration with the polar heads t m e d towards the electrode surface. The peak positions of h t h CH2 stretching and C=O stretching bands show Little variation with the electrode potentials although their i ...
Chapter 18: Chemical Equilibrium
... time. The reactants, H2 and N2, are consumed in the reaction, so their concentrations gradually decrease. After a period of time, however, the concentrations of H2, N2, and NH3 no longer change. All concentrations become constant, as shown by the horizontal lines on the right side of the diagram. Th ...
... time. The reactants, H2 and N2, are consumed in the reaction, so their concentrations gradually decrease. After a period of time, however, the concentrations of H2, N2, and NH3 no longer change. All concentrations become constant, as shown by the horizontal lines on the right side of the diagram. Th ...
Chapter 18 pdf
... time. The reactants, H2 and N2, are consumed in the reaction, so their concentrations gradually decrease. After a period of time, however, the concentrations of H2, N2, and NH3 no longer change. All concentrations become constant, as shown by the horizontal lines on the right side of the diagram. Th ...
... time. The reactants, H2 and N2, are consumed in the reaction, so their concentrations gradually decrease. After a period of time, however, the concentrations of H2, N2, and NH3 no longer change. All concentrations become constant, as shown by the horizontal lines on the right side of the diagram. Th ...
Thermochemistry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... that harness energy-producing processes. Humans continually devise new technologies that use chemical reactions to produce materials with useful properties. Since the invention of fire, humans have also worked to devise technologies that harness energy. These technologies depend on the fact that eve ...
... that harness energy-producing processes. Humans continually devise new technologies that use chemical reactions to produce materials with useful properties. Since the invention of fire, humans have also worked to devise technologies that harness energy. These technologies depend on the fact that eve ...
Complete Solution Manual
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
Complete Solution Manual
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
... The zero point for standard reduction potentials (E) is the standard hydrogen electrode. The half-reaction is: 2 H+ + 2 e → H2. This half-reaction is assigned a standard potential of zero, and all other reduction half-reactions are measured relative to this zero point. Substances less easily reduc ...
edexcel_u1_2010_2013..
... of hydrogen produced was 66 cm3, measured at room temperature and pressure. (i) Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus you would use to carry out this experiment, showing how you would collect the hydrogen produced and ...
... of hydrogen produced was 66 cm3, measured at room temperature and pressure. (i) Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus you would use to carry out this experiment, showing how you would collect the hydrogen produced and ...
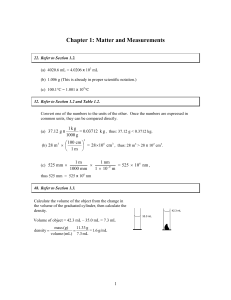
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurements
... nonmetal can combine with other non-metals to form molecular compounds such as those mentioned in Section 2.4 (indeed, a whole field of chemistry, called organic chemistry, is dedicated to the study of such compounds). Carbon can, however, also form ionic compounds such as calcium carbide (used in o ...
... nonmetal can combine with other non-metals to form molecular compounds such as those mentioned in Section 2.4 (indeed, a whole field of chemistry, called organic chemistry, is dedicated to the study of such compounds). Carbon can, however, also form ionic compounds such as calcium carbide (used in o ...
Document
... Molecular (Covalent) Compounds Covalent compounds contain nonmetals that “share” electrons to form molecules. (molecular compounds) ...
... Molecular (Covalent) Compounds Covalent compounds contain nonmetals that “share” electrons to form molecules. (molecular compounds) ...
Chapter 15 - Cengage Learning
... 15. In this problem we are asked to calculate how much of a concentrated stock solution, which is 12 M HCl, is needed to prepare a dilute HCl solution. We will need to know how many moles of HCl are present in 2.5 L of 1.0 M HCl, that is, in the dilute solution. Then we need to find a volume of the ...
... 15. In this problem we are asked to calculate how much of a concentrated stock solution, which is 12 M HCl, is needed to prepare a dilute HCl solution. We will need to know how many moles of HCl are present in 2.5 L of 1.0 M HCl, that is, in the dilute solution. Then we need to find a volume of the ...
Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... A) H2O B) CH3OH C) CH3CH2OH D) HF E) NaF Ans: E Category: Easy Section: 4.1 2. Which of the following compounds is a weak electrolyte? A) HNO3 B) NaNO3 C) HNO2 D) NaNO2 E) NaOH Ans: C Category: Easy Section: 4.1 3. Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte? A) H2O D) CH3CH2OH (ethanol ...
... A) H2O B) CH3OH C) CH3CH2OH D) HF E) NaF Ans: E Category: Easy Section: 4.1 2. Which of the following compounds is a weak electrolyte? A) HNO3 B) NaNO3 C) HNO2 D) NaNO2 E) NaOH Ans: C Category: Easy Section: 4.1 3. Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte? A) H2O D) CH3CH2OH (ethanol ...
engineering chemistry
... properties of the particle. The word 'atom' comes from the Greek word 'atomos', meaning 'unable to be cut'. The original meaning of atom was the smallest, indivisible form of a chemical particle. Now we know how to divide atoms into sub-atomic particles, the definition of an atom includes the concep ...
... properties of the particle. The word 'atom' comes from the Greek word 'atomos', meaning 'unable to be cut'. The original meaning of atom was the smallest, indivisible form of a chemical particle. Now we know how to divide atoms into sub-atomic particles, the definition of an atom includes the concep ...
