animations of selected figures
... Figure 2.6 Part 1 Joining DNA after a single enzyme has cut it Vector DNA Donor DNA Vector plus one or more donor fragments ...
... Figure 2.6 Part 1 Joining DNA after a single enzyme has cut it Vector DNA Donor DNA Vector plus one or more donor fragments ...
Transcription and Translation
... • tRNA – carries the amino acids to the ribosomes to be made into proteins • Most biology classes focus on the production of mRNA in the nucleus for transcription. ...
... • tRNA – carries the amino acids to the ribosomes to be made into proteins • Most biology classes focus on the production of mRNA in the nucleus for transcription. ...
Microbial Genetics - University of Montana
... Mechanism of Conjugation • tra gene regulation – Expressed immediately after transfer to recipient is completed • Subsequently repressed, with sporadic periods of expression – prevents exploitation of pilus as bacteriophage ...
... Mechanism of Conjugation • tra gene regulation – Expressed immediately after transfer to recipient is completed • Subsequently repressed, with sporadic periods of expression – prevents exploitation of pilus as bacteriophage ...
PDF - BioInfo Publication
... DNA molecules since they do not contain any kind of ferromagnetic material and direct exposure of DNA to radiation with relatively higher frequency (higher than that used in cellular phones) would serve as a better indicator of any damage done to the biomolecules due to non-thermal and thermal effec ...
... DNA molecules since they do not contain any kind of ferromagnetic material and direct exposure of DNA to radiation with relatively higher frequency (higher than that used in cellular phones) would serve as a better indicator of any damage done to the biomolecules due to non-thermal and thermal effec ...
overview - El Paso High School
... DNA replication begins with the binding of a large protein complex—the pre-replication complex—to a specific site on the DNA molecule. The complex contains DNA polymerase, which catalyzes addition of nucleotides. The complex binds to a region on the chromosome called the origin of replication (ori). ...
... DNA replication begins with the binding of a large protein complex—the pre-replication complex—to a specific site on the DNA molecule. The complex contains DNA polymerase, which catalyzes addition of nucleotides. The complex binds to a region on the chromosome called the origin of replication (ori). ...
Molecular Systematics
... • What happens when an antibody specific for a protein from one organism is mixed with the same protein from a different organism? ...
... • What happens when an antibody specific for a protein from one organism is mixed with the same protein from a different organism? ...
Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 2/6
... I can describe the concepts and principles within Mendelian Genetics, and solve for simple genetic problems, sex linked problems, genetic diseases in both Punnett’s square form and pedigree form. Use a Punnetts Square to solve the problems on the board. “Solve in Reverse” activity. If given one pare ...
... I can describe the concepts and principles within Mendelian Genetics, and solve for simple genetic problems, sex linked problems, genetic diseases in both Punnett’s square form and pedigree form. Use a Punnetts Square to solve the problems on the board. “Solve in Reverse” activity. If given one pare ...
Ku Binds Telomeric DNA in Vitro - Titia de Lange Lab
... vitro (58, 59). Thus, G-quartet structures may exist at eukaryotic telomeres, possibly in a transient manner in some cell types. Our findings suggest that the long overhangs found at mammalian telomeres, even if folded into G-quartet structures, will not prevent Ku from binding to the DNA. Therefore ...
... vitro (58, 59). Thus, G-quartet structures may exist at eukaryotic telomeres, possibly in a transient manner in some cell types. Our findings suggest that the long overhangs found at mammalian telomeres, even if folded into G-quartet structures, will not prevent Ku from binding to the DNA. Therefore ...
Chapter 3 Proteins: - California State University San Marcos
... ► DNA Primase uses rNTPs to synthesize short primers on lagging Strand ► Primers ~10 nucleotides long and spaced ~100-200 bp ► DNA repair system removes RNA primer; replaces it w/DNA ► DNA ligase joins fragments ...
... ► DNA Primase uses rNTPs to synthesize short primers on lagging Strand ► Primers ~10 nucleotides long and spaced ~100-200 bp ► DNA repair system removes RNA primer; replaces it w/DNA ► DNA ligase joins fragments ...
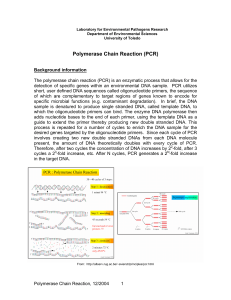
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Department of Environmental
... the primers and the template DNA. The range of MgCl2 usually tested is from 0.5 - 4 mM in 0.5 mM increments, while the default starting point is often is 1.5 mM. Low MgCl2 concentrations can help to eliminate non-specific priming and background PCR products and are desirable when fidelity of DNA syn ...
... the primers and the template DNA. The range of MgCl2 usually tested is from 0.5 - 4 mM in 0.5 mM increments, while the default starting point is often is 1.5 mM. Low MgCl2 concentrations can help to eliminate non-specific priming and background PCR products and are desirable when fidelity of DNA syn ...
Vocabulary handout
... are stretched out very thin to allow surfaces for the various chemical reactions that involve chromosomes to take place. When the nucleus is stained and examined, it appears uniformly colored and the chromosomes collectively are termed chromatin. It is critical to remember that even though individua ...
... are stretched out very thin to allow surfaces for the various chemical reactions that involve chromosomes to take place. When the nucleus is stained and examined, it appears uniformly colored and the chromosomes collectively are termed chromatin. It is critical to remember that even though individua ...
