Ch 20 Reading Guide - Dublin City Schools
... 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hydrolytic enzyme in the plasmid. 4. Describe the role of an expression vector. 5. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. ...
... 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hydrolytic enzyme in the plasmid. 4. Describe the role of an expression vector. 5. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. ...
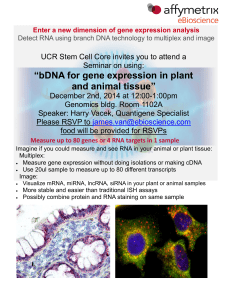
“bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue”
... Enter a new dimension of gene expression analysis Detect RNA using branch DNA technology to multiplex and image ...
... Enter a new dimension of gene expression analysis Detect RNA using branch DNA technology to multiplex and image ...
Levels of Organization
... Group of populations that live together in a defined area (Ex: businesses, people, pets, etc. in Alvin) ...
... Group of populations that live together in a defined area (Ex: businesses, people, pets, etc. in Alvin) ...
BacteriaDiversityMDS_07_v2
... • pH: 0 to 11 (3 - 5 units for any one species) • [NaCl]: 0 to 6 M (~saturation) depending on species ...
... • pH: 0 to 11 (3 - 5 units for any one species) • [NaCl]: 0 to 6 M (~saturation) depending on species ...
PPT
... The first step to model DTG-PCR Ji Youn Lee Cell and microbial engineering laboratory Seoul National University ...
... The first step to model DTG-PCR Ji Youn Lee Cell and microbial engineering laboratory Seoul National University ...
If there are “CUES” listed within the question, please USE them and
... b. What size (in kilobases) fragment(s) would result when MstII is used to cut DNA with the sickle allele? c. Sketch and label the patterns of cuts with normal and sickle alleles on a gel. d. Could an individual have both patterns? Explain. e. How can this information be used to make a DNA test for ...
... b. What size (in kilobases) fragment(s) would result when MstII is used to cut DNA with the sickle allele? c. Sketch and label the patterns of cuts with normal and sickle alleles on a gel. d. Could an individual have both patterns? Explain. e. How can this information be used to make a DNA test for ...
EE150a – Genomic Signal and Information Processing
... lot of control over the landscape of the probes on the array • Second topic for presentations considers a combinatorial design of such arrays • [How to deal with cross-hybridization on arrays used for expression level measurements is the topic of the third lecture.] ...
... lot of control over the landscape of the probes on the array • Second topic for presentations considers a combinatorial design of such arrays • [How to deal with cross-hybridization on arrays used for expression level measurements is the topic of the third lecture.] ...
HigH-THrougHpuT dna sequencing
... always paired with its complementary base on the opposing strand. A on one strand is paired with T on the other strand, T with A, G with C, and C with G. Variations of the nucleotide sequence are a normal feature of DNA. However, if these changes affect the way a gene functions, they can result in d ...
... always paired with its complementary base on the opposing strand. A on one strand is paired with T on the other strand, T with A, G with C, and C with G. Variations of the nucleotide sequence are a normal feature of DNA. However, if these changes affect the way a gene functions, they can result in d ...
amino acids
... 4 only ~1.5% of the human genome encodes proteins and ~80% is not related to genes or their regulation. ...
... 4 only ~1.5% of the human genome encodes proteins and ~80% is not related to genes or their regulation. ...
Name
... A gene of interest is identified. The plasmid and gene of interest are both cut with the same restriction enzyme. The gene is then inserted into the bacteria and DNA ligase binds the two fragments together ...
... A gene of interest is identified. The plasmid and gene of interest are both cut with the same restriction enzyme. The gene is then inserted into the bacteria and DNA ligase binds the two fragments together ...
Bio1100Ch20
... announced sequencing over 90% of the human genome. • By mid-2001, the genomes of about 50 species had been completely (or almost completely) sequenced. •Include yeast, a nematode, a plant and many bacteria ...
... announced sequencing over 90% of the human genome. • By mid-2001, the genomes of about 50 species had been completely (or almost completely) sequenced. •Include yeast, a nematode, a plant and many bacteria ...
24 October - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
PDF - Microbiome Journal
... argue that the proper terms should be “16S rRNA genes” or “16S rRNA gene sequencing/analysis.” Additionally, the word microflora has been used for a long time in the scientific and medical literature. However, its definition does not justify its use to describe microbial communities associated with ...
... argue that the proper terms should be “16S rRNA genes” or “16S rRNA gene sequencing/analysis.” Additionally, the word microflora has been used for a long time in the scientific and medical literature. However, its definition does not justify its use to describe microbial communities associated with ...
Chapter 20
... How can we determine the function of different genes? RNAi; silence a gene and see what it did Insert synthetic double stranded RNA’s that match a gene that will inactivate translation This was used to identify the function of C. elegans genes ...
... How can we determine the function of different genes? RNAi; silence a gene and see what it did Insert synthetic double stranded RNA’s that match a gene that will inactivate translation This was used to identify the function of C. elegans genes ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Foreign genes have been introduced into plant cells. Foreign genes transferred to cotton, corn, and potato strains have made these plants resistant to pests. Transgenic Animals Techniques have been developed to insert genes into the eggs of animals. Gene pharming is the use of transgenic farm animal ...
... Foreign genes have been introduced into plant cells. Foreign genes transferred to cotton, corn, and potato strains have made these plants resistant to pests. Transgenic Animals Techniques have been developed to insert genes into the eggs of animals. Gene pharming is the use of transgenic farm animal ...
2.2 Sequencing learning grid File
... What is another term for genetic engineering? What is genetic engineering? What does transgenic mean? What is a vector? Give three methods used to get genes into recipient ...
... What is another term for genetic engineering? What is genetic engineering? What does transgenic mean? What is a vector? Give three methods used to get genes into recipient ...
Genetic Technology
... How is genetic technology used in agriculture, medicine, and forensics? What concerns are there regarding genetic engineering? ...
... How is genetic technology used in agriculture, medicine, and forensics? What concerns are there regarding genetic engineering? ...