chapter 09
... The Molecular Orbital Model Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Bonding in Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Combining the Localized Electron and Molecular Orbital Models ...
... The Molecular Orbital Model Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Bonding in Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Combining the Localized Electron and Molecular Orbital Models ...
syllabus - WordPress.com
... Since separation of charge is a seat of potential, the charges of opposite signs on the fixed and diffused parts of the double layeraround the colloidal particle results in a difference in potential between these layers. This potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opp ...
... Since separation of charge is a seat of potential, the charges of opposite signs on the fixed and diffused parts of the double layeraround the colloidal particle results in a difference in potential between these layers. This potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opp ...
Chapter 9
... The Molecular Orbital Model Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Bonding in Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Combining the Localized Electron and Molecular Orbital Models ...
... The Molecular Orbital Model Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Bonding in Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Combining the Localized Electron and Molecular Orbital Models ...
Reactions between dyes of the Alizarin Green series and vanadates
... In all ternary complexes VL2S4 (I) or VL 2 S 6 (II, III) the number of the bonded molecules of tenside is greater than the number of the sulfo groups in the complex. This fact leads to the assumption that the second (/) or third (II, III) molecule of tenside is bonded to convenient negative or stron ...
... In all ternary complexes VL2S4 (I) or VL 2 S 6 (II, III) the number of the bonded molecules of tenside is greater than the number of the sulfo groups in the complex. This fact leads to the assumption that the second (/) or third (II, III) molecule of tenside is bonded to convenient negative or stron ...
- sartep.com
... (B) ionic bonding (C) hydrogen bonding (D) resonance (E) London dispersion forces 55._______________Is used to explain the fact that the carbon-to-oxygen bonds in carbonate are identical 56._______________Is used to explain the fact that sodium chloride is a solid at room temperature 57.____________ ...
... (B) ionic bonding (C) hydrogen bonding (D) resonance (E) London dispersion forces 55._______________Is used to explain the fact that the carbon-to-oxygen bonds in carbonate are identical 56._______________Is used to explain the fact that sodium chloride is a solid at room temperature 57.____________ ...
Document
... 2007 by the combustion of 3.5 x 1015 g gasolne • Assuming that gasoline is octane, C8H18, the equation for the reaction is ...
... 2007 by the combustion of 3.5 x 1015 g gasolne • Assuming that gasoline is octane, C8H18, the equation for the reaction is ...
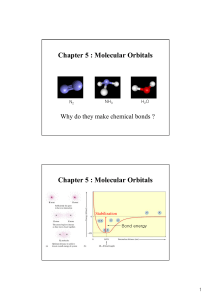
Molecular Orbitals Chapter 5 : Molecular Orbitals
... Delocalized electron bonding model •Molecular orbital (MO) theory ...
... Delocalized electron bonding model •Molecular orbital (MO) theory ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... serial dilutions to find the lowest [Pb2+] and [F ] that form a precipitate when mixed. If the student uses the concentration of the ions in the combined solution to determine Ksp, will the value of Ksp calculated be too large, too small or just right? Explain. ...
... serial dilutions to find the lowest [Pb2+] and [F ] that form a precipitate when mixed. If the student uses the concentration of the ions in the combined solution to determine Ksp, will the value of Ksp calculated be too large, too small or just right? Explain. ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1
... In a covalent bond, electrons are attracted to two nuclei, but sometimes one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly than the other. When one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, the bonding electrons are located closer to one nucleus than the other. This creates an uneven distribution ...
... In a covalent bond, electrons are attracted to two nuclei, but sometimes one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly than the other. When one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, the bonding electrons are located closer to one nucleus than the other. This creates an uneven distribution ...
Modern inorganic chemistry
... The element of atomic number 19 is potassium, strongly resembling both sodium and lithium in its physical and chemical properties. The atomic spectrum of potassium also confirms its position as a Group I element with an electronic configuration resembling that of sodium. These facts indicate that th ...
... The element of atomic number 19 is potassium, strongly resembling both sodium and lithium in its physical and chemical properties. The atomic spectrum of potassium also confirms its position as a Group I element with an electronic configuration resembling that of sodium. These facts indicate that th ...
Chemistry 1250 - Sp17 Solutions for Midterm 1
... metal and nonmetal it is ionic. Generally if the compound contains only nonmetals or nonmetal and semimetal it is molecular. The most common exceptions to this is when a compound contains ammonium ions, NH4+, such as NH4Cl, (NH4)2SO4, etc. All the elements in the compounds listed (and others with NH ...
... metal and nonmetal it is ionic. Generally if the compound contains only nonmetals or nonmetal and semimetal it is molecular. The most common exceptions to this is when a compound contains ammonium ions, NH4+, such as NH4Cl, (NH4)2SO4, etc. All the elements in the compounds listed (and others with NH ...
chemistry - Ethiopian Ministry of Education
... 1.1.2 Major Fields of Chemistry The universe is just like a very big chemical laboratory, rearranging atoms and subatomic particles to produce elements and compounds. While planets are made up of rocks which are nothing but arrangement of compounds, an atmosphere is a mixture of compounds separated ...
... 1.1.2 Major Fields of Chemistry The universe is just like a very big chemical laboratory, rearranging atoms and subatomic particles to produce elements and compounds. While planets are made up of rocks which are nothing but arrangement of compounds, an atmosphere is a mixture of compounds separated ...
