Analysis and Characterization of Nucleic Acids and Proteins
... Clinical and forensic analyses require characterization of specific genes or genomic regions at the molecular level. Because of their sequence‐specific activity, restriction endonucleases provide a convenient tool for molecular characterization of DNA ...
... Clinical and forensic analyses require characterization of specific genes or genomic regions at the molecular level. Because of their sequence‐specific activity, restriction endonucleases provide a convenient tool for molecular characterization of DNA ...
(THCA) synthase gene in
... two groups, ‘‘drug-type’’ and ‘‘fiber-type’’. The 62 nucleotides from the six ‘‘drug-type’’ strains (#013, #020, #054, #001, #053 and #010) were substituted with different nucleotides from the seven ‘‘fiber-type’’ strains (#009, #045, #078, #011, #068, #066 and #005); the nucleotide substitutions fo ...
... two groups, ‘‘drug-type’’ and ‘‘fiber-type’’. The 62 nucleotides from the six ‘‘drug-type’’ strains (#013, #020, #054, #001, #053 and #010) were substituted with different nucleotides from the seven ‘‘fiber-type’’ strains (#009, #045, #078, #011, #068, #066 and #005); the nucleotide substitutions fo ...
Supporting information S1.
... Supporting information S1. Detailed explanation of plasmids and strains construction The suicide vector pKNG101 was used to introduce the CAT* reporter gene within the Escherichia coli chromosome (Table S2). This plasmid contains a defective pir minus origin of replication (oriR6K), the strAB genes ...
... Supporting information S1. Detailed explanation of plasmids and strains construction The suicide vector pKNG101 was used to introduce the CAT* reporter gene within the Escherichia coli chromosome (Table S2). This plasmid contains a defective pir minus origin of replication (oriR6K), the strAB genes ...
Minireview Alpha Satellite and the Quest for the Human Centromere
... question. Functional centromeric DNAs need to be identified and mapped precisely within populations, and within extensive phylogenies that contain both closely related and distant species that are accessible to experimental manipulation. Lessons learned from centromere studies may be relevant to und ...
... question. Functional centromeric DNAs need to be identified and mapped precisely within populations, and within extensive phylogenies that contain both closely related and distant species that are accessible to experimental manipulation. Lessons learned from centromere studies may be relevant to und ...
Rolling circle transcription on smallest size double stranded DNA
... revolutionary Nature paper has since the early seventies been exploited in the creation of novel DNA combinations from naturally occurring sequences (Cohen, et al. 1973). The basis of this versatile method of combining separate DNA fragments into one unit is the predictable nature with which two com ...
... revolutionary Nature paper has since the early seventies been exploited in the creation of novel DNA combinations from naturally occurring sequences (Cohen, et al. 1973). The basis of this versatile method of combining separate DNA fragments into one unit is the predictable nature with which two com ...
The Role of Mismatch Repair in Bacterial Evolution
... The spread of mutators occurs because they can create or acquire a beneficial mutation (e.g. antibiotic resistance) that gives them advantage over non-adapted bacteria. In an asexual population, the mutator may then spread with the advantageous gene, by a phenomenon called »hitch-hiking« (29) and in ...
... The spread of mutators occurs because they can create or acquire a beneficial mutation (e.g. antibiotic resistance) that gives them advantage over non-adapted bacteria. In an asexual population, the mutator may then spread with the advantageous gene, by a phenomenon called »hitch-hiking« (29) and in ...
Determination of guanine-plus-cytosine content of
... A dual-laser flow cytometer was used to analyse different species of bacteria for the molar percentage of guanineplus-cytosine (% G + C) without the need for DNA extraction or purification. Ethanol-fixed bacterial cells were stained with a combination of DNA-specific fluorochromes, Hoechst 33258 and ...
... A dual-laser flow cytometer was used to analyse different species of bacteria for the molar percentage of guanineplus-cytosine (% G + C) without the need for DNA extraction or purification. Ethanol-fixed bacterial cells were stained with a combination of DNA-specific fluorochromes, Hoechst 33258 and ...
Primary Sequence of Ovomucoid Messenger RNA
... contains cDNA synthesized from mRNAom, was described previously (33). This plasmid contained a 650 by DNAom insert, but lacked -150 by corresponding to the 5' end of mRNA om . To obtain cDNA sequences containing the 5' end of the mRNA sequence, we have synthesized and cloned another cDNA molecule wi ...
