A new ferrochelatase mutation combined with low
... enzyme of the heme biosynthetic pathway, which catalyses the insertion of a ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX to form protoheme. Patients with EPP are clinically characterized by painful photosensitivity due to accumulation of protoporphyrin in the skin, and high levels of free protoporphyrin in e ...
... enzyme of the heme biosynthetic pathway, which catalyses the insertion of a ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX to form protoheme. Patients with EPP are clinically characterized by painful photosensitivity due to accumulation of protoporphyrin in the skin, and high levels of free protoporphyrin in e ...
8-Cell and Molecular Biology (Transcription)
... Finally, we will see that for many genes RNA is the final product Although, we will focus on the production of the proteins encoded by the genome in this section Like proteins many of these RNAs fold into precise three dimensional structures that have: ...
... Finally, we will see that for many genes RNA is the final product Although, we will focus on the production of the proteins encoded by the genome in this section Like proteins many of these RNAs fold into precise three dimensional structures that have: ...
Topic 1: Statistical analysis (2 hours)
... A researcher measured the mean size of leaves from two trees of the same species in different habitats. State one statistical test used to see if there is a significant difference in the leaf size. ...
... A researcher measured the mean size of leaves from two trees of the same species in different habitats. State one statistical test used to see if there is a significant difference in the leaf size. ...
BIOLOGY (Theory) 57/2 SECTION – A 1. Name the two gases
... (a) Runner (b) Offset Ans. a) Runner - Oxalis b) Offset - water hyacinth ...
... (a) Runner (b) Offset Ans. a) Runner - Oxalis b) Offset - water hyacinth ...
CHAPTER 14 DNA applications in society
... Some of these recombinant proteins, such as Humulin®, replaced products that were previously extracted from tissues of other species. Other recombinant proteins, such as human growth hormone (rec hGH), replaced products that were extracted from tissues of dead people (cadavers). Other recombinant pr ...
... Some of these recombinant proteins, such as Humulin®, replaced products that were previously extracted from tissues of other species. Other recombinant proteins, such as human growth hormone (rec hGH), replaced products that were extracted from tissues of dead people (cadavers). Other recombinant pr ...
Chapter 17 Practice Multple Choice
... b. complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA. c. the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid. d. changeable, depending on the amino acid that attaches to the tRNA. e. catalytic, making the tRNA a ribozyme. ____ 24. Which of the following is not true of RNA processing? a. Exons are ...
... b. complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA. c. the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid. d. changeable, depending on the amino acid that attaches to the tRNA. e. catalytic, making the tRNA a ribozyme. ____ 24. Which of the following is not true of RNA processing? a. Exons are ...
Homologous Recombination 1. Query: Could you explain what
... in our drawings; 3:1 is the same as 6:2; recall the yeast and Ascobolus paradigm that we discussed). In the regions immediately adjacent to the left and right Holliday junctions, you can see asymmetric heteroduplex, blue/green on one DNA duplex but not the other. If the marker of interest to us (M a ...
... in our drawings; 3:1 is the same as 6:2; recall the yeast and Ascobolus paradigm that we discussed). In the regions immediately adjacent to the left and right Holliday junctions, you can see asymmetric heteroduplex, blue/green on one DNA duplex but not the other. If the marker of interest to us (M a ...
MayerFrankiPoster
... the photosynthetic process requires phycobilisome (PBS) light-harvesting protein complexes that efficiently capture solar energy (Figure 2). Cell density and bioproduct formation in cyanobacterial cultures is limited by an ‘overshadowing’ effect. Cells growing at the surface of a culture capture mos ...
... the photosynthetic process requires phycobilisome (PBS) light-harvesting protein complexes that efficiently capture solar energy (Figure 2). Cell density and bioproduct formation in cyanobacterial cultures is limited by an ‘overshadowing’ effect. Cells growing at the surface of a culture capture mos ...
Effect of defects on thermal denaturation of DNA Oligomers
... used in the case of homogeneous chain is no longer valid. Attempts have, however, been made to use the model Hamiltonian of Eq.(1) for heterogeneous chains either by modelling the heterogeneity with quenched disorder [6] or by properly choosing basis sets of orthonormal functions for the kernels ap ...
... used in the case of homogeneous chain is no longer valid. Attempts have, however, been made to use the model Hamiltonian of Eq.(1) for heterogeneous chains either by modelling the heterogeneity with quenched disorder [6] or by properly choosing basis sets of orthonormal functions for the kernels ap ...
Computational Biology
... These clusters, or CpG islands, are targets for proteins that bind to unmethylated CpGs and initiate gene transcription. In contrast, methylated CpGs are generally associated with silent DNA, can block methylation-sensitive proteins and can be easily mutated. The loss of normal DNA methylation patte ...
... These clusters, or CpG islands, are targets for proteins that bind to unmethylated CpGs and initiate gene transcription. In contrast, methylated CpGs are generally associated with silent DNA, can block methylation-sensitive proteins and can be easily mutated. The loss of normal DNA methylation patte ...
