BD99010EFV-M
... The application does not require an external Schottky diode as commonly used in conventional DC/DC converter IC’s. The low-side power transistor provides two advantages: it reduces the switching losses by careful on-chip timing to prevent shoot-through and improves the leakage current (resulting in ...
... The application does not require an external Schottky diode as commonly used in conventional DC/DC converter IC’s. The low-side power transistor provides two advantages: it reduces the switching losses by careful on-chip timing to prevent shoot-through and improves the leakage current (resulting in ...
ESG89001 Electro magnetic compatibility and printed circuit board
... which path is most convenient, VEE or VCC. This choice is determined by the mutual coupling present between the signaltrace and one of the supply traces. Between two decoupling capacitors, one for each IC, and the inductance, Ltrace, formed by the supply traces, a series resonant circuit ...
... which path is most convenient, VEE or VCC. This choice is determined by the mutual coupling present between the signaltrace and one of the supply traces. Between two decoupling capacitors, one for each IC, and the inductance, Ltrace, formed by the supply traces, a series resonant circuit ...
Ohm`s Law
... R = ρ *L/A; ρ = 1.4 × 104 * 10‐9 Ohm*m = 1.4 × 10‐5 Ohm*m ; L = 1 cm = 10‐2m; A = 7.85*10‐9 m2 R = 1.4*10‐5 Ohm*m*10‐2 m/ 7.85*10‐9 m2 = 17.8 Ohm Compare: Cu – wire, R1 = 21.7 mOhm ≈ 0.02 Ohm; Carbon‐resistor, R2 = 17.8 Ohm ≈ 18 Ohm; To have the current through the Cuwire of 0.1 A, the required v ...
... R = ρ *L/A; ρ = 1.4 × 104 * 10‐9 Ohm*m = 1.4 × 10‐5 Ohm*m ; L = 1 cm = 10‐2m; A = 7.85*10‐9 m2 R = 1.4*10‐5 Ohm*m*10‐2 m/ 7.85*10‐9 m2 = 17.8 Ohm Compare: Cu – wire, R1 = 21.7 mOhm ≈ 0.02 Ohm; Carbon‐resistor, R2 = 17.8 Ohm ≈ 18 Ohm; To have the current through the Cuwire of 0.1 A, the required v ...
MAX7036 300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver with Internal IF Filter General Description
... has a power-down pin to put it in a low-current sleep mode, making it ideal for cost- and power-sensitive applications. The low-noise amplifier (LNA), phaselocked loop (PLL), mixer, IF filter, received-signalstrength indicator (RSSI), and baseband sections are all on-chip. The MAX7036 uses a very-lo ...
... has a power-down pin to put it in a low-current sleep mode, making it ideal for cost- and power-sensitive applications. The low-noise amplifier (LNA), phaselocked loop (PLL), mixer, IF filter, received-signalstrength indicator (RSSI), and baseband sections are all on-chip. The MAX7036 uses a very-lo ...
The CDM8:4s Professional DJ Mixer
... Any use of the controls, or any adjustment, or the performance of any procedure other than those specified herein may result in serious damage to your health. The mixer should not be opened or repaired by anyone except properly qualified service personnel. Double insulated - when servicing, use only ...
... Any use of the controls, or any adjustment, or the performance of any procedure other than those specified herein may result in serious damage to your health. The mixer should not be opened or repaired by anyone except properly qualified service personnel. Double insulated - when servicing, use only ...
MAX1760/MAX1760H 0.8A, Low-Noise, 1MHz, Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description
... The MAX1760 features an internal, P-channel synchronous rectifier to enhance efficiency. Synchronous rectification provides 5% improved efficiency over similar nonsynchronous boost regulators. In PWM mode, the synchronous rectifier is turned on during the second half of each switching cycle. In low- ...
... The MAX1760 features an internal, P-channel synchronous rectifier to enhance efficiency. Synchronous rectification provides 5% improved efficiency over similar nonsynchronous boost regulators. In PWM mode, the synchronous rectifier is turned on during the second half of each switching cycle. In low- ...
a 60 MHz, 2000 V/ Monolithic Op Amp AD844
... presents the usual high impedance. The voltage on this input is transferred to the inverting input (Pin 2) with a low offset voltage, ensured by the close matching of like polarity transistors operating under essentially identical bias conditions. Laser trimming nulls the residual offset voltage, do ...
