MT-088 TUTORIAL Analog Switches and Multiplexers Basics
... Today, analog switches and multiplexers are available in a wide variety of configurations, options, etc., to suit nearly all applications. On-resistances less than 0.5 Ω, picoampere leakage currents, signal bandwidths greater than 1 GHz, and single 1.8-V supply operation are now possible with modern ...
... Today, analog switches and multiplexers are available in a wide variety of configurations, options, etc., to suit nearly all applications. On-resistances less than 0.5 Ω, picoampere leakage currents, signal bandwidths greater than 1 GHz, and single 1.8-V supply operation are now possible with modern ...
Introduction and theory
... Part one was related to the P-N junction diode. The Circuit was arranged as shown. This experiment involved both room temperature characteristic values (taken as soon as the circuit is closed) and steady state values which let I and V become constant. We attempted to measure a current when the diod ...
... Part one was related to the P-N junction diode. The Circuit was arranged as shown. This experiment involved both room temperature characteristic values (taken as soon as the circuit is closed) and steady state values which let I and V become constant. We attempted to measure a current when the diod ...
Document
... A transducer is a device or structure that transforms a physical quantity into an electrical one or a device / structure that transforms an electrical quantity into a physical one. For example: A microphone transforms changes in sound pressure level into changes in voltage. A condenser microphone is ...
... A transducer is a device or structure that transforms a physical quantity into an electrical one or a device / structure that transforms an electrical quantity into a physical one. For example: A microphone transforms changes in sound pressure level into changes in voltage. A condenser microphone is ...
electronics
... A transducer is a device or structure that transforms a physical quantity into an electrical one or a device / structure that transforms an electrical quantity into a physical one. For example: A microphone transforms changes in sound pressure level into changes in voltage. A condenser microphone is ...
... A transducer is a device or structure that transforms a physical quantity into an electrical one or a device / structure that transforms an electrical quantity into a physical one. For example: A microphone transforms changes in sound pressure level into changes in voltage. A condenser microphone is ...
In the circuit shown below, the switch closes at t = 0. a) Find iL(t → ∞).
... The switch is open just before the switch is closed, and the L acts like a wire. Inspection of the circuit reveals that it is a current-divider. ...
... The switch is open just before the switch is closed, and the L acts like a wire. Inspection of the circuit reveals that it is a current-divider. ...
FK2611361140
... by increasing the sustainability of the Integrated Circuits (ICs) on higher temperature. From above it is clear that ESD protection circuit using CMOS, clamps higher voltage than a SCR but is not so fast to detect ESD transient pulse, this is owing to lower ON resistance of SCR and a more uniform di ...
... by increasing the sustainability of the Integrated Circuits (ICs) on higher temperature. From above it is clear that ESD protection circuit using CMOS, clamps higher voltage than a SCR but is not so fast to detect ESD transient pulse, this is owing to lower ON resistance of SCR and a more uniform di ...
May 12th Homework Advanced
... is connected to the others along a single wire (in series). In others, each light is attached to its own wire (in parallel). 1. Suppose a single light bulb burns out. How do you think this will affect lights that are strung along a single wire? _______________________________________________________ ...
... is connected to the others along a single wire (in series). In others, each light is attached to its own wire (in parallel). 1. Suppose a single light bulb burns out. How do you think this will affect lights that are strung along a single wire? _______________________________________________________ ...
Design and Analysis of Two-Stage Operational
... DCRUST Murthal is 174.25. KEYWORDS: Operational trans conductance amplifier (OTA); GBW; CMRR; DC Gain; Power ...
... DCRUST Murthal is 174.25. KEYWORDS: Operational trans conductance amplifier (OTA); GBW; CMRR; DC Gain; Power ...
Scribe Notes
... capacitance between the rows and column as opposed to measuring it with respect to ground. Physics Note: the fringe field from a capacitor (electric field differences at the edges of the parallel plate capacitors) interact with nearby capacitors. Since we no longer assume that the plates are infinit ...
... capacitance between the rows and column as opposed to measuring it with respect to ground. Physics Note: the fringe field from a capacitor (electric field differences at the edges of the parallel plate capacitors) interact with nearby capacitors. Since we no longer assume that the plates are infinit ...
