Lecture 15 Chapter 28 Circuits
... • Kirchhoff’s loop rule – in traversing a circuit loop the sum of the changes in V is zero, ∆V =0 • Resistance rule – Move through resistor in direction of current V =-iR, in opposite direction V =+iR • Emf rule – Move through emf device in direction of emf arrow V =+E, in opposite direction V =-E ...
... • Kirchhoff’s loop rule – in traversing a circuit loop the sum of the changes in V is zero, ∆V =0 • Resistance rule – Move through resistor in direction of current V =-iR, in opposite direction V =+iR • Emf rule – Move through emf device in direction of emf arrow V =+E, in opposite direction V =-E ...
A Digitally Controlled Oscillator System for SAW
... There are three types of varactors available in this 90-nm CMOS process: a MIM varactor (Fig. 2, [9]), a MOS varactor, and a junction-diode varactor. In order to have a wide frequency , a fully tuning range while having a minimal VCO gain, discrete tuning technique has been adopted [3], hence the os ...
... There are three types of varactors available in this 90-nm CMOS process: a MIM varactor (Fig. 2, [9]), a MOS varactor, and a junction-diode varactor. In order to have a wide frequency , a fully tuning range while having a minimal VCO gain, discrete tuning technique has been adopted [3], hence the os ...
FEATURES HIGH LEVEL BLOCK DIAGRAM
... voltage range of the ADP5042 LDOs extend the battery life of portable devices. The two LDOs maintain power supply rejection greater than 60 dB for frequencies as high as 10 kHz while operating with a low headroom voltage. Each regulator is activated by a high level on the respective enable pin. The ...
... voltage range of the ADP5042 LDOs extend the battery life of portable devices. The two LDOs maintain power supply rejection greater than 60 dB for frequencies as high as 10 kHz while operating with a low headroom voltage. Each regulator is activated by a high level on the respective enable pin. The ...
UCC27517A Single-Channel High-Speed Low
... to operate over a wide VDD range of 4.5 to 18 V, and a wide temperature range of –40°C to 140°C. Internal undervoltage lockout (UVLO) circuitry on the VDD pin holds the output low outside VDD operating range. The capability to operate at low voltage levels, such as below 5 V, along with best-in- cla ...
... to operate over a wide VDD range of 4.5 to 18 V, and a wide temperature range of –40°C to 140°C. Internal undervoltage lockout (UVLO) circuitry on the VDD pin holds the output low outside VDD operating range. The capability to operate at low voltage levels, such as below 5 V, along with best-in- cla ...
MAX17031 Dual Quick-PWM Step-Down Controller with Low- General Description
... avoid audible noise. Ultrasonic mode forces the controller to maintain switching frequencies greater than 20kHz at light loads. The SKIP input also has an accurate logic threshold, allowing it to be used as a secondary feedback input to refresh an external charge pump or secondary winding without ov ...
... avoid audible noise. Ultrasonic mode forces the controller to maintain switching frequencies greater than 20kHz at light loads. The SKIP input also has an accurate logic threshold, allowing it to be used as a secondary feedback input to refresh an external charge pump or secondary winding without ov ...
iC-NVH 6-bit Sin/D Flash Converter - iC-Haus
... This specification is for a newly developed product. iC-Haus therefore reserves the right to change or update, without notice, any information contained herein, design and specification; and to discontinue or limit production or distribution of any product versions. Please contact iC-Haus to ascerta ...
... This specification is for a newly developed product. iC-Haus therefore reserves the right to change or update, without notice, any information contained herein, design and specification; and to discontinue or limit production or distribution of any product versions. Please contact iC-Haus to ascerta ...
MAX451 Quad, Rail-to-Rail, Fault-Protected, SPST Analog Switches General Description
... constructed by three series FETs. This produces good off characteristics, but fairly high on-resistance when the signals are within about 3V of each supply rail. As the voltage on one side of the switch approaches within about 3V of either supply rail (a fault condition), the switch impedance become ...
