LMK00105 Ultra-low Jitter LVCMOS Fanout Buffer/Level Translator
... operation, dual supply operation enables lower power consumption and output-level compatibility. Bank A (CLKout0 and CLKout1) and Bank B (CLKout2 to CLKout4) may also be operated at different Vddo voltages, provided neither Vddo voltage exceeds Vdd. NOTE Care should be taken to ensure the Vddo volta ...
... operation, dual supply operation enables lower power consumption and output-level compatibility. Bank A (CLKout0 and CLKout1) and Bank B (CLKout2 to CLKout4) may also be operated at different Vddo voltages, provided neither Vddo voltage exceeds Vdd. NOTE Care should be taken to ensure the Vddo volta ...
数据资料缩写本 DS28E22 1-Wire SHA-256安全认证器, 带有2Kb用户EEPROM
... relevant supply voltage range are guaranteed by design and characterization. Typical values are not guaranteed. Note 2: System requirement. Note 3: Maximum allowable pullup resistance is a function of the number of 1-Wire devices in the system and 1-Wire recovery times. The specified value here ap ...
... relevant supply voltage range are guaranteed by design and characterization. Typical values are not guaranteed. Note 2: System requirement. Note 3: Maximum allowable pullup resistance is a function of the number of 1-Wire devices in the system and 1-Wire recovery times. The specified value here ap ...
TPS62290 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The Power Save Mode is enabled with MODE Pin set to low level. If the load current decreases, the converter will enter Power Save Mode operation automatically. During Power Save Mode the converter skips switching and operates with reduced frequency in PFM mode with a minimum quiescent current to mai ...
... The Power Save Mode is enabled with MODE Pin set to low level. If the load current decreases, the converter will enter Power Save Mode operation automatically. During Power Save Mode the converter skips switching and operates with reduced frequency in PFM mode with a minimum quiescent current to mai ...
IRPLLNR1
... power will be too low, and the ballast may not ignite the lamp and/or deactivate in the event of a non-strike condition. This is because RT (R20) programs the minimum operating frequency which corresponds to the ignition frequency. If this frequency is too high, the resulting lamp voltage may be too ...
... power will be too low, and the ballast may not ignite the lamp and/or deactivate in the event of a non-strike condition. This is because RT (R20) programs the minimum operating frequency which corresponds to the ignition frequency. If this frequency is too high, the resulting lamp voltage may be too ...
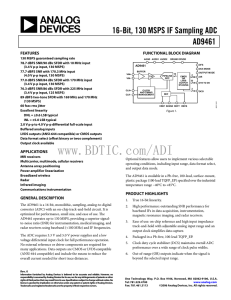
16-Bit, 130 MSPS IF Sampling ADC AD9461 FEATURES
... magnetic resonance imaging, and radar receivers. ...
... magnetic resonance imaging, and radar receivers. ...
LMK60E2-150M, LMK60E2-156M
... To ensure that the maximum junction temperature of LMK60XX is below 120°C, it can be calculated that the maximum PCB temperature without airflow should be at 90°C or below when the device is optimized for best performance resulting in maximum on-chip power dissipation of 0.68 W. 9.1.2 Best Practices ...
... To ensure that the maximum junction temperature of LMK60XX is below 120°C, it can be calculated that the maximum PCB temperature without airflow should be at 90°C or below when the device is optimized for best performance resulting in maximum on-chip power dissipation of 0.68 W. 9.1.2 Best Practices ...
10. Diodes – Basic Diode Concepts
... * Graphical load-line analysis is too cumbersome for complex circuits, * We may apply “Ideal-Diode Model” to simplify the analysis: (1) in forward direction: short-circuit assumption, zero voltage drop; (2) in reverse direction: open-circuit assumption. * The ideal-diode model can be used when the f ...
... * Graphical load-line analysis is too cumbersome for complex circuits, * We may apply “Ideal-Diode Model” to simplify the analysis: (1) in forward direction: short-circuit assumption, zero voltage drop; (2) in reverse direction: open-circuit assumption. * The ideal-diode model can be used when the f ...
INA180 Low- and High-Side Voltage Output
... requires higher bandwidth and slew rates is system fault detection, where the INA180 is used with an external comparator and a reference to quickly detect when the sensed current is out of range. 8.3.2 Wide Input Common-Mode Voltage Range The INA180 supports input common-mode voltages from –0.2 V to ...
