Ch. 12 Introduction to Biotechnology
... transforming agriculture • New genetic varieties of animals and plants are being produced – A plant with a new trait can be created using the Ti plasmid ...
... transforming agriculture • New genetic varieties of animals and plants are being produced – A plant with a new trait can be created using the Ti plasmid ...
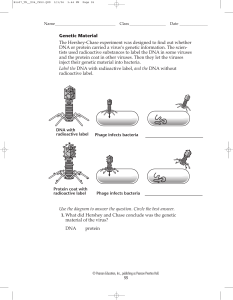
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without radioactive label. ...
... Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without radioactive label. ...
Les 1-DNA Structure-review
... Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
... Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
DNA Extraction
... resulting DNA can be spooled (wound) on a stirring rod and pulled from the solution at this point. The extraction and purification of DNA are of primary importance to the field of biotechnology and forensics. DNA extraction allows for analysis including the detection of genetic disorders, identifica ...
... resulting DNA can be spooled (wound) on a stirring rod and pulled from the solution at this point. The extraction and purification of DNA are of primary importance to the field of biotechnology and forensics. DNA extraction allows for analysis including the detection of genetic disorders, identifica ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... o Aerobic vs. Anaerobic environments: fermentations (alcoholic, lactic acid), Genetics Mendels laws (law of segregation, law of independent assortment) Incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, epistasis, pleiotropy, polygenic traits, genes influenced by the environment Probability ...
... o Aerobic vs. Anaerobic environments: fermentations (alcoholic, lactic acid), Genetics Mendels laws (law of segregation, law of independent assortment) Incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, epistasis, pleiotropy, polygenic traits, genes influenced by the environment Probability ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... Describe the Endosymbiotic hypothesis. Essentially, modern cells are a product of ancient eukaryotes engulfing free-living mitochondria and/or chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria ...
... Describe the Endosymbiotic hypothesis. Essentially, modern cells are a product of ancient eukaryotes engulfing free-living mitochondria and/or chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria ...
Btec Quiz 1Samples
... Be sure to put your name and student ID number on the mark-sense sheet on the bottom right corner ( No ID on the sense sheet will results in 0 mark). 1. Biotechnology is broadly defined as using living organisms, or products of living organisms for human benefit to make a product or solve a proble ...
... Be sure to put your name and student ID number on the mark-sense sheet on the bottom right corner ( No ID on the sense sheet will results in 0 mark). 1. Biotechnology is broadly defined as using living organisms, or products of living organisms for human benefit to make a product or solve a proble ...
Genetically Modified Organisms
... Conventional plant breeding includes techniques such as cross pollination, chromosome doubling, and mutation breeding. Selecting the best plants to serve as parent lines and DNA marker assisted selection (MAS) are also considered to be components of conventional breeding. Conventionally bred plants ...
... Conventional plant breeding includes techniques such as cross pollination, chromosome doubling, and mutation breeding. Selecting the best plants to serve as parent lines and DNA marker assisted selection (MAS) are also considered to be components of conventional breeding. Conventionally bred plants ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction and DNA Sequencing
... • Polymerase chain reaction amplification of cDNA can also be used to detect specific transcripts in a RNA sample. • In this procedure, known as RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase is used to copy all of the mRNAs in an RNA sample into cDNA. • Usually, oligo dT molecules, that anneal to the poly A tails o ...
... • Polymerase chain reaction amplification of cDNA can also be used to detect specific transcripts in a RNA sample. • In this procedure, known as RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase is used to copy all of the mRNAs in an RNA sample into cDNA. • Usually, oligo dT molecules, that anneal to the poly A tails o ...
Biotechnology
... diabetes used insulin derived from the pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulinmaking genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
... diabetes used insulin derived from the pancreas of cows and pigs (limited production) • Today, most human insulin comes from human insulinmaking genes transferred into simple cells such as bacteria or baker’s yeast (unlimited supply) – Identical to insulin made by the human pancreas ...
Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology
... It has been explained to me and I have understood that: ...
... It has been explained to me and I have understood that: ...
File - Hope Christian College Parent and Student Portal
... bits of DNA…which can then attach to other strands of DNA …as long as the ends have complimentary nucleotides This means that biologists can use a certain enzyme to cut the plasmid at a particular point and insert a gene of interest which has been identified in humans and also removed using a probe ...
... bits of DNA…which can then attach to other strands of DNA …as long as the ends have complimentary nucleotides This means that biologists can use a certain enzyme to cut the plasmid at a particular point and insert a gene of interest which has been identified in humans and also removed using a probe ...