... presents the usual high impedance. The voltage on this input is transferred to the inverting input (Pin 2) with a low offset voltage, ensured by the close matching of like polarity transistors operating under essentially identical bias conditions. Laser trimming nulls the residual offset voltage, do ...
alan sherry
... temperature sensing element . RTD sensors generate output signals in one of two ways: through a change in output voltage or through a change in resistance of the sensor's electrical circuit. The Platinum RTD, Resistance Temperature Detector is one of the most linear, stable, and reproducible tempera ...
... temperature sensing element . RTD sensors generate output signals in one of two ways: through a change in output voltage or through a change in resistance of the sensor's electrical circuit. The Platinum RTD, Resistance Temperature Detector is one of the most linear, stable, and reproducible tempera ...
AN-6024 — FMS6xxx Product Series Understanding Analog Video Signal Clamps, Bias, Description
... and prevents the signal from falling below this level. In bias mode, the input is biased to the mid-scale reference voltage level through an on-chip high-impedance source. ...
... and prevents the signal from falling below this level. In bias mode, the input is biased to the mid-scale reference voltage level through an on-chip high-impedance source. ...
University Bremerhaven Embedded System Design Example (Class
... The KIS Principle (Keep It Simple) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... The KIS Principle (Keep It Simple) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Behavioral Buffer Modeling with HSPICE – Intel Buffer
... resistor tied to the n and p loads. In this case the loads are 50 ohms. We need to insure we don’t divide by zero and also do not result in an exact 0 ohm resistance. Introduction ...
... resistor tied to the n and p loads. In this case the loads are 50 ohms. We need to insure we don’t divide by zero and also do not result in an exact 0 ohm resistance. Introduction ...
FEATURES APPLICATIONS DESCRIPTION
... components: current sense resistor, RCS, the output inductor and the output capacitor(s) to ground. If the voltage on the CS1, and CS2 pins exceed 0.2 V (resistance greater than 40 kΩ), a fault is declared and the device does not start. This is a fault detection feature that insures the output induc ...
... components: current sense resistor, RCS, the output inductor and the output capacitor(s) to ground. If the voltage on the CS1, and CS2 pins exceed 0.2 V (resistance greater than 40 kΩ), a fault is declared and the device does not start. This is a fault detection feature that insures the output induc ...
10 µA-100 mA, 0.05% Error, High-Side Current
... amount of power. Selecting an ideal shunt resistor can be difficult, since resistors with very low tolerances typically can’t dissipate significant power, and resistors with high power handling typically aren’t available in low tolerances. A compromise was found for this design by selecting a 6.8 Ω ...
... amount of power. Selecting an ideal shunt resistor can be difficult, since resistors with very low tolerances typically can’t dissipate significant power, and resistors with high power handling typically aren’t available in low tolerances. A compromise was found for this design by selecting a 6.8 Ω ...
UCC29002 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... to its non−inverting input and the VCSO signal to its inverting input. If the average per module current, represented by the load share bus is higher than the module’s own output current, an error signal will be developed across the compensation components connected between the EAO pin and ground. T ...
... to its non−inverting input and the VCSO signal to its inverting input. If the average per module current, represented by the load share bus is higher than the module’s own output current, an error signal will be developed across the compensation components connected between the EAO pin and ground. T ...
MAX1925/MAX1926 Switch-Mode 1-Cell Li+ Chargers General Description Features
... EVALU E L B A AVAIL ...
... EVALU E L B A AVAIL ...
Precautions for Avoiding Static Electricity E
... Static within the work environment must be suppressed to within 100V. Materials that generate static must therefore be avoided, and a humidifier used to prevent low levels of humidity. The effects of measures implemented to reduce static should also be reviewed periodically. ...
... Static within the work environment must be suppressed to within 100V. Materials that generate static must therefore be avoided, and a humidifier used to prevent low levels of humidity. The effects of measures implemented to reduce static should also be reviewed periodically. ...
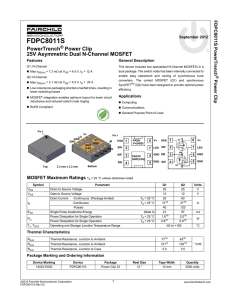
FDPC8011S PowerTrench Power Clip
... "The input ceramic bypass capacitor between VIN and GND should be placed as close as possible to the pins V+ / V+(HSD) PAD and GND / GND(LSS) PAD to help reduce parasitic inductance and high frequency ringing. Several capacitors may be placed in parallel, and capacitors may be placed on both the t ...
... "The input ceramic bypass capacitor between VIN and GND should be placed as close as possible to the pins V+ / V+(HSD) PAD and GND / GND(LSS) PAD to help reduce parasitic inductance and high frequency ringing. Several capacitors may be placed in parallel, and capacitors may be placed on both the t ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.