MEDICAL CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE
... The solubility of the substances. The solubility of gases in liquids. The dependence of the solubility of gases on the pressure (Henry-Dalton’s law), nature of the gas and solvent, temperature. Effect of electrolytes on the solubility of gases (Sechenov’s law). Solubility of gases in the blood. Deco ...
... The solubility of the substances. The solubility of gases in liquids. The dependence of the solubility of gases on the pressure (Henry-Dalton’s law), nature of the gas and solvent, temperature. Effect of electrolytes on the solubility of gases (Sechenov’s law). Solubility of gases in the blood. Deco ...
AS Chemistry 1
... Atoms are the particles whose symbols are found in the periodic table of elements given in all your examination papers and also in Section 12 of this workbook. You can see that there are only about 100 of them. The middle part of the atom, the nucleus, contains one or more protons. It is the number ...
... Atoms are the particles whose symbols are found in the periodic table of elements given in all your examination papers and also in Section 12 of this workbook. You can see that there are only about 100 of them. The middle part of the atom, the nucleus, contains one or more protons. It is the number ...
SCH4U TEXT BOOK
... The Carbon Atom There are several million organic compounds, but only about a quarter of a million inorganic compounds (compounds that are not based on carbon). Why are there so many organic compounds? The answer lies in the bonding properties of carbon. As shown in Figure 1.1, each carbon atom usua ...
... The Carbon Atom There are several million organic compounds, but only about a quarter of a million inorganic compounds (compounds that are not based on carbon). Why are there so many organic compounds? The answer lies in the bonding properties of carbon. As shown in Figure 1.1, each carbon atom usua ...
Atomic and electronic structure of MoS2 nanoparticles
... chemical activity of the edges and find that hydrogen may adsorb at both the Mo edge and the S edge. Based on the DFT results we construct a thermodynamic model for the MoS2 edges allowing us to investigate their atomic structure under various conditions. It is shown that both the metallic and insul ...
... chemical activity of the edges and find that hydrogen may adsorb at both the Mo edge and the S edge. Based on the DFT results we construct a thermodynamic model for the MoS2 edges allowing us to investigate their atomic structure under various conditions. It is shown that both the metallic and insul ...
Chapter 4 "Reactions in Aqueous Solution"
... molecules are held together by electrostatic attractions (dotted lines) between the partially negatively charged oxygen atom of one molecule and the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms on adjacent molecules. As a result, the water molecules in liquid water form transient networks with struct ...
... molecules are held together by electrostatic attractions (dotted lines) between the partially negatively charged oxygen atom of one molecule and the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms on adjacent molecules. As a result, the water molecules in liquid water form transient networks with struct ...
Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... molecules are held together by electrostatic attractions (dotted lines) between the partially negatively charged oxygen atom of one molecule and the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms on adjacent molecules. As a result, the water molecules in liquid water form transient networks with struct ...
... molecules are held together by electrostatic attractions (dotted lines) between the partially negatively charged oxygen atom of one molecule and the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms on adjacent molecules. As a result, the water molecules in liquid water form transient networks with struct ...
Organic Chemistry with a Biological Emphasis Volume I
... Composed of the four elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen, capsaicin is produced by the pepper plant for the purpose of warding off hungry mammals. The molecule binds to and activates a mammalian receptor protein called TrpV1, which in normal circumstances has the job of detecting high tem ...
... Composed of the four elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen, capsaicin is produced by the pepper plant for the purpose of warding off hungry mammals. The molecule binds to and activates a mammalian receptor protein called TrpV1, which in normal circumstances has the job of detecting high tem ...
OCR A Level Chemistry A H432 Specification
... each covering different key concepts of chemistry. Teaching of practical skills is integrated with the theoretical topics and they’re assessed both through written papers and, for A level only, the Practical Endorsement. Chemistry B (Salters) – a context-led approach. Learners study chemistry in a r ...
... each covering different key concepts of chemistry. Teaching of practical skills is integrated with the theoretical topics and they’re assessed both through written papers and, for A level only, the Practical Endorsement. Chemistry B (Salters) – a context-led approach. Learners study chemistry in a r ...
MULTIPLY CHOICE QUESTIONS ON MEDICAL CHEMISTRY
... 1.9. Thermodynamic systems may be divided into following types according to the way of their interaction with the surroundings: А. physical and chemical B. one-, two- and threecomponents C. homogeneous and heterogeneous D. isolated, closed, open E. equilibrium and nonequilibrium 1.10. Chemical therm ...
... 1.9. Thermodynamic systems may be divided into following types according to the way of their interaction with the surroundings: А. physical and chemical B. one-, two- and threecomponents C. homogeneous and heterogeneous D. isolated, closed, open E. equilibrium and nonequilibrium 1.10. Chemical therm ...
Mercury(II) Removal with Modified Magnetic Chitosan Adsorbents
... In the spectra of CS–Hg(II) and CSm–Hg(II), the interactions were mainly affirmed by the reduction of the intensity of the peak assigned to the –NH group in amine, confirming that nitrogen atoms are the main adsorption sites for Hg(II) adsorption on CS and CSm. It is well known that nitrogen–ligand ...
... In the spectra of CS–Hg(II) and CSm–Hg(II), the interactions were mainly affirmed by the reduction of the intensity of the peak assigned to the –NH group in amine, confirming that nitrogen atoms are the main adsorption sites for Hg(II) adsorption on CS and CSm. It is well known that nitrogen–ligand ...