MS Word file
... be transferred naturally. R plasmids have evolved in the past 60 years since the beginning of widespread use of antibiotics. The transfer of R plasmids is not restricted to bacteria of the same or even related species. Transformation: A bacterium takes up DNA from the medium. Recombination takes pla ...
... be transferred naturally. R plasmids have evolved in the past 60 years since the beginning of widespread use of antibiotics. The transfer of R plasmids is not restricted to bacteria of the same or even related species. Transformation: A bacterium takes up DNA from the medium. Recombination takes pla ...
blah
... values in phosphate buffer, Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 (0.02 M/0.02 M), CAu = 1.6×10-4 M, I = 0.08 M, T = 25 oC. The slight blue-shift from pH 10 to pH 7 indicates some NP destabilization that turns, for pH < 6.5, in a large red-shift indicating nanoparticles aggregation. ...
... values in phosphate buffer, Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 (0.02 M/0.02 M), CAu = 1.6×10-4 M, I = 0.08 M, T = 25 oC. The slight blue-shift from pH 10 to pH 7 indicates some NP destabilization that turns, for pH < 6.5, in a large red-shift indicating nanoparticles aggregation. ...
110381P - Genome Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd.
... to 2,000 base pairs. The 100 bp DNA Ladder consists of 13 double strand DNA fragments ranging in sizes from 100 to 1,000 bp in 100 bp increments, and additional fragments of 1,200, 1,600, 2,000 bp. The 500, 1,000 and 2,000 bp bands are two to three times brighter for easy identification. ...
... to 2,000 base pairs. The 100 bp DNA Ladder consists of 13 double strand DNA fragments ranging in sizes from 100 to 1,000 bp in 100 bp increments, and additional fragments of 1,200, 1,600, 2,000 bp. The 500, 1,000 and 2,000 bp bands are two to three times brighter for easy identification. ...
downloadable file
... Sequencing DNA is a way to determine the order of the four nucleotides along a strand of DNA. Sequencing DNA has become vital to the fields of basic research, biotechnology, forensics and medical diagnostics. In the late 1970’s, biology saw the first two methods to sequence DNA. One method, Maxam-Gi ...
... Sequencing DNA is a way to determine the order of the four nucleotides along a strand of DNA. Sequencing DNA has become vital to the fields of basic research, biotechnology, forensics and medical diagnostics. In the late 1970’s, biology saw the first two methods to sequence DNA. One method, Maxam-Gi ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Define: Nucleotide
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
Revised 2015 15.2 PowerPoint
... The recombinant plasmid has a genetic marker, such as a gene for antibiotic resistance. A genetic marker is a gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry the plasmid from those that ...
... The recombinant plasmid has a genetic marker, such as a gene for antibiotic resistance. A genetic marker is a gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry the plasmid from those that ...
1. Chromosome structure a. Nucleosome
... 6. transposable elements (transposons can be simple or complex) B. Genetic engineering 1. Toolkit includes plasmid (piece of round DNA from bacteria/yeast) or other vector such as viruses; restriction enzymes; host cell (usually bacteria like E. coli) 2. Restriction enzymes cut genes at restriction ...
... 6. transposable elements (transposons can be simple or complex) B. Genetic engineering 1. Toolkit includes plasmid (piece of round DNA from bacteria/yeast) or other vector such as viruses; restriction enzymes; host cell (usually bacteria like E. coli) 2. Restriction enzymes cut genes at restriction ...
Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
... Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #6: Molecular Biology ...
... Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #6: Molecular Biology ...
2011 Spring Biology Final Review
... ribosome to provide instruction to make a protein there. 13. Every three letters on the mRNA strand. Codes for specific amino acids. 14. The site of protein synthesis 15. Instructions found in the nucleus to make proteins. 16. When DNA is used as a template to make a mRNA strand ...
... ribosome to provide instruction to make a protein there. 13. Every three letters on the mRNA strand. Codes for specific amino acids. 14. The site of protein synthesis 15. Instructions found in the nucleus to make proteins. 16. When DNA is used as a template to make a mRNA strand ...
File - Ms. Wilson`s Biology Class
... “unzip.” Read the script, answer the questions below, and then, click “OK”. 1. In a real cell, what does the DNA molecule do before it unzips? _____________________ 2. What molecules break the rungs (bases) apart? ________________________ Drag the correct bases over to “synthesize” the new DNA halve ...
... “unzip.” Read the script, answer the questions below, and then, click “OK”. 1. In a real cell, what does the DNA molecule do before it unzips? _____________________ 2. What molecules break the rungs (bases) apart? ________________________ Drag the correct bases over to “synthesize” the new DNA halve ...
General Microbiology Lecture Twelve Identification of Bacteria
... • Bacteria can develop resistance to many antibiotics. The range and degree of resistance to antibiotics can be measured using antibiotic sensitive test, which involve placing small antibiotic impregnated disks on a gar plate inoculated with the bacteria. • The bacteria will not grow near the disk i ...
... • Bacteria can develop resistance to many antibiotics. The range and degree of resistance to antibiotics can be measured using antibiotic sensitive test, which involve placing small antibiotic impregnated disks on a gar plate inoculated with the bacteria. • The bacteria will not grow near the disk i ...
BIO.2
... organelles within cells were described and specific functions were demonstrated to be associated with each organelle. Cells were observed to be differentiated to specific functions in different tissues. b) scientific explanations of the development of organisms through time (biological evolution) Pr ...