... constructed by three series FETs. This produces good off characteristics, but fairly high on-resistance when the signals are within about 3V of each supply rail. As the voltage on one side of the switch approaches within about 3V of either supply rail (a fault condition), the switch impedance become ...
AD8014
... The AD8014 is a revolutionary current feedback operational amplifier that attains new levels of combined bandwidth, power, output drive and distortion. Analog Devices, Inc. uses a proprietary circuit architecture to enable the highest performance amplifier at the lowest power. Not only is it technic ...
... The AD8014 is a revolutionary current feedback operational amplifier that attains new levels of combined bandwidth, power, output drive and distortion. Analog Devices, Inc. uses a proprietary circuit architecture to enable the highest performance amplifier at the lowest power. Not only is it technic ...
LT3021/LT3021-1.2/ LT3021-1.5/LT3021-1.8
... voltage, not the 0.5V output voltage. Specifications for fixed output voltage devices are referred to the output voltage. Note 7: Dropout voltage is the minimum input to output voltage differential needed to maintain regulation at a specified output current. In dropout the output voltage equals: (VIN – ...
... voltage, not the 0.5V output voltage. Specifications for fixed output voltage devices are referred to the output voltage. Note 7: Dropout voltage is the minimum input to output voltage differential needed to maintain regulation at a specified output current. In dropout the output voltage equals: (VIN – ...
Website Glossary of Terms 1
... A technology using glass or plastic threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable is a bundle of either glass or plastic threads capable of transmitting messages modulated into light waves. Typically, fiber optic cable has greater bandwidth allowing them to carry more data than metal wires. ...
... A technology using glass or plastic threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable is a bundle of either glass or plastic threads capable of transmitting messages modulated into light waves. Typically, fiber optic cable has greater bandwidth allowing them to carry more data than metal wires. ...
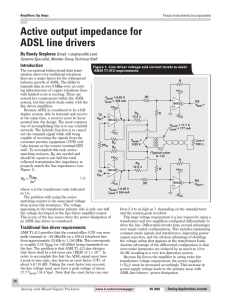
Active output impedance for ADSL line drivers
... The problem with using the seriesmatching resistor is the associated voltage drop across this resistance. The voltage appearing at the transformer primary side is only one-half from 5.3 to as high as 7, depending on the manufacturer the voltage developed at the line driver amplifier output. and the ...
... The problem with using the seriesmatching resistor is the associated voltage drop across this resistance. The voltage appearing at the transformer primary side is only one-half from 5.3 to as high as 7, depending on the manufacturer the voltage developed at the line driver amplifier output. and the ...
Chapter 3 Methods of Analysis
... So far, we have analyzed relatively simple circuits by applying Kirchhoff’s laws in combination with Ohm’s law. We can use this approach for all circuits, but as they become structurally more complicated and involve more and more elements, this direct method soon becomes cumbersome. In this chapter ...
... So far, we have analyzed relatively simple circuits by applying Kirchhoff’s laws in combination with Ohm’s law. We can use this approach for all circuits, but as they become structurally more complicated and involve more and more elements, this direct method soon becomes cumbersome. In this chapter ...
PI Design Advice.pdf
... advantage b) is helpful to prevent slew rate issues. the slew rate is the required voltage swing per unit time. the required current to prevent slew rate limiting is a function of signal frequency, signal amplitude, and driven load capacitance... as any of those three factors goes up, so too does t ...
... advantage b) is helpful to prevent slew rate issues. the slew rate is the required voltage swing per unit time. the required current to prevent slew rate limiting is a function of signal frequency, signal amplitude, and driven load capacitance... as any of those three factors goes up, so too does t ...
Lecture 17: BJT Biasing. Current Mirror.
... In this current mirror, Q1 is called a diode-connected BJT because the collector and base terminals are connected together. For proper operation of this circuit, it is very important that the BJTs be “matched,” meaning they having the same , characteristic curves, etc. Usually this means that the B ...
... In this current mirror, Q1 is called a diode-connected BJT because the collector and base terminals are connected together. For proper operation of this circuit, it is very important that the BJTs be “matched,” meaning they having the same , characteristic curves, etc. Usually this means that the B ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.