74VHC4040 12-Stage Binary Counter 74VHC4040 12-Sta
... The VHC4040 is an advanced high-speed CMOS device fabricated with silicon gate CMOS technology. It achieves the high-speed operation similar to equivalent Bipolar Schottky TTL while maintaining the CMOS low power dissipation. The VHC4040 is a 12-stage counter which increments on the negative edge of ...
... The VHC4040 is an advanced high-speed CMOS device fabricated with silicon gate CMOS technology. It achieves the high-speed operation similar to equivalent Bipolar Schottky TTL while maintaining the CMOS low power dissipation. The VHC4040 is a 12-stage counter which increments on the negative edge of ...
Activity 6A
... electromagnetic noise due to the elimination of commutation chokes; (3) faster turn-off, permitting high switching frequencies; and (4) improved efficiency of converters. In low-power applications, GTOs have the following advantages over bipolar transistors: (1) a higher blocking voltage capability; ...
... electromagnetic noise due to the elimination of commutation chokes; (3) faster turn-off, permitting high switching frequencies; and (4) improved efficiency of converters. In low-power applications, GTOs have the following advantages over bipolar transistors: (1) a higher blocking voltage capability; ...
Supplementary Material for Phosphorene: A Unexplored 2D Semiconductor with a
... effective Schottky barrier for holes. In the ON-State, e.g. at Vbg=-30 V, both conduction and valence bands are pushed upwards, leaving a reduced Schottky barrier width, which facilitates the hole injection from the contact metal in a thermally assisted tunneling process. In contrast to this, in the ...
... effective Schottky barrier for holes. In the ON-State, e.g. at Vbg=-30 V, both conduction and valence bands are pushed upwards, leaving a reduced Schottky barrier width, which facilitates the hole injection from the contact metal in a thermally assisted tunneling process. In contrast to this, in the ...
Electric circuits - World of Teaching
... same anywhere in the circuit An ammeter can be placed anywhere in the circuit If we get one gap in the circuit the current stops flowing ...
... same anywhere in the circuit An ammeter can be placed anywhere in the circuit If we get one gap in the circuit the current stops flowing ...
Lab 7
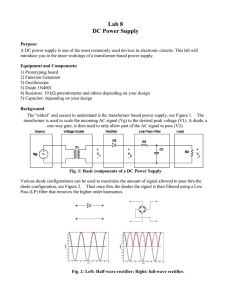
... Purpose: A DC power supply is one of the most commonly used devices in electronic circuits. This lab will introduce you to the inner workings of a transformer based power supply. Equipment and Components: 1) Prototyping board 2) Function Generator 3) Oscilloscope 3) Diode 1N4001 4) Resistors: 10 kΩ ...
... Purpose: A DC power supply is one of the most commonly used devices in electronic circuits. This lab will introduce you to the inner workings of a transformer based power supply. Equipment and Components: 1) Prototyping board 2) Function Generator 3) Oscilloscope 3) Diode 1N4001 4) Resistors: 10 kΩ ...
Lab E3
... this circuit has no branches, the current is the same everywhere in the circuit. C. Determining Resistance 1) You will next determine the resistance of a light bulb for several different values of applied voltage difference. Record your measured values for voltage difference and current for four dif ...
... this circuit has no branches, the current is the same everywhere in the circuit. C. Determining Resistance 1) You will next determine the resistance of a light bulb for several different values of applied voltage difference. Record your measured values for voltage difference and current for four dif ...
Chapter 2
... • Independent Source: Establishes a voltage or current in a circuit without relying on voltages or currents elsewhere in the circuit • Dependent Source: Establishes a voltage or current whose value depends on the value of a voltage or current elsewhere in the circuit (also known as controlled source ...
... • Independent Source: Establishes a voltage or current in a circuit without relying on voltages or currents elsewhere in the circuit • Dependent Source: Establishes a voltage or current whose value depends on the value of a voltage or current elsewhere in the circuit (also known as controlled source ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm`s Law
... expectation. Unfortunately, it is common for the components to be returned to incorrect bins. The power rating of a resistor depends on its size. Using the vernier calipers measure the length and diameter of one of your resistors. Compare your measurements with the data on the page from a component ...
... expectation. Unfortunately, it is common for the components to be returned to incorrect bins. The power rating of a resistor depends on its size. Using the vernier calipers measure the length and diameter of one of your resistors. Compare your measurements with the data on the page from a component ...
L298N datasheet
... publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics. The ...
... publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics. The ...
Chapter 4 Exercises and Answers
... full adder is a circuit that computes the sum of two bits, taking into account the carry bit. What is the Boolean expression for a full adder? C is the carry in. Sum is (A B) C) Carry out is (A AND B) OR ((A B) AND C) What is a multiplexer? A multiplexer is a circuit that uses input control si ...
... full adder is a circuit that computes the sum of two bits, taking into account the carry bit. What is the Boolean expression for a full adder? C is the carry in. Sum is (A B) C) Carry out is (A AND B) OR ((A B) AND C) What is a multiplexer? A multiplexer is a circuit that uses input control si ...
Chapter 17 - RL Circuits
... • Power factor of an inductive load can be increased by the addition of a capacitor in parallel – The capacitor compensates for the the phase lag of the total current by creating a capacitive component of current that is 180 out of phase with the inductive component – This has a canceling effect an ...
... • Power factor of an inductive load can be increased by the addition of a capacitor in parallel – The capacitor compensates for the the phase lag of the total current by creating a capacitive component of current that is 180 out of phase with the inductive component – This has a canceling effect an ...
Lab: Current and Voltage in a circuit
... 1. Set your multimeter to read DC Voltage (the symbol V with the straight line and dotted line over the top). Make sure your red lead is in the appropriate port of the multimeter—it should be in the port labeled with the V, which means you may need to change this from where it was when you measured ...
... 1. Set your multimeter to read DC Voltage (the symbol V with the straight line and dotted line over the top). Make sure your red lead is in the appropriate port of the multimeter—it should be in the port labeled with the V, which means you may need to change this from where it was when you measured ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm’s Law
... The power rating of a resistor depends on its size. Using the vernier calipers measure the length and diameter of one of your resistors. Compare your measurements with the data on the page from a component catalog at http://www.pa.msu.edu/courses/2013spring/PHY440/docs/DigiRes.pdf. What are the powe ...
... The power rating of a resistor depends on its size. Using the vernier calipers measure the length and diameter of one of your resistors. Compare your measurements with the data on the page from a component catalog at http://www.pa.msu.edu/courses/2013spring/PHY440/docs/DigiRes.pdf. What are the powe ...
Students: Serge Yakushevsky, Dima Vilensky
... insolation caused by shading changes. The project’s main goals are to find new power- effective and cheap solutions and to build a system that will maximize the efficiency of a PV string by using electrical circuitry. PV modules are generally connected in series in order to produce the significant v ...
... insolation caused by shading changes. The project’s main goals are to find new power- effective and cheap solutions and to build a system that will maximize the efficiency of a PV string by using electrical circuitry. PV modules are generally connected in series in order to produce the significant v ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.