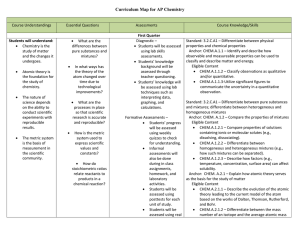
AP Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... properties of atoms allow for the prediction of physical and chemical properties. Eligible Content CHEM.A.2.3.1 – Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arrangement of elements on the periodic table. Compare and/or predict the properties (e.g., electron affinity, ionizatio ...
... properties of atoms allow for the prediction of physical and chemical properties. Eligible Content CHEM.A.2.3.1 – Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arrangement of elements on the periodic table. Compare and/or predict the properties (e.g., electron affinity, ionizatio ...
Acid‒base reaction
... (In modern times, the use of H+ is regarded as a shorthand for H3O+, since it is now known that the bare proton H+ does not exist as a free species in solution.) This leads to the definition that in Arrhenius acid–base reactions, a salt and water is formed from the reaction between an acid and a bas ...
... (In modern times, the use of H+ is regarded as a shorthand for H3O+, since it is now known that the bare proton H+ does not exist as a free species in solution.) This leads to the definition that in Arrhenius acid–base reactions, a salt and water is formed from the reaction between an acid and a bas ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
... 36. a. Two formula units KClO3 decompose to form two formula units KCl and three molecules O2. b. Four molecules NH3 react with six molecules NO to form five molecules N2 and six molecules H2O. c. Four atoms K react with one molecule O2 to form two formula units K2O. 37. a. Two mol KClO3 decompose t ...
... 36. a. Two formula units KClO3 decompose to form two formula units KCl and three molecules O2. b. Four molecules NH3 react with six molecules NO to form five molecules N2 and six molecules H2O. c. Four atoms K react with one molecule O2 to form two formula units K2O. 37. a. Two mol KClO3 decompose t ...
Ligand Conformation Enforces Trigonal
... occupied by ligand donor atoms only and containing just pyrazolato bridges. The variable-temperature magnetic measurements revealed unusually strong antiferromagnetic coupling between the two copper(II) ions, compared with that of similar doubly bridged copper(II) dinuclear complexes. The magnetic p ...
... occupied by ligand donor atoms only and containing just pyrazolato bridges. The variable-temperature magnetic measurements revealed unusually strong antiferromagnetic coupling between the two copper(II) ions, compared with that of similar doubly bridged copper(II) dinuclear complexes. The magnetic p ...
Chapter 4
... a solution of known concentration (the titrant) into a solution containing the substance being analyzed (the analyte). Equivalence point – enough titrant added to react exactly with the analyte. Endpoint – the indicator changes color so you can tell the equivalence point has been ...
... a solution of known concentration (the titrant) into a solution containing the substance being analyzed (the analyte). Equivalence point – enough titrant added to react exactly with the analyte. Endpoint – the indicator changes color so you can tell the equivalence point has been ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... 5. Even though the rates of reactant and product production are equal, it is rare for the concentrations of both the reactant or product to be equal. There’s usual more of one than the other. ...
... 5. Even though the rates of reactant and product production are equal, it is rare for the concentrations of both the reactant or product to be equal. There’s usual more of one than the other. ...
Downloaded - Maynooth University ePrints and eTheses Archive
... the most versatile and useful building blocks in supramolecular chemistry,5–14 as they are intriguing platforms for constructing selective receptors because of their preorganised basket structure assembled from their four phenol rings. They are widely used for the creation of selective metal cation ...
... the most versatile and useful building blocks in supramolecular chemistry,5–14 as they are intriguing platforms for constructing selective receptors because of their preorganised basket structure assembled from their four phenol rings. They are widely used for the creation of selective metal cation ...
Chapter 19: Acids and Bases
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
Band Gap Extraction from Individual Two
... microscopy (HAADF-STEM) is an excellent tool for characterizing the nanosheets loaded with metal and metal oxide nanoparticles.19 In addition, they used the sheets as an electron transport layer in solution-processed multijunction polymer solar cells.14 The group of Ishihara showed a high photocatal ...
... microscopy (HAADF-STEM) is an excellent tool for characterizing the nanosheets loaded with metal and metal oxide nanoparticles.19 In addition, they used the sheets as an electron transport layer in solution-processed multijunction polymer solar cells.14 The group of Ishihara showed a high photocatal ...
Examiners` Report November 2012 GCSE Chemistry
... This was the second 5CH2H paper to be offered; the first being set in June 2012. This question paper assessed the specification items to be in Unit 2 Discovering Chemistry which forms part of the Additional Science course along with the corresponding biology and physics units, and also as part of th ...
... This was the second 5CH2H paper to be offered; the first being set in June 2012. This question paper assessed the specification items to be in Unit 2 Discovering Chemistry which forms part of the Additional Science course along with the corresponding biology and physics units, and also as part of th ...
ISOTONICITY
... Step 1: Find how much sodium chloride is needed to render the formulation isotonic with body fluids. (Remember isotonicity refers to 0.9% or 0.9 g/100 mL). Step 2: Find the amount of sodium chloride represented by the ingredients in the prescription by multiplying the quantity of each ingredient by ...
... Step 1: Find how much sodium chloride is needed to render the formulation isotonic with body fluids. (Remember isotonicity refers to 0.9% or 0.9 g/100 mL). Step 2: Find the amount of sodium chloride represented by the ingredients in the prescription by multiplying the quantity of each ingredient by ...
CHAPTER 15 ACIDS AND BASES
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M (Why only two significant figures?) This will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChatelier's principle, Section 14.5). The extra hydrogen ion shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the un-ionized acid, and to two ...
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M (Why only two significant figures?) This will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChatelier's principle, Section 14.5). The extra hydrogen ion shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the un-ionized acid, and to two ...