... contains cDNA synthesized from mRNAom, was described previously (33). This plasmid contained a 650 by DNAom insert, but lacked -150 by corresponding to the 5' end of mRNA om . To obtain cDNA sequences containing the 5' end of the mRNA sequence, we have synthesized and cloned another cDNA molecule wi ...
number of fifty human tumours
... cells are measured, it is nearly always found that the majority are grouped together, although the level of the mode varies widely in different tumours. A few cells may be expected to be synthesising DNA and to have values up to twice the "resting " value for this reason, but clearly these usually f ...
... cells are measured, it is nearly always found that the majority are grouped together, although the level of the mode varies widely in different tumours. A few cells may be expected to be synthesising DNA and to have values up to twice the "resting " value for this reason, but clearly these usually f ...
FEBS Letters
... Recently, it has been found that heterotrophic bacteria synthesize isoprenoids following a pathway totally di¡erent from the classical mevalonate pathway [1,2]. In the novel pathway, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvate are the substrates for an initial transketolase reaction resulting in 1-deoxy ...
... Recently, it has been found that heterotrophic bacteria synthesize isoprenoids following a pathway totally di¡erent from the classical mevalonate pathway [1,2]. In the novel pathway, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvate are the substrates for an initial transketolase reaction resulting in 1-deoxy ...
90718 Internal v2 3.6 A2 Generic 2006
... The following guidelines are supplied to enable teachers to carry out valid and consistent assessment using this internal assessment resource. These teacher guidelines do not need to be submitted for moderation. Achievement standard 90718 requires students to be able to describe two biotechnological ...
... The following guidelines are supplied to enable teachers to carry out valid and consistent assessment using this internal assessment resource. These teacher guidelines do not need to be submitted for moderation. Achievement standard 90718 requires students to be able to describe two biotechnological ...
Biosafety Protocol Registration Form
... restricted agents is cloned into non-pathogenic prokaryotic or lower eukaryotic host-vector systems. For cloning toxin molecules with LD-50 of less than 100 nanograms per kilogram body weight, check section III-B above. Section D-2 does not apply. D-3: Experiments involving the use of infectious DNA ...
... restricted agents is cloned into non-pathogenic prokaryotic or lower eukaryotic host-vector systems. For cloning toxin molecules with LD-50 of less than 100 nanograms per kilogram body weight, check section III-B above. Section D-2 does not apply. D-3: Experiments involving the use of infectious DNA ...
For example, Gall diseases on the roots of tobacco plants were first
... The crown is the point at the soil line where the main root joins the stem where is galls typically form at. But the galls may also develop on secondary or lateral roots and on the main stem and branches above the soil line The study of the development of crown gall disease in plants is important, n ...
... The crown is the point at the soil line where the main root joins the stem where is galls typically form at. But the galls may also develop on secondary or lateral roots and on the main stem and branches above the soil line The study of the development of crown gall disease in plants is important, n ...
Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human
... • The experimental design of ChIPSeq is considerably simpler. • ChIPSeq typically can achieve higher genomic coverage than ChIP-chip (also depends on read length vs. probe length). • The data from ChIPSeq is arguably cleaner and easier to process. • Costs are comparable (?). Mar. 19, 2008 ...
... • The experimental design of ChIPSeq is considerably simpler. • ChIPSeq typically can achieve higher genomic coverage than ChIP-chip (also depends on read length vs. probe length). • The data from ChIPSeq is arguably cleaner and easier to process. • Costs are comparable (?). Mar. 19, 2008 ...
unit – vi genetics - Sakshieducation.com
... 1) 3164.7 million nucleotide base pairs were observed in a human genome 2) The average number of base pairs in human gene is 3000 ...
... 1) 3164.7 million nucleotide base pairs were observed in a human genome 2) The average number of base pairs in human gene is 3000 ...
simultaneous detection of colorectal cancer mutations in stool
... Summary: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second main cause of cancer-related death in the Western world and like many other tumours is curable if detected at an early stage. Current detection options include faecal occult blood testing and invasive direct visualisation techniques such as flexible sig ...