... organelles within cells were described and specific functions were demonstrated to be associated with each organelle. Cells were observed to be differentiated to specific functions in different tissues. b) scientific explanations of the development of organisms through time (biological evolution) Pr ...
Gel electrophoresis - University of California, Santa Barbara
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
bch224 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... plasmids for the formation of recombinant DNA to take place. The sticky ends of the genes anneal with complimentary strands on the sticky ends of plasmids and DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of the phosphoester bond. Not all plasmids pick up DNA. After the reaction, the mixture is transferred fro ...
... plasmids for the formation of recombinant DNA to take place. The sticky ends of the genes anneal with complimentary strands on the sticky ends of plasmids and DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of the phosphoester bond. Not all plasmids pick up DNA. After the reaction, the mixture is transferred fro ...
Fact Sheet Describing Recombinant DNA and Elements
... Yeasts, eukaryotic unicellular fungi, contribute a great deal to the study of molecular genetics. They are popular organisms to clone and express DNA in because they are eukaryotes, and can therefore splice out introns, the non-coding sequences in the middle of many eukaryotic genes. For the past tw ...
... Yeasts, eukaryotic unicellular fungi, contribute a great deal to the study of molecular genetics. They are popular organisms to clone and express DNA in because they are eukaryotes, and can therefore splice out introns, the non-coding sequences in the middle of many eukaryotic genes. For the past tw ...
DNA and RNA
... into mice and observed that they did not die. Griffith's fourth experiment was to inject heat treated, killed, smooth strain mixed with the rough strain. ...
... into mice and observed that they did not die. Griffith's fourth experiment was to inject heat treated, killed, smooth strain mixed with the rough strain. ...
DNA - EPHS Knowles Biology
... 2. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? 3. Name the three components of a nucleotide. 4. What does DNA stand for? 5. What does RNA stand for? 6. What are the building blocks of proteins? 7. How many amino acids are found in the human body? 8. Where does replication occur in the cell? 9. Wh ...
... 2. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? 3. Name the three components of a nucleotide. 4. What does DNA stand for? 5. What does RNA stand for? 6. What are the building blocks of proteins? 7. How many amino acids are found in the human body? 8. Where does replication occur in the cell? 9. Wh ...
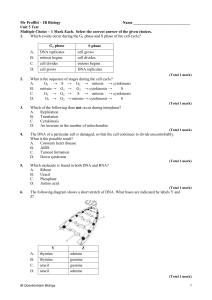
Mr Proffitt – IB Biology Name Unit 3 Test Multiple Choice – 1 Mark
... Essay – CHOOSE ONE. Answer one of the following essay choices. Take note of the command terms, and number of marks awarded for each question. – 11 Marks. 19. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. ...
... Essay – CHOOSE ONE. Answer one of the following essay choices. Take note of the command terms, and number of marks awarded for each question. – 11 Marks. 19. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. ...
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
... DNA are simultaneously co-extracted with similar efficiencies, then gDNA copies can also provide a simple and direct estimate of cell numbers which in turn provides a normalisation factor for total RNA quantity. A prerequisite for using this approach is that the extraction efficiency of both DNA and ...
... DNA are simultaneously co-extracted with similar efficiencies, then gDNA copies can also provide a simple and direct estimate of cell numbers which in turn provides a normalisation factor for total RNA quantity. A prerequisite for using this approach is that the extraction efficiency of both DNA and ...
T. Hill
... A light-emitting DNA probe can also be used for detection of the PCR product. Various probe designs exist but use the bringing together or separation of two fluorophores (when the DNA probe binds to the target) and exploit the transfer of fluorescence resonance energy between them (excitation of one ...
... A light-emitting DNA probe can also be used for detection of the PCR product. Various probe designs exist but use the bringing together or separation of two fluorophores (when the DNA probe binds to the target) and exploit the transfer of fluorescence resonance energy between them (excitation of one ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... The following genotypes were found in a male cat and a Gene Trait female cat: BbSs (male) and bbSS (female). B Black fur The phenotype of the offspring from these parents willb White fur a. All have black fur S Short fur b. All have white fur s Long fur c. All have long fur d. All have short fur 16. ...
... The following genotypes were found in a male cat and a Gene Trait female cat: BbSs (male) and bbSS (female). B Black fur The phenotype of the offspring from these parents willb White fur a. All have black fur S Short fur b. All have white fur s Long fur c. All have long fur d. All have short fur 16. ...
Beginning to crack the code of `junk DNA`
... To figure it out, Kazazian was able to identify some unique stretches of code in the line1 sequence affecting one of the boys. Using what is called a genetic probe, he was able to find the same sequence in a line1 element in the boy's mother, but it was in a different place, on Chromosome 22. (Human ...
... To figure it out, Kazazian was able to identify some unique stretches of code in the line1 sequence affecting one of the boys. Using what is called a genetic probe, he was able to find the same sequence in a line1 element in the boy's mother, but it was in a different place, on Chromosome 22. (Human ...
Inherited Diseases PowerPoint
... • The genetic material is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and contains the instructions for the growth and development of the individual. • The changed genetic material is passed from parent to child. ...
... • The genetic material is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and contains the instructions for the growth and development of the individual. • The changed genetic material is passed from parent to child. ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.