DNA fingerprinting
... • The number of the VNTRs can vary significantly from individual to individual • In humans such sequences are often bordered by restriction endonuclease sites. • The fragment sizes resulting from digestion depend on the number of copies between the restriction sites • This gives rise to unique RFLP ...
... • The number of the VNTRs can vary significantly from individual to individual • In humans such sequences are often bordered by restriction endonuclease sites. • The fragment sizes resulting from digestion depend on the number of copies between the restriction sites • This gives rise to unique RFLP ...
Slide 1
... The Conservative Method This model suggested that the original, parental DNA molecule would remain intact. It said that a separate, new DNA molecule would be made from scratch. The Semi-Conservative Method Proposed that the original, parental molecule would split in half, into two separate strands ...
... The Conservative Method This model suggested that the original, parental DNA molecule would remain intact. It said that a separate, new DNA molecule would be made from scratch. The Semi-Conservative Method Proposed that the original, parental molecule would split in half, into two separate strands ...
The Story of Molecular Biology and Its Creators
... “Once information has passed into protein it cannot get out again”… Crick’s choice of the word “dogma” was not a call for blind faith in what was really a central hypothesis. According to Horace Judson in his book The Eighth Day of Creation, it was because Crick had it in his mind that “a dogma was ...
... “Once information has passed into protein it cannot get out again”… Crick’s choice of the word “dogma” was not a call for blind faith in what was really a central hypothesis. According to Horace Judson in his book The Eighth Day of Creation, it was because Crick had it in his mind that “a dogma was ...
The Story of Molecular Biology and Its Creators
... “Once information has passed into protein it cannot get out again”… Crick’s choice of the word “dogma” was not a call for blind faith in what was really a central hypothesis. According to Horace Judson in his book The Eighth Day of Creation, it was because Crick had it in his mind that “a dogma was ...
... “Once information has passed into protein it cannot get out again”… Crick’s choice of the word “dogma” was not a call for blind faith in what was really a central hypothesis. According to Horace Judson in his book The Eighth Day of Creation, it was because Crick had it in his mind that “a dogma was ...
a@%,,$, 03%
... 15. In the 1960's the flow of cell functioning information in prokaryotic.cells was identified as (A) transcription of DNA genetic information -> translation of mRNA message -> formation of proteins necessary for cell function (B) replication of DNA genetic information -> cell division - > cell divi ...
... 15. In the 1960's the flow of cell functioning information in prokaryotic.cells was identified as (A) transcription of DNA genetic information -> translation of mRNA message -> formation of proteins necessary for cell function (B) replication of DNA genetic information -> cell division - > cell divi ...
Presentation File
... court that entered the judgment of conviction a motion requesting DNA testing ...
... court that entered the judgment of conviction a motion requesting DNA testing ...
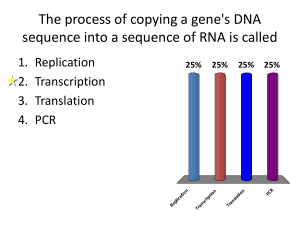
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
Biotechnological Tools and Techniques
... • circular pieces of non-chromosomal DNA found in bacteria cells • artificial plasmids have been engineered to contain an area with many recognition sites (and none in other areas) ...
... • circular pieces of non-chromosomal DNA found in bacteria cells • artificial plasmids have been engineered to contain an area with many recognition sites (and none in other areas) ...
1. RNA is a different nucleic acid and differs from DNA on 3 things
... 3. These “_____________” are called ________. Genes make other molecules called ____________. Proteins enable a cell to _________________________ _________________, such as working with other groups of cells to make hearing possible. ...
... 3. These “_____________” are called ________. Genes make other molecules called ____________. Proteins enable a cell to _________________________ _________________, such as working with other groups of cells to make hearing possible. ...
Mini lab 11.1 and 11.2
... Responses are clear, complete and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject matter Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment ...
... Responses are clear, complete and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject matter Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment ...
Bio 313 worksheet 7 - Iowa State University
... a. Cells in G1, before switching to medium with 14N b. Cells in G2, after switching to medium with 14N c. Cells in anaphase of mitosis, after switching to medium with 14N d. Cells in metaphase I of meiosis, after switching to medium with 14N e. Cells in anaphase II of meiosis, after switching to med ...
... a. Cells in G1, before switching to medium with 14N b. Cells in G2, after switching to medium with 14N c. Cells in anaphase of mitosis, after switching to medium with 14N d. Cells in metaphase I of meiosis, after switching to medium with 14N e. Cells in anaphase II of meiosis, after switching to med ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.