... requires higher bandwidth and slew rates is system fault detection, where the INA180 is used with an external comparator and a reference to quickly detect when the sensed current is out of range. 8.3.2 Wide Input Common-Mode Voltage Range The INA180 supports input common-mode voltages from –0.2 V to ...
FEATURES APPLICATIONS D
... exceptionally low harmonic distortion, particularly in differential configurations. Adequate output current is provided to drive the potentially heavy load of a twisted-pair line. Harmonic distortion for a 2VPP differential output operating from +5V to +12V supplies is ≤ −95dBc through 1MHz input fr ...
... exceptionally low harmonic distortion, particularly in differential configurations. Adequate output current is provided to drive the potentially heavy load of a twisted-pair line. Harmonic distortion for a 2VPP differential output operating from +5V to +12V supplies is ≤ −95dBc through 1MHz input fr ...
a 32-Channel Precision Infinite Sample-and-Hold AD5533B
... gain/offset stage is switched directly to VIN. The addressed channel begins to acquire VIN on the rising edge of TRACK. See TRACK Input section for further information. This input can also be used as a means of resetting the complete device to its power-on-reset conditions. This is achieved by apply ...
... gain/offset stage is switched directly to VIN. The addressed channel begins to acquire VIN on the rising edge of TRACK. See TRACK Input section for further information. This input can also be used as a means of resetting the complete device to its power-on-reset conditions. This is achieved by apply ...
Fryze Power Theory with Adaptive-HCC based Active Power Line
... The hysteresis band HB can be modulated at different points of the fundamental frequency cycle to control the switching pattern of the inverter. The calculated hysteresis bandwidth HB is applied to the variable HCC. The variable hysteresis current control is created by S-functions in Matlab to produ ...
... The hysteresis band HB can be modulated at different points of the fundamental frequency cycle to control the switching pattern of the inverter. The calculated hysteresis bandwidth HB is applied to the variable HCC. The variable hysteresis current control is created by S-functions in Matlab to produ ...
Precision Logarithmic and Log Ratio Amplifier
... the LOG112 performance. Input currents larger than 3.5mA result in increased nonlinearity. An absolute maximum input current rating of 10mA is included to prevent excessive power dissipation that may damage the input transistor. On ±5V supplies, the total input current (I1 + I2) is limited to 4.5mA. ...
... the LOG112 performance. Input currents larger than 3.5mA result in increased nonlinearity. An absolute maximum input current rating of 10mA is included to prevent excessive power dissipation that may damage the input transistor. On ±5V supplies, the total input current (I1 + I2) is limited to 4.5mA. ...
PDF
... Fig: 4 Boost ability comparison of the classical Zsource impedance network and the Z-source impedance network with switched inductor To compare the individual boost ability of classical Zsource impedance network and the Z-source impedance network with switched inductor, the curves of the boost facto ...
... Fig: 4 Boost ability comparison of the classical Zsource impedance network and the Z-source impedance network with switched inductor To compare the individual boost ability of classical Zsource impedance network and the Z-source impedance network with switched inductor, the curves of the boost facto ...
Electricity – Resistance and Power
... The resistance of a wire depends on several factors: Material – Different materials have different resistances because some materials are better conductors. Nichrome wire has a higher resistance than a copper wire of the same size. Length – The longer a wire is the higher its resistance. When el ...
... The resistance of a wire depends on several factors: Material – Different materials have different resistances because some materials are better conductors. Nichrome wire has a higher resistance than a copper wire of the same size. Length – The longer a wire is the higher its resistance. When el ...
MAX1844 High-Speed Step-Down Controller with Accurate Current Limit for Notebook Computers General Description
... using an external current-sense resistor in series with the synchronous rectifier. Alternatively, the synchronous rectifier itself can be used for less accurate current sensing at the lowest possible power dissipation. Single-stage buck conversion allows the MAX1844 to directly step down high-voltag ...
... using an external current-sense resistor in series with the synchronous rectifier. Alternatively, the synchronous rectifier itself can be used for less accurate current sensing at the lowest possible power dissipation. Single-stage buck conversion allows the MAX1844 to directly step down high-voltag ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.