Electron Microscopy
... Inelastically scattered electrons can be utilized two ways Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy: The inelastic loss of energy by the incident electrons is characteristic of the elements that were interacted with. These energies are unique to each bonding state of each element and thus can be used to e ...
... Inelastically scattered electrons can be utilized two ways Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy: The inelastic loss of energy by the incident electrons is characteristic of the elements that were interacted with. These energies are unique to each bonding state of each element and thus can be used to e ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... 1. Which element has the smallest atomic number? F 2. Which element has the largest atomic number? H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductor ...
... 1. Which element has the smallest atomic number? F 2. Which element has the largest atomic number? H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductor ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
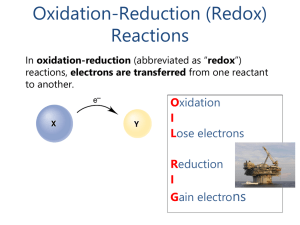
... Oxidation Number (or Oxidation State): actual or hypothetical charge of an atom in a compound if it existed as a monatomic ion ...
... Oxidation Number (or Oxidation State): actual or hypothetical charge of an atom in a compound if it existed as a monatomic ion ...
CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... ions, (2) ions that carry the same charges and are generated from atoms of the same periodic group, and (3) ions that carry different charges but are generated from the same atom. In case (1), ions carrying a greater negative charge are always larger; in case (2), ions from atoms having a greater at ...
... ions, (2) ions that carry the same charges and are generated from atoms of the same periodic group, and (3) ions that carry different charges but are generated from the same atom. In case (1), ions carrying a greater negative charge are always larger; in case (2), ions from atoms having a greater at ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... One substance breaks down or decomposes into 2 or more simpler substances. Most reactions require heat, light or electricity. ...
... One substance breaks down or decomposes into 2 or more simpler substances. Most reactions require heat, light or electricity. ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... when two or more orbitals of equal energy are available, the electrons occupy them singly first before filling them in pairs. AG ...
... when two or more orbitals of equal energy are available, the electrons occupy them singly first before filling them in pairs. AG ...
fied molal concentration. The molality, or molal concentration, is the
... faster the ball will roll. If we decrease the steepness enough, the ball won’t roll at all. Now, let’s apply this analogy to electrical potential. We replace the ball with electrically charged particles. Increasing the potential causes charge to move, and the greater the potential, the more charge m ...
... faster the ball will roll. If we decrease the steepness enough, the ball won’t roll at all. Now, let’s apply this analogy to electrical potential. We replace the ball with electrically charged particles. Increasing the potential causes charge to move, and the greater the potential, the more charge m ...
Exam 3 Key
... For each of the following, write the word, words, or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (2 points each) 1. The condition of an atom that has at least one of its electrons in orbitals that do not represent the lowest possible potential energy is called a(n) excited state. 2. A(n ...
... For each of the following, write the word, words, or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (2 points each) 1. The condition of an atom that has at least one of its electrons in orbitals that do not represent the lowest possible potential energy is called a(n) excited state. 2. A(n ...
Document
... The atomic number, Z, equals the number of protons in the nucleus. The neutron number, N, is the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number, A, is the number of nucleons in the nucleus. A=Z+N “Nucleon” is a generic term used to refer to either a proton or a neutron. The mass number is not th ...
... The atomic number, Z, equals the number of protons in the nucleus. The neutron number, N, is the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number, A, is the number of nucleons in the nucleus. A=Z+N “Nucleon” is a generic term used to refer to either a proton or a neutron. The mass number is not th ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... 10. Calculate the average atomic mass of copper if 69.17% of the copper atoms occurring in nature are 63Cu and 30.83% are 65Cu. ...
... 10. Calculate the average atomic mass of copper if 69.17% of the copper atoms occurring in nature are 63Cu and 30.83% are 65Cu. ...
Chapter 12 - "Chemical Formulas and Equations"
... • A replacement reaction is one where an atom or a polyatomic ion is exchanged for another tom or polyatomic ion. • These types of reactions occur as some elements have a greater ability to hold or attract electrons to themselves. • Elements that have the least ability to hold electrons are the most ...
... • A replacement reaction is one where an atom or a polyatomic ion is exchanged for another tom or polyatomic ion. • These types of reactions occur as some elements have a greater ability to hold or attract electrons to themselves. • Elements that have the least ability to hold electrons are the most ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
50 Forgotten Facts
... 28) ONLY metals with more than one listed charge need a Roman numeral after their name (Stock system) when naming an ionic compound. Nonmetals with more than one oxidation state will also need a Roman numeral in their name if they are the less electronegative atom in a molecular compound. [P. T., Ta ...
