Journal of Biological Engineering
... them around (flipping the pancakes), and then reattaches Also acts as an on/off switch for another protein production if the proper sequence of DNA is achieved If incorrect resistance to applied antibiotic is dispersed and bacteria dies ...
... them around (flipping the pancakes), and then reattaches Also acts as an on/off switch for another protein production if the proper sequence of DNA is achieved If incorrect resistance to applied antibiotic is dispersed and bacteria dies ...
Structure and Function of DNA
... C. Mutations can affect the reproductive cells of an organism by changing the sequence of nucleotides within a gene in a sperm or egg cell. If these cells take part in fertilization, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring. (meiosis) ...
... C. Mutations can affect the reproductive cells of an organism by changing the sequence of nucleotides within a gene in a sperm or egg cell. If these cells take part in fertilization, the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring. (meiosis) ...
Lecture 27
... as the sole carbon source. However mutants unable to synthesize leucine require its presence in the growth medium. • Mutants that are resistant to an antibiotic can grow whereas wild-type cells cannot. • Some mutants have proteins that are temperature sensitive. • Use replica plating to screen for c ...
... as the sole carbon source. However mutants unable to synthesize leucine require its presence in the growth medium. • Mutants that are resistant to an antibiotic can grow whereas wild-type cells cannot. • Some mutants have proteins that are temperature sensitive. • Use replica plating to screen for c ...
Nylon/DNA: Single-Stranded DNA with a Covalently Stitched Nylon
... have expanded from genetic information carriers and messengers to include catalysis and regulation of a number of cellular processes.1 In addition, many nucleic acid-based structures have been developed with medicinal applications, catalytic properties, and prebiotic chemistry implications.1 Notable ...
... have expanded from genetic information carriers and messengers to include catalysis and regulation of a number of cellular processes.1 In addition, many nucleic acid-based structures have been developed with medicinal applications, catalytic properties, and prebiotic chemistry implications.1 Notable ...
You Light Up My Life
... Understand how the instructions for producing heritable traits are encoded in DNA. Know the parts of a nucleotide, and know how nucleotides are linked together to make DNA. Understand how DNA is replicated and what materials are needed for replication. Know how the structure and behavior of DNA dete ...
... Understand how the instructions for producing heritable traits are encoded in DNA. Know the parts of a nucleotide, and know how nucleotides are linked together to make DNA. Understand how DNA is replicated and what materials are needed for replication. Know how the structure and behavior of DNA dete ...
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... Ordering Information Kits may be ordered online on our website: www.fastiddna.com. Or, contact Genetic ID at [email protected] or call +1 641 472 9979. Please see Kit Components on Page 3 for catalog ...
... Ordering Information Kits may be ordered online on our website: www.fastiddna.com. Or, contact Genetic ID at [email protected] or call +1 641 472 9979. Please see Kit Components on Page 3 for catalog ...
Final Exam
... Explain the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis. Why is there a difference? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Explain the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis. Why is there a difference? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Biology and Ethics
... infects the wound sites in dicotyledonous plant causing the formation of the crown gall tumors. – Capable to transfer a particular DNA segment (T-DNA) of the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid into the nucleus of infected cells where it is integrated fully into the host genome and transcribed, causing the ...
... infects the wound sites in dicotyledonous plant causing the formation of the crown gall tumors. – Capable to transfer a particular DNA segment (T-DNA) of the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid into the nucleus of infected cells where it is integrated fully into the host genome and transcribed, causing the ...
DNA Translocation Through Nanopores
... dsDNA revealed a strong increase of the threading force upon decreasing the diameter of the pore. This can be attributed to a reduction of the electroosmotic flow in smaller pores, which always opposes the electrostatic force acting on the DNA molecule. Coating the nanopore walls with an electricall ...
... dsDNA revealed a strong increase of the threading force upon decreasing the diameter of the pore. This can be attributed to a reduction of the electroosmotic flow in smaller pores, which always opposes the electrostatic force acting on the DNA molecule. Coating the nanopore walls with an electricall ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... It selectively targets T-cells in a host’s immune system, and infects them. Once inside the host cell, reverse transcriptase makes a dsDNA copy of the viral RNA genome. The dsDNA incorporates itself into the host’s genome, where it can then direct synthesis of more viral particles. HIV is Human Immu ...
... It selectively targets T-cells in a host’s immune system, and infects them. Once inside the host cell, reverse transcriptase makes a dsDNA copy of the viral RNA genome. The dsDNA incorporates itself into the host’s genome, where it can then direct synthesis of more viral particles. HIV is Human Immu ...