Replication - UniMAP Portal
... the hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide bases, which exposes the bases in a replication fork. Other protein molecules stabilize the single strands so that they do not rejoin while replication proceeds After helicase untwists and separates the strands, a molecule of an enzyme called DNA p ...
... the hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide bases, which exposes the bases in a replication fork. Other protein molecules stabilize the single strands so that they do not rejoin while replication proceeds After helicase untwists and separates the strands, a molecule of an enzyme called DNA p ...
Some - Laker Science
... Understand the evolution viruses. Describe the three processes that lead to the emergence of new diseases. Biotechnology Objectives (3, 5, 6, 7) Know vocabulary associated with biotechnology. Know the importance and function of restriction enzymes in biotechnology and their origin. Understand and de ...
... Understand the evolution viruses. Describe the three processes that lead to the emergence of new diseases. Biotechnology Objectives (3, 5, 6, 7) Know vocabulary associated with biotechnology. Know the importance and function of restriction enzymes in biotechnology and their origin. Understand and de ...
PDS 803482 Ron Blood and Cell DNA Mini
... Ron’s Blood and Cell DNA Mini Kit is designed for quick preparation of pure DNA. The kit contains spin columns, buffers and reagents necessary for cell lysis, DNA binding, washing and elution of DNA into small volume. Each kit contains a manual with detailed protocols of DNA extraction and purificat ...
... Ron’s Blood and Cell DNA Mini Kit is designed for quick preparation of pure DNA. The kit contains spin columns, buffers and reagents necessary for cell lysis, DNA binding, washing and elution of DNA into small volume. Each kit contains a manual with detailed protocols of DNA extraction and purificat ...
chapter 20 notes
... Gel electrophoresis separates macromolecules on the basis of their rate of movement through a gel in an electric field. How far a DNA molecule travels while the current is on is inversely proportional to its length. A mixture of DNA molecules, usually fragments produced by restriction enzyme digesti ...
... Gel electrophoresis separates macromolecules on the basis of their rate of movement through a gel in an electric field. How far a DNA molecule travels while the current is on is inversely proportional to its length. A mixture of DNA molecules, usually fragments produced by restriction enzyme digesti ...
DNA Sequencing
... Gel electrophoresis separates macromolecules on the basis of their rate of movement through a gel in an electric field. How far a DNA molecule travels while the current is on is inversely proportional to its length. A mixture of DNA molecules, usually fragments produced by restriction enzyme digesti ...
... Gel electrophoresis separates macromolecules on the basis of their rate of movement through a gel in an electric field. How far a DNA molecule travels while the current is on is inversely proportional to its length. A mixture of DNA molecules, usually fragments produced by restriction enzyme digesti ...
Heredity - lrobards
... single amino acid in the hemoglobin protein of red blood cells, leaving hemoglobin less able to carry oxygen and also causing the hemoglobin to deform to a sickle shape when the oxygen content of the blood is low. Phenylketonuria: an autosomal recessive disease caused by a single gene defect that ...
... single amino acid in the hemoglobin protein of red blood cells, leaving hemoglobin less able to carry oxygen and also causing the hemoglobin to deform to a sickle shape when the oxygen content of the blood is low. Phenylketonuria: an autosomal recessive disease caused by a single gene defect that ...
5.2.3 Genomes and Gene Technology MS
... treat, non-Hodgkins lymphoma/some types of cancer/leukaemia; treat/cure for, Alzheimer’s disease; treat/cure for, Parkinson’s disease; treat paraplegics/repair injury to, nerves/spinal cord; treat, genetic disorders affecting nerves/Huntington’s/Tay Sachs/Lou ...
... treat, non-Hodgkins lymphoma/some types of cancer/leukaemia; treat/cure for, Alzheimer’s disease; treat/cure for, Parkinson’s disease; treat paraplegics/repair injury to, nerves/spinal cord; treat, genetic disorders affecting nerves/Huntington’s/Tay Sachs/Lou ...
A Review on Y-Chromosomal based DNA Profiling and Bayesian
... particular gender then the tandem repeats of 2-5 base pair long are checked on the Y-Chromosome in case of male and on the autosomal chromosomes in case of females. If the DNA found is contaminated then we can use mitochondrial part of the cell for better results. The process for Y-STR analysis has ...
... particular gender then the tandem repeats of 2-5 base pair long are checked on the Y-Chromosome in case of male and on the autosomal chromosomes in case of females. If the DNA found is contaminated then we can use mitochondrial part of the cell for better results. The process for Y-STR analysis has ...
Transcription & Translation
... 1. Enzymes unzip DNA (just like in replication) 2. RNA nucleotides bind to the exposed DNA nucleotides a. AGC TAA CCG (DNA) UCG AUU GGC (RNA) 3. RNA strand breaks free, leaves nucleus, heads to ribosome ...
... 1. Enzymes unzip DNA (just like in replication) 2. RNA nucleotides bind to the exposed DNA nucleotides a. AGC TAA CCG (DNA) UCG AUU GGC (RNA) 3. RNA strand breaks free, leaves nucleus, heads to ribosome ...
Build-a-Bug - Wando High School
... creativity to describe other characteristics of your organism (habitat, diet, personality, etc.). Also, indicate if there are any other bugs in the room that may be of the same species (i.e. have similar traits to your bug). Write this on notebook paper. Transfer RNA is a single strand of RNA that l ...
... creativity to describe other characteristics of your organism (habitat, diet, personality, etc.). Also, indicate if there are any other bugs in the room that may be of the same species (i.e. have similar traits to your bug). Write this on notebook paper. Transfer RNA is a single strand of RNA that l ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.