Genetics Option - Worked Examples
... Gene cloning means making identical copies of a gene. This is normally done by using recombinant DNA technology, e.g. by inserting the gene into the DNA of a plasmid, causing the plasmid to be taken up by a bacterium, and allowing the bacterium to reproduce by placing it on a growth medium. Gene the ...
... Gene cloning means making identical copies of a gene. This is normally done by using recombinant DNA technology, e.g. by inserting the gene into the DNA of a plasmid, causing the plasmid to be taken up by a bacterium, and allowing the bacterium to reproduce by placing it on a growth medium. Gene the ...
1a.Genetics Key Terms
... A diagram used to predict the results of reproduction between different organisms ...
... A diagram used to predict the results of reproduction between different organisms ...
2150401 - Gujarat Technological University
... Discovery of conjugation, Conjugation by E coli F factor, structure of F vector, Regulation of F factor fertility, Establishment of cell contact: DNA mobilization and transfer and separation of mating pair, Hfr conjugation and chromosomal transfer, F prime Conjugation and merodiploids, Conjugation o ...
... Discovery of conjugation, Conjugation by E coli F factor, structure of F vector, Regulation of F factor fertility, Establishment of cell contact: DNA mobilization and transfer and separation of mating pair, Hfr conjugation and chromosomal transfer, F prime Conjugation and merodiploids, Conjugation o ...
Name: Period: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM Topic/Concept What you
... food for shrews (small mammals) and some bird species. Scientists studied 1-acre plots in various parts of a state to determine the average number of sawfly cocoons, shrews, and robins. The data collected are shown in the table ...
... food for shrews (small mammals) and some bird species. Scientists studied 1-acre plots in various parts of a state to determine the average number of sawfly cocoons, shrews, and robins. The data collected are shown in the table ...
DNA - Bishop Shanahan High School
... dominance and are independently sorted; used pea plants 1905 Bateson and Punnett – some “factors” are linked; used pea plants 1910 Morgan – chromosome theory, linkage maps; used fruit flies General thought: PROTEINS must be the heredity factor! DNA is just a structural molecule for the proteins. WHY ...
... dominance and are independently sorted; used pea plants 1905 Bateson and Punnett – some “factors” are linked; used pea plants 1910 Morgan – chromosome theory, linkage maps; used fruit flies General thought: PROTEINS must be the heredity factor! DNA is just a structural molecule for the proteins. WHY ...
Research Focused Undergraduate Education
... Reasons for Plant Gene Transfer Golden Rice Grains such as rice, produce all but two of the enzymes needed to produce beta carotene (vit A precursor) Rice feeds half the world’s population Vit A deficiencies are associated with blindness, night blindness, diabetes, anemia and easy infection ...
... Reasons for Plant Gene Transfer Golden Rice Grains such as rice, produce all but two of the enzymes needed to produce beta carotene (vit A precursor) Rice feeds half the world’s population Vit A deficiencies are associated with blindness, night blindness, diabetes, anemia and easy infection ...
1_3_nucl_acid_2.ppt
... • Transfer the size-separated DNA fragments out of the agarose gel and onto a membrane (nylon or nitrocellulose) to make an immobilized replica of the gel pattern. • Hybridize the membrane to a specific, labeled nucleic acid probe and determine which DNA fragments contain that labeled sequence. ...
... • Transfer the size-separated DNA fragments out of the agarose gel and onto a membrane (nylon or nitrocellulose) to make an immobilized replica of the gel pattern. • Hybridize the membrane to a specific, labeled nucleic acid probe and determine which DNA fragments contain that labeled sequence. ...
Student Handout - University of California, Irvine
... ____________ pieces of DNA will have more difficulty moving through the gel than ___________ fragments. Thus, larger fragments will move _____________ than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different __________ of DNA fragments. 10 min. ...
... ____________ pieces of DNA will have more difficulty moving through the gel than ___________ fragments. Thus, larger fragments will move _____________ than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different __________ of DNA fragments. 10 min. ...
Troubling and Terrific Technology
... computers to exam stretches of DNA and find the parts that actually code for genes (look for start/stop codons etc) Belief now is that there are only 30-40000 genes - most of our genome is non coding Most vertebrate genes can code for 2 or 3 polypeptides by changing the splicing of mRNA ...
... computers to exam stretches of DNA and find the parts that actually code for genes (look for start/stop codons etc) Belief now is that there are only 30-40000 genes - most of our genome is non coding Most vertebrate genes can code for 2 or 3 polypeptides by changing the splicing of mRNA ...
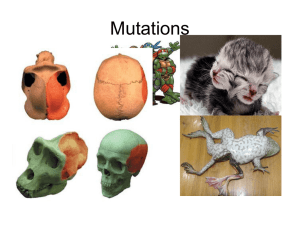
25L-Mutations - Doral Academy Preparatory
... A third way a mutation can occur is when ________ ________ are removed from the original DNA sequence. See examples on page 3(Human Genetic Disorders) and page 4 (Types of mutations that can occur). Fortunately most mutations are _____________. Two common methods of repair are when damaged base or ...
... A third way a mutation can occur is when ________ ________ are removed from the original DNA sequence. See examples on page 3(Human Genetic Disorders) and page 4 (Types of mutations that can occur). Fortunately most mutations are _____________. Two common methods of repair are when damaged base or ...