... 28) ONLY metals with more than one listed charge need a Roman numeral after their name (Stock system) when naming an ionic compound. Nonmetals with more than one oxidation state will also need a Roman numeral in their name if they are the less electronegative atom in a molecular compound. [P. T., Ta ...
A`r ji r/ Ii
... a. the total number of protons and neulrons in the nucleus of an atom b. the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element c. 1/12 the mass of a carboni2 atom d. the number of protons in the nucleus of an element e. atoms with the same number of protons but differe ...
... a. the total number of protons and neulrons in the nucleus of an atom b. the weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element c. 1/12 the mass of a carboni2 atom d. the number of protons in the nucleus of an element e. atoms with the same number of protons but differe ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... isotopes of an element, as they occur naturally, taking their abundances into account and expressed on a scale relative to 1/12th the mass of 12C. Electron Configuration of Atoms: When building up the electron configuration of an atom, the electrons occupy the lowest available energy level. The lowe ...
... isotopes of an element, as they occur naturally, taking their abundances into account and expressed on a scale relative to 1/12th the mass of 12C. Electron Configuration of Atoms: When building up the electron configuration of an atom, the electrons occupy the lowest available energy level. The lowe ...
Mock Final Exam
... 60. What is required to move electrons from one orbital to another? 6.6: Orbital filling and electron configuration 61. What is the electron configuration of chlorine? 62. What is common to the electron configuration of elements found in the same row of the periodic table? ...
... 60. What is required to move electrons from one orbital to another? 6.6: Orbital filling and electron configuration 61. What is the electron configuration of chlorine? 62. What is common to the electron configuration of elements found in the same row of the periodic table? ...
Group 2 Elements
... elements down the group •know the reactions of the elements Mg to Ba in Group 2 with oxygen, chlorine and water •understand the formation of characteristic flame colours by Group 1 and 2 compounds in terms of electron transitions •know the flame colours for Groups 1 and 2 compounds •understand exper ...
... elements down the group •know the reactions of the elements Mg to Ba in Group 2 with oxygen, chlorine and water •understand the formation of characteristic flame colours by Group 1 and 2 compounds in terms of electron transitions •know the flame colours for Groups 1 and 2 compounds •understand exper ...
File
... 4. Which best describes the relationship between subatomic particles in any neutral atom? A. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. B. The number of protons equals the number of neutrons. C. The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons. D. The number of neutrons is greater th ...
... 4. Which best describes the relationship between subatomic particles in any neutral atom? A. The number of protons equals the number of electrons. B. The number of protons equals the number of neutrons. C. The number of neutrons equals the number of electrons. D. The number of neutrons is greater th ...
Chemistry Standard Course of Study -- Detailed - UNCG GK-12
... Describe how ions are formed and which arrangements are stable (filled d-level, or halffilled d-level). Appropriately use the term cation as a positively charged ion and anion as negatively charged ion. Predict ionic charges for representative elements based on valence electrons. Describe io ...
... Describe how ions are formed and which arrangements are stable (filled d-level, or halffilled d-level). Appropriately use the term cation as a positively charged ion and anion as negatively charged ion. Predict ionic charges for representative elements based on valence electrons. Describe io ...
Chapter 4: Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... oxidation numbers is 0. 2. For the atoms in an ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion. 3. In compounds, the group 1A metals all have an oxidation number of +1 and the group 2A metals all have an oxidation number of +2. 4. In compounds, the oxidation number of f ...
... oxidation numbers is 0. 2. For the atoms in an ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers is equal to the charge on the ion. 3. In compounds, the group 1A metals all have an oxidation number of +1 and the group 2A metals all have an oxidation number of +2. 4. In compounds, the oxidation number of f ...
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... Spin and Orbital contributions to Magnetic susceptibility The value of λ is negligible for very light atoms, but increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ ...
... Spin and Orbital contributions to Magnetic susceptibility The value of λ is negligible for very light atoms, but increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ ...
Summarised Notes
... b) Compare the structure of simple molecular substances, eg methane; iodine, with those of giant molecular substances, eg poly(ethene); sand (silicon dioxide); diamond; graphite in order to deduce their properties ...
... b) Compare the structure of simple molecular substances, eg methane; iodine, with those of giant molecular substances, eg poly(ethene); sand (silicon dioxide); diamond; graphite in order to deduce their properties ...
PDF (Size: 41K)
... Explain, with reference to the standard electrode potential for sodium and hydrogen, why sodium is manufactured using this method rather than by the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride. Na+(aq) + e– ...
... Explain, with reference to the standard electrode potential for sodium and hydrogen, why sodium is manufactured using this method rather than by the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride. Na+(aq) + e– ...