Motorola ML145403, ML145404, ML145405, ML145408
... These devices are silicon gate CMOS ICs that combine both the transmitter and receiver to fulfill the electrical specifications of EIA Standard 232–E and CCITT V.28. The drivers feature true TTL input compatibility, slew rate limiting outputs, 300 Ω power–off source impedance, and output typically s ...
... These devices are silicon gate CMOS ICs that combine both the transmitter and receiver to fulfill the electrical specifications of EIA Standard 232–E and CCITT V.28. The drivers feature true TTL input compatibility, slew rate limiting outputs, 300 Ω power–off source impedance, and output typically s ...
Voltage Divider Design Considerations - Saint
... In Figure 1, bypass capacitors are used between D9 and D10 to ground. (For high rate applications, other dynodes may be bypassed also, i.g., D7 and D8 in Figure 1.) In our application, a pulse of light generated in the NaI(Tl) crystal strikes the photocathode and causes a pulse of photoelectrons to ...
... In Figure 1, bypass capacitors are used between D9 and D10 to ground. (For high rate applications, other dynodes may be bypassed also, i.g., D7 and D8 in Figure 1.) In our application, a pulse of light generated in the NaI(Tl) crystal strikes the photocathode and causes a pulse of photoelectrons to ...
MAX8815A 1A, 97% Efficiency, 30µA Quiescent Current Step-Up Converter with True Shutdown
... threshold, the PWM comparator and oscillator are disabled. In this low-power mode, switching occurs only as needed to service the output. This improves the efficiency for light loads, and the device consumes only 30µA under no-load conditions. The threshold for entering skip mode is approximately 90 ...
... threshold, the PWM comparator and oscillator are disabled. In this low-power mode, switching occurs only as needed to service the output. This improves the efficiency for light loads, and the device consumes only 30µA under no-load conditions. The threshold for entering skip mode is approximately 90 ...
SSM2143 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... of the two parts results in excellent THD+N and SNR and a noise floor of typically –105 dB over a 20 Hz to 20 kHz bandwidth. ...
... of the two parts results in excellent THD+N and SNR and a noise floor of typically –105 dB over a 20 Hz to 20 kHz bandwidth. ...
Step Response Parallel RLC Circuit
... Objective of Lecture Derive the equations that relate the voltages across a ...
... Objective of Lecture Derive the equations that relate the voltages across a ...
Budapest University of Technology and Economics
... this is the fact that they are small in size and their power consumption is low. A considerable part of these sensors uses capacitive conversion methods for sensing, because this way low current consumption and high resolution are easily achievable. Another particular advantage of capacitive sensors ...
... this is the fact that they are small in size and their power consumption is low. A considerable part of these sensors uses capacitive conversion methods for sensing, because this way low current consumption and high resolution are easily achievable. Another particular advantage of capacitive sensors ...
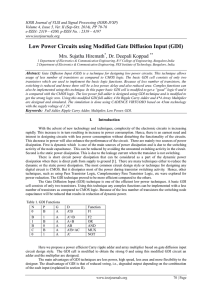
g Accelerometer ADXL335 Preliminary Technical Data
... orthogonal with little cross axis sensitivity. Mechanical misalignment of the sensor die to the package is the chief source of cross axis sensitivity. Mechanical misalignment can, of course, be calibrated out at the system level. ...
... orthogonal with little cross axis sensitivity. Mechanical misalignment of the sensor die to the package is the chief source of cross axis sensitivity. Mechanical misalignment can, of course, be calibrated out at the system level. ...
display
... primary side of a given transformer. These pulses couple from one transformer coil to another and are detected by the circuitry on the secondary side of the transformer. This circuitry then recreates the input digital signal at the output. In addition, a refresh circuit is included at the input side ...
... primary side of a given transformer. These pulses couple from one transformer coil to another and are detected by the circuitry on the secondary side of the transformer. This circuitry then recreates the input digital signal at the output. In addition, a refresh circuit is included at the input side ...
Electric Circuits - Mayfield City Schools
... with temperature and current. A light bulb’s resistance increases when there is more current because the bulb gets hotter when more current passes through it. ...
... with temperature and current. A light bulb’s resistance increases when there is more current because the bulb gets hotter when more current passes through it. ...
A 21mW 8-b 125 MS/s ADC in 0.09 mm2 0.13 um
... samples at a rate of 125 MSample/s. Several ADC architectures are capable of achieving these specifications, e.g., flash ADCs [1], [2], pipeline ADCs [3]–[9], folding ADCs [10]–[17], and subranging ADCs [18]–[23]. However, when small die area and low-power and low-voltage operation are of primary im ...
... samples at a rate of 125 MSample/s. Several ADC architectures are capable of achieving these specifications, e.g., flash ADCs [1], [2], pipeline ADCs [3]–[9], folding ADCs [10]–[17], and subranging ADCs [18]–[23]. However, when small die area and low-power and low-voltage operation are of primary im ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... dissipation. First is dynamic which is one of the main sources of power dissipation and is due to the switching activity of the node capacitance. This can be reduced by avoiding the unwanted switching activity in the circuit. Second is the static power dissipation. This is due to the leakage current ...
... dissipation. First is dynamic which is one of the main sources of power dissipation and is due to the switching activity of the node capacitance. This can be reduced by avoiding the unwanted switching activity in the circuit. Second is the static power dissipation. This is due to the leakage current ...
Installation Instruction for Three Phase Wye, 277/480, 220/380, 230
... The units are provided with 18-24 inches of #10 THHN Stranded wire. For best performance, mount the unit so that all wires can be cut and connected in the shortest and most direct path possible. For every inch of conductor added to the installation, you increase the let-through voltage of the surge ...
... The units are provided with 18-24 inches of #10 THHN Stranded wire. For best performance, mount the unit so that all wires can be cut and connected in the shortest and most direct path possible. For every inch of conductor added to the installation, you increase the let-through voltage of the surge ...
Inverter
... Vdd, Vt unchanged Area scales down by 1/S2 Cox scales up by S due to tox Gate capacitance = CoxWL scales down by 1/S scales up by S Linear and saturation region current scales up by S Current density scales up by S3 P=Vdd*I, power density scales up by S3 Power consumption is a major design issue ...
... Vdd, Vt unchanged Area scales down by 1/S2 Cox scales up by S due to tox Gate capacitance = CoxWL scales down by 1/S scales up by S Linear and saturation region current scales up by S Current density scales up by S3 P=Vdd*I, power density scales up by S3 Power consumption is a major design issue ...
UC2907 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... (–) SENSE: (Pin 4) This is a high-impedance pin allowing remote sensing of the system ground, bypassing any voltage drops which might appear in the power return line. This point should be considered as the true ground. Unless otherwise stated, all voltages are with respect to this point. Artificial ...
... (–) SENSE: (Pin 4) This is a high-impedance pin allowing remote sensing of the system ground, bypassing any voltage drops which might appear in the power return line. This point should be considered as the true ground. Unless otherwise stated, all voltages are with respect to this point. Artificial ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.