... Summary: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second main cause of cancer-related death in the Western world and like many other tumours is curable if detected at an early stage. Current detection options include faecal occult blood testing and invasive direct visualisation techniques such as flexible sig ...
Functional expression of lepidopteran
... genera Heliothis, Spodoptera and Trichoplusia [1]. However, the use of baculoviruses as insect control agents has met with limited success due to lack of field persistence and slower speed of action on insect mortality when compared to classical chemical insecticides [10]. In order to enhance the ef ...
... genera Heliothis, Spodoptera and Trichoplusia [1]. However, the use of baculoviruses as insect control agents has met with limited success due to lack of field persistence and slower speed of action on insect mortality when compared to classical chemical insecticides [10]. In order to enhance the ef ...
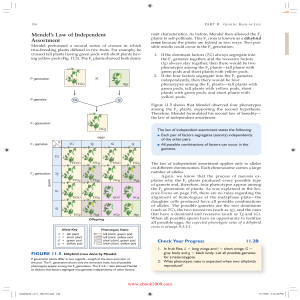
! Mendel`s Law of Independent Assortment
... alleles, and all four children could have cystic fibrosis. We can use the product rule and the sum rule of probability to predict the results of a dihybrid cross, such as the one shown in Figure 11.5. The Punnett square carries out the multiplication for us, and we add the results to find that the p ...
... alleles, and all four children could have cystic fibrosis. We can use the product rule and the sum rule of probability to predict the results of a dihybrid cross, such as the one shown in Figure 11.5. The Punnett square carries out the multiplication for us, and we add the results to find that the p ...
Gene Section FANCG (Fanconi anemia, complementation group G)
... Fanconi anaemia's prognosis is poor; mean survival is 20 years: patients die of bone marrow failure (infections, haemorrhages), leukaemia, or solid cancer. It has recently been shown that significant phenotypic differences were found between the various complementation groups. FA group G patients ha ...
... Fanconi anaemia's prognosis is poor; mean survival is 20 years: patients die of bone marrow failure (infections, haemorrhages), leukaemia, or solid cancer. It has recently been shown that significant phenotypic differences were found between the various complementation groups. FA group G patients ha ...
Human Biology - Genetics
... What is the composition of a chromosome? Karyotyping was not introduced until the 1950s. However, as early as the 1920s, scientists agreed that chromosomes were made of two chemical substances- deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and protein. After these substances were identified, the next question was, “W ...
... What is the composition of a chromosome? Karyotyping was not introduced until the 1950s. However, as early as the 1920s, scientists agreed that chromosomes were made of two chemical substances- deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and protein. After these substances were identified, the next question was, “W ...
General Biology I Final Exam
... when molecules with the same molecular formula have bonded together in different orders. Any of two or more chemical compounds, having the same molecular formula but different ...
... when molecules with the same molecular formula have bonded together in different orders. Any of two or more chemical compounds, having the same molecular formula but different ...
AZT resistance of simian foamy virus reverse transcriptase is based
... coli harboring three (K211I, S345T, E350K) or four mutations (K211I, I224T, S345T, E350K) in the reverse transcriptase gene. Our analyses show that the polymerization activity of these mutants is impaired. In contrast to the AZT-resistant reverse transcriptase of HIV-1, the AZT resistant enzymes of ...
... coli harboring three (K211I, S345T, E350K) or four mutations (K211I, I224T, S345T, E350K) in the reverse transcriptase gene. Our analyses show that the polymerization activity of these mutants is impaired. In contrast to the AZT-resistant reverse transcriptase of HIV-1, the AZT resistant enzymes of ...
The serC-aroA operon of Escherichia coli
... Digestion products were extracted with phenol/chloroform and ethanol-precipitated before analysis on polyacrylamide gels. RESULTS Sub-cloning of the aroA gene The 4.6 kb PstI fragment, inserted in pKD501 (Duncan et al., 1984a) is considerably larger than the size required to encode EPSP synthase, th ...
... Digestion products were extracted with phenol/chloroform and ethanol-precipitated before analysis on polyacrylamide gels. RESULTS Sub-cloning of the aroA gene The 4.6 kb PstI fragment, inserted in pKD501 (Duncan et al., 1984a) is considerably larger than the size required to encode EPSP synthase, th ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.