Genetics and Biotechnology Test Review
... 2. How do you represent dominant and recessive alleles using letters? 3. What is genetics? 4. What is heredity? 5. Who was the father of genetics? 6. Be able to analyze a pedigree. 7. Does a parent have to show a trait in order for their offspring to show it? 8. What is codominance? 9. What is incom ...
... 2. How do you represent dominant and recessive alleles using letters? 3. What is genetics? 4. What is heredity? 5. Who was the father of genetics? 6. Be able to analyze a pedigree. 7. Does a parent have to show a trait in order for their offspring to show it? 8. What is codominance? 9. What is incom ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... • What are the components of genes? • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
... • What are the components of genes? • How does a gene relate to the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA <> RNA > Protein? • How does a gene encode a protein? • How is the mathematical evidence used to predict genes? • How does biological evidence (from RNA and proteins) confirm gene predictions? ...
Human Genetics and Molecular Biology Review Packet
... 7) How does the structure of DNA predict its function as the source of an organism’s genetic information? a) How does the structure of the double helix predict how it is copied? b) What did scientists infer about the information that must be contained in the DNA sequence? 8) Some of the energy in su ...
... 7) How does the structure of DNA predict its function as the source of an organism’s genetic information? a) How does the structure of the double helix predict how it is copied? b) What did scientists infer about the information that must be contained in the DNA sequence? 8) Some of the energy in su ...
Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
... inside a viral capsid Crossover occurs between new transduced DNA and new host DNA ...
... inside a viral capsid Crossover occurs between new transduced DNA and new host DNA ...
Chemical basis of Inheritance Review KEY - Pelletier Pages
... 8. What kind of bond occurs between the bases of the complementary strands of DNA? Hydrogen bonds A-T 2 bonds, G-C three bonds 9. What kind of bond occurs between the sugar and phosphate units on the DNA backbone? Phosphodiester bonds 10. How is DNA replicated? Explain. Discuss the relevance of 3’ a ...
... 8. What kind of bond occurs between the bases of the complementary strands of DNA? Hydrogen bonds A-T 2 bonds, G-C three bonds 9. What kind of bond occurs between the sugar and phosphate units on the DNA backbone? Phosphodiester bonds 10. How is DNA replicated? Explain. Discuss the relevance of 3’ a ...
Lecture 15 POWERPOINT here
... expressed at all times - just those for the nutrients present in the environment at that time Multicellular organisms exhibit even more elaborate gene expression - we have brain cells, liver cells, kidney cells, etc. that produce different sets of proteins from different genes. We also have the sa ...
... expressed at all times - just those for the nutrients present in the environment at that time Multicellular organisms exhibit even more elaborate gene expression - we have brain cells, liver cells, kidney cells, etc. that produce different sets of proteins from different genes. We also have the sa ...
7.014 Problem Set 3
... d) On the drawing above, indicate the position(s) of the primer(s) needed to create an entire complementary strand. Label 5’ and 3’ of the primer(s). e) Would the new double stranded molecule assume the shape similar to one in the drawing? Why or why not? ...
... d) On the drawing above, indicate the position(s) of the primer(s) needed to create an entire complementary strand. Label 5’ and 3’ of the primer(s). e) Would the new double stranded molecule assume the shape similar to one in the drawing? Why or why not? ...
CHAPTER18-20test
... Questions 46-49 refer to the techniques, tools or substances below. Answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a. restriction enzymes b. gene cloning c. DNA ligase d. gel electrophoresis e. reverse transcriptase 46. Produces many copies of a gene for basic research or for large-scale ...
... Questions 46-49 refer to the techniques, tools or substances below. Answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a. restriction enzymes b. gene cloning c. DNA ligase d. gel electrophoresis e. reverse transcriptase 46. Produces many copies of a gene for basic research or for large-scale ...
Chapter 14: Human Heredity Thomas Hunt Morgan: studied
... Risks – since most members of a breed are genetically similar, more chance of bringing together 2 recessive alleles for a genetic defect. Some inbred dogs end up being blind, have deformities. Biotechnology: application of a technological process or invention to living things. Selective breeding is ...
... Risks – since most members of a breed are genetically similar, more chance of bringing together 2 recessive alleles for a genetic defect. Some inbred dogs end up being blind, have deformities. Biotechnology: application of a technological process or invention to living things. Selective breeding is ...
cell division notes -
... disorder) - p. 145 other abnormalities related to XY and gender: Animations on sex determination | Gender testing of female athletes | sex unknown: NOVA website on gender ambiguities ...
... disorder) - p. 145 other abnormalities related to XY and gender: Animations on sex determination | Gender testing of female athletes | sex unknown: NOVA website on gender ambiguities ...
Chapter Outline - Ltcconline.net
... species to produce a protein from another species by transplanting DNA I. Transcription: From DNA to RNA 1. Transcription a. makes: 2. RNA nucleotides are linked by the transcription enzyme: J. Initiation of Transcription 1. The “start transcribing” signal is a nucleotide sequence called a promoter, ...
... species to produce a protein from another species by transplanting DNA I. Transcription: From DNA to RNA 1. Transcription a. makes: 2. RNA nucleotides are linked by the transcription enzyme: J. Initiation of Transcription 1. The “start transcribing” signal is a nucleotide sequence called a promoter, ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Chromosomes are composed mostly of DNA, which is shaped like a twisted ladder, or “double helix”. The sides of the double helix are made up of sugar molecules called deoxyribose, ...
... Chromosomes are composed mostly of DNA, which is shaped like a twisted ladder, or “double helix”. The sides of the double helix are made up of sugar molecules called deoxyribose, ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.