chapter sb basic applications of: operational transconductance
... bias current that controls the gain in a manner similar to the two quadrant transconductance multiplier (see chapter 5c on VGA design). There are no resistors on the chip instead a series of transistor current mirrors are used. The output is a current rather than a voltage. The fact that the OTA is ...
... bias current that controls the gain in a manner similar to the two quadrant transconductance multiplier (see chapter 5c on VGA design). There are no resistors on the chip instead a series of transistor current mirrors are used. The output is a current rather than a voltage. The fact that the OTA is ...
74F189 64-Bit Random Access Memory with 3
... The F189 is a high-speed 64-bit RAM organized as a 16word by 4-bit array. Address inputs are buffered to minimize loading and are fully decoded on-chip. The outputs are 3-STATE and are in the high impedance state whenever the Chip Select (CS) input is HIGH. The outputs are active only in the Read mo ...
... The F189 is a high-speed 64-bit RAM organized as a 16word by 4-bit array. Address inputs are buffered to minimize loading and are fully decoded on-chip. The outputs are 3-STATE and are in the high impedance state whenever the Chip Select (CS) input is HIGH. The outputs are active only in the Read mo ...
Homework 4
... 39. (II) A power station delivers 620 kW of power at 12,000 V to a factory through wires with total resistance 3.0 . How much less power is wasted if the electricity is delivered at 50,000 V rather than 12,000 V? Solution Find the current used to deliver the power in each case, and then find the po ...
... 39. (II) A power station delivers 620 kW of power at 12,000 V to a factory through wires with total resistance 3.0 . How much less power is wasted if the electricity is delivered at 50,000 V rather than 12,000 V? Solution Find the current used to deliver the power in each case, and then find the po ...
BSNL_TTA_Networktransmission
... (a) current sources but no voltage sources (b) voltage sources but no current sources (c) both current and voltage sources (d) no voltage or current sources 47. Two resistances are connected in parallel and each dissipates 50 waits. The total power supplied by the source is (a) 25 watts (b) 50 watts ...
... (a) current sources but no voltage sources (b) voltage sources but no current sources (c) both current and voltage sources (d) no voltage or current sources 47. Two resistances are connected in parallel and each dissipates 50 waits. The total power supplied by the source is (a) 25 watts (b) 50 watts ...
AN-376-1 - HP Memory Project
... determine the polarity of the requested output value. This defines which is the correct power supply output to adjust away from the preset voltage or the current limit. The outputs of the pair are then programmed to the appropriate levels. Note that when programming current, the non-controlling sour ...
... determine the polarity of the requested output value. This defines which is the correct power supply output to adjust away from the preset voltage or the current limit. The outputs of the pair are then programmed to the appropriate levels. Note that when programming current, the non-controlling sour ...
Sensor Array 742 x 554 Pixels Frame Buffer
... required by multi-capture, each pixel has a front-end transistor, M1-M4, connected in series with a multiplexing switch transistor, M5-M8, as shown in Fig. 12.1.3. The reset transistors, M9M12, for each of the four pixels, reset their respective photodiodes to the value of the RAMP voltage when the ...
... required by multi-capture, each pixel has a front-end transistor, M1-M4, connected in series with a multiplexing switch transistor, M5-M8, as shown in Fig. 12.1.3. The reset transistors, M9M12, for each of the four pixels, reset their respective photodiodes to the value of the RAMP voltage when the ...
Sheet 4
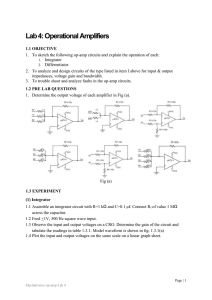
... 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble shoot and analyze faults in the op-amp circuits ...
... 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble shoot and analyze faults in the op-amp circuits ...
DN05091/D: 3 LED Low Voltage Parallel-to
... advantage is that there are no additional propagation delays or signal paths which might inadvertently cause flickering. The other anti-flicker structure in this circuit is the threshold detector. Very minimalistic control circuits as shown in other design notes (see DN05084 or DN05084) would have d ...
... advantage is that there are no additional propagation delays or signal paths which might inadvertently cause flickering. The other anti-flicker structure in this circuit is the threshold detector. Very minimalistic control circuits as shown in other design notes (see DN05084 or DN05084) would have d ...
Electricity and Circuit Review - ANSWERS File
... In series, if one thing gets turned off (or burns out, etc.) everything else goes off, too, because they all have the same current. In parallel, you can turn off one thing, and the other branches stay on, because they are each ...
... In series, if one thing gets turned off (or burns out, etc.) everything else goes off, too, because they all have the same current. In parallel, you can turn off one thing, and the other branches stay on, because they are each ...
A Cross-Coupled CMOS Negative Capacitor for Wideband Metamaterial Applications
... CMOS negative capacitor circuit. In Section III, simulation results in Agilent ADS are shown for the prototype circuit. In Section IV, measurement results of the fabricated circuit are shown. Finally, in Section V, the simulated and measured results are compared, and results presented for the device ...
... CMOS negative capacitor circuit. In Section III, simulation results in Agilent ADS are shown for the prototype circuit. In Section IV, measurement results of the fabricated circuit are shown. Finally, in Section V, the simulated and measured results are compared, and results presented for the device ...
Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDT Construction The
... 2. Produces a high resolution of more than 10 millimeter. 3.Produces a high sensitivity of more than 40 volts/millimeter. 4. Small in size and weighs less. It is rugged in design and can also be assigned easily. 5. Produces low hysteresis and thus has easy repeatability. ...
... 2. Produces a high resolution of more than 10 millimeter. 3.Produces a high sensitivity of more than 40 volts/millimeter. 4. Small in size and weighs less. It is rugged in design and can also be assigned easily. 5. Produces low hysteresis and thus has easy repeatability. ...
Lesson Plan
... 1. Record all data and calculations in the tables below or on a separate piece of paper. 2. Connect voltmeter in parallel to one of the resistors. 3. Connect ammeter in series adjacent to the resistor being measured. 4. Measure and record voltage and current for all three resistors (Do not exceed 12 ...
... 1. Record all data and calculations in the tables below or on a separate piece of paper. 2. Connect voltmeter in parallel to one of the resistors. 3. Connect ammeter in series adjacent to the resistor being measured. 4. Measure and record voltage and current for all three resistors (Do not exceed 12 ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.