PHYS_3342_101311
... Potential drop at all resistances In an old, “used-up” battery emf is nearly the same, but internal resistance increases enormously ...
... Potential drop at all resistances In an old, “used-up” battery emf is nearly the same, but internal resistance increases enormously ...
June 1999 - Vicphysics
... Power = Voltage x Current (1), Current = 60 W / 240 V = ¼ amp. Vp / Vs = Np / Ns (1). Ns = (Vs / Vp) x Np = (264/240) x 1000 = 909. As in Q’n 1 for the 60 W globe to glow appropriately, the RMS current should be 0.25 A, which should also be the current through globe X (in series). (2) The voltage ac ...
... Power = Voltage x Current (1), Current = 60 W / 240 V = ¼ amp. Vp / Vs = Np / Ns (1). Ns = (Vs / Vp) x Np = (264/240) x 1000 = 909. As in Q’n 1 for the 60 W globe to glow appropriately, the RMS current should be 0.25 A, which should also be the current through globe X (in series). (2) The voltage ac ...
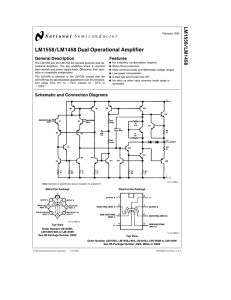
LM1558/LM1458 Dual Operational Amplifier
... bias network and power supply leads. Otherwise, their operation is completely independent. The LM1458 is identical to the LM1558 except that the LM1458 has its specifications guaranteed over the temperature range from 0§ C to a 70§ C instead of b55§ C to a 125§ C. ...
... bias network and power supply leads. Otherwise, their operation is completely independent. The LM1458 is identical to the LM1558 except that the LM1458 has its specifications guaranteed over the temperature range from 0§ C to a 70§ C instead of b55§ C to a 125§ C. ...
ELECTRICITY NOTES OHM`S LAW: The relationship between
... Current only flows when there is a potential difference in energy between two locations that are connected. Always flows from high potential to low potential. Measured in Amperes (A). Electric currents flow out of the positive end of a battery and back to the negative end. The amount of cu ...
... Current only flows when there is a potential difference in energy between two locations that are connected. Always flows from high potential to low potential. Measured in Amperes (A). Electric currents flow out of the positive end of a battery and back to the negative end. The amount of cu ...
MOSFET Theory - Department of Electronics
... Designers usually change size (usually width) of transistor to get the right amount of current Saturation (ON) and cut-off (OFF) are the more important modes in operation of digital circuits ...
... Designers usually change size (usually width) of transistor to get the right amount of current Saturation (ON) and cut-off (OFF) are the more important modes in operation of digital circuits ...
Ohm`s Law Practice Problems
... ANSWER KEY Ohm’s Law Practice Problems Part 1. Directions: Solve each problem below. Show your work. 1. A circuit has a voltage of 25 volts and a 5-ohm resistance. What is the current? 5 amps I = 25 volts/5 ohms I = 5 amps 2. A CD player has a resistance of 40 ohms in a circuit that supplies 4 volts ...
... ANSWER KEY Ohm’s Law Practice Problems Part 1. Directions: Solve each problem below. Show your work. 1. A circuit has a voltage of 25 volts and a 5-ohm resistance. What is the current? 5 amps I = 25 volts/5 ohms I = 5 amps 2. A CD player has a resistance of 40 ohms in a circuit that supplies 4 volts ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... stage transistors MR1 and MR2. These transistors reset both latch outputs to ground. During decision-making phase, clk = Vdd, both the tail transistors are on, M3 and M4 transistors are off. At the beginning of this phase, the control transistors MC1 and Mc2 are still off (since fn and fp are about ...
... stage transistors MR1 and MR2. These transistors reset both latch outputs to ground. During decision-making phase, clk = Vdd, both the tail transistors are on, M3 and M4 transistors are off. At the beginning of this phase, the control transistors MC1 and Mc2 are still off (since fn and fp are about ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.