Nucleic acid engineering
... The proposed secondary structure for E. coli 16S rRNA, based on comparative sequence analysis in which the folding pattern is assumed to be conserved across different species. The molecule can be subdivided into four domains—I, II, III, and IV—on the basis of contiguous stretches of the chain that ...
... The proposed secondary structure for E. coli 16S rRNA, based on comparative sequence analysis in which the folding pattern is assumed to be conserved across different species. The molecule can be subdivided into four domains—I, II, III, and IV—on the basis of contiguous stretches of the chain that ...
PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 2007 1. A. Essentially
... would be different. Note for the extra credit: The patterns would look like this: D. You need to use an expression microarray in order to answer this question. To set up this experiment you will need to have two populations of RNA molecules. The first comes from sporulating B. Subtillis, the second ...
... would be different. Note for the extra credit: The patterns would look like this: D. You need to use an expression microarray in order to answer this question. To set up this experiment you will need to have two populations of RNA molecules. The first comes from sporulating B. Subtillis, the second ...
DNA damage studies in cases of Trisomy 21 using Comet Assay
... Single Strand Breaks and oxidized bases (Purines and pyrimidines) in the cases of DS compared to controls. Results of oxidative DNA damage in lymphocytes dem-onstrated elevated DNA damage in DS children in both the stress-induced state and after the repair period [15]. The elevated levels of DNA dam ...
... Single Strand Breaks and oxidized bases (Purines and pyrimidines) in the cases of DS compared to controls. Results of oxidative DNA damage in lymphocytes dem-onstrated elevated DNA damage in DS children in both the stress-induced state and after the repair period [15]. The elevated levels of DNA dam ...
Biochemistry
... In the case of the LDH, this enzyme is particularly active in the protozoa that cause malaria. Drug companies have tried to find specific molecules that block the active site of LDH. At the moment, an effective drug is the compound oxamic acid (aminooxoethanoic acid), H2NCOCOOH. This molecule has a ...
... In the case of the LDH, this enzyme is particularly active in the protozoa that cause malaria. Drug companies have tried to find specific molecules that block the active site of LDH. At the moment, an effective drug is the compound oxamic acid (aminooxoethanoic acid), H2NCOCOOH. This molecule has a ...
The Universal Dogma of Genetics
... Genetic information written in codons is translated into amino acid sequences • In order for translation to proceed, the sequence of the 4 nucleotides in RNA (A,U, C,G) must somehow specify the 20 amino acids used to make up proteins • The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a trip ...
... Genetic information written in codons is translated into amino acid sequences • In order for translation to proceed, the sequence of the 4 nucleotides in RNA (A,U, C,G) must somehow specify the 20 amino acids used to make up proteins • The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a trip ...
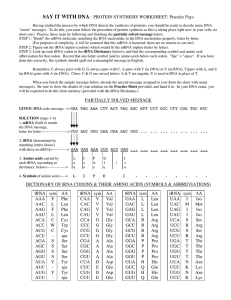
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice Pays Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your ce ...
... SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice Pays Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your ce ...
Prometheus & Myriad
... – No evidence for a “tragedy of the anticommons” regarding basic research • >9,000 scientific journal articles on BRCA genes post-patenting ...
... – No evidence for a “tragedy of the anticommons” regarding basic research • >9,000 scientific journal articles on BRCA genes post-patenting ...
Introduction to Molecular Biology
... DNA. All living organisms have common characteristics such as replication, nutrition, growing and interaction with their environment. An organism is composed of organs which perform specific functions. Organs are made of tissues which are composed of aggregation of cells that have similar functions. ...
... DNA. All living organisms have common characteristics such as replication, nutrition, growing and interaction with their environment. An organism is composed of organs which perform specific functions. Organs are made of tissues which are composed of aggregation of cells that have similar functions. ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... is curled into the desired shape, and an oxidizing agent is applied to form new disulfide bridges which hold the hair in the new shape. Problem #2 What is the major force responsible for the formation of an αhelix in protein secondary structure? Solution hydrogen bonding Problem #3 In a globular pro ...
... is curled into the desired shape, and an oxidizing agent is applied to form new disulfide bridges which hold the hair in the new shape. Problem #2 What is the major force responsible for the formation of an αhelix in protein secondary structure? Solution hydrogen bonding Problem #3 In a globular pro ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.