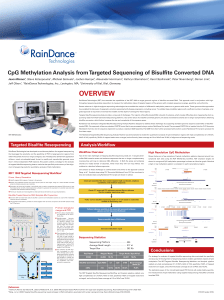
CpG methylation analysis from targeted
... fluorinated carrier oil with a block-copolymer surfactant to generate the equivalent of a picoliter scale test tube compatible with standard molecular biology. ...
... fluorinated carrier oil with a block-copolymer surfactant to generate the equivalent of a picoliter scale test tube compatible with standard molecular biology. ...
Extension Activity 1: Plasmid Mapping STUDENT MANU AL
... used in the DNA fingerprinting activity were constructed from the same pTZ18U plasmid parent but had different foreign fragments of DNA inserted into them. In the DNA fingerprinting exercise, only two restriction enzymes were used, but other enzymes could also have been used to cut these plasmids. T ...
... used in the DNA fingerprinting activity were constructed from the same pTZ18U plasmid parent but had different foreign fragments of DNA inserted into them. In the DNA fingerprinting exercise, only two restriction enzymes were used, but other enzymes could also have been used to cut these plasmids. T ...
Introduction of Microarray
... new and better molecular diagnostics new molecular targets for therapy finding and refining biological pathways Mutation and polymorphism detection ...
... new and better molecular diagnostics new molecular targets for therapy finding and refining biological pathways Mutation and polymorphism detection ...
Measuring Arsenite using E. coli reporter strains
... with specific DNA regions and its ability to react with arsenite. By using genetic engineering an artificial coupling was created between a DNA fragment containing the binding site for ArsR and a DNA fragment with the gene for the reporter protein (eGFP for enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein, Fig. 1 ...
... with specific DNA regions and its ability to react with arsenite. By using genetic engineering an artificial coupling was created between a DNA fragment containing the binding site for ArsR and a DNA fragment with the gene for the reporter protein (eGFP for enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein, Fig. 1 ...
Primary Sequence of Ovomucoid Messenger RNA as Determined
... contains cDNA synthesized from mRNAom, was described previously (33). This plasmid contained a 650 by DNAom insert, but lacked -150 by corresponding to the 5' end of mRNA om . To obtain cDNA sequences containing the 5' end of the mRNA sequence, we have synthesized and cloned another cDNA molecule wi ...
... contains cDNA synthesized from mRNAom, was described previously (33). This plasmid contained a 650 by DNAom insert, but lacked -150 by corresponding to the 5' end of mRNA om . To obtain cDNA sequences containing the 5' end of the mRNA sequence, we have synthesized and cloned another cDNA molecule wi ...
Ex2_09dev - Columbia University
... insertion of methionine (met), using the first tRNA. The start codon, AUG, serves both to start translation and to insert met. The second tRNA used in translation should correspond to the codon after the AUG, not the one after that (UUU). Translation does not start at the codon after the AUG; it sta ...
... insertion of methionine (met), using the first tRNA. The start codon, AUG, serves both to start translation and to insert met. The second tRNA used in translation should correspond to the codon after the AUG, not the one after that (UUU). Translation does not start at the codon after the AUG; it sta ...
S1 Document.
... Vector using HaloTag_F and HaloTag_R primers to introduce an Nde I restriction site at the 5′-end and a BamH I restriction site at the 3′-end (Table S1). The amplified fragment was digested with Nde I and BamH I and then introduced into the same sites in the expression plasmid for GFPuv3-pD-SecM148– ...
... Vector using HaloTag_F and HaloTag_R primers to introduce an Nde I restriction site at the 5′-end and a BamH I restriction site at the 3′-end (Table S1). The amplified fragment was digested with Nde I and BamH I and then introduced into the same sites in the expression plasmid for GFPuv3-pD-SecM148– ...
Template-Directed Synthesis of Structurally Defined Branched
... using monodisperse samples of short- and long-chain DNA sequences, which are routinely prepared via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or extracted from genomic sources (e.g., M13 phage DNA). Enzymatic template-directed synthesis enables rapid production of monodisperse and sequence-defined DNAbased pol ...
... using monodisperse samples of short- and long-chain DNA sequences, which are routinely prepared via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or extracted from genomic sources (e.g., M13 phage DNA). Enzymatic template-directed synthesis enables rapid production of monodisperse and sequence-defined DNAbased pol ...
Learning About DNA
... Before we can observe and study cells, we must learn to use a very important scientific tool, the microscope. Micro means “very small,” while scope means “to look at.” Over time, scientists developed a tool to make things look larger than their actual size. Microscopes use lenses (curved pieces of g ...
... Before we can observe and study cells, we must learn to use a very important scientific tool, the microscope. Micro means “very small,” while scope means “to look at.” Over time, scientists developed a tool to make things look larger than their actual size. Microscopes use lenses (curved pieces of g ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.