Slide 1
... Protein coding gene - A DNA sequence coding for a single polypeptide Gene expression – mechanism by which hereditary factors are coded for and expressed Genes control inherited variation via: DNA, RNA and protein *Transcription – transfer of genetic information from DNA via synthesis of RNA *Transla ...
... Protein coding gene - A DNA sequence coding for a single polypeptide Gene expression – mechanism by which hereditary factors are coded for and expressed Genes control inherited variation via: DNA, RNA and protein *Transcription – transfer of genetic information from DNA via synthesis of RNA *Transla ...
Removed DNA - Cloudfront.net
... that potentially lasts for enough generations to serve as a unit of natural selection”.(39) As such a gene is an inherited unit which is somewhere between a nucleotide and a chromosome. Systemic Concept: The gene is a combination of (one or more) nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) sequences, defined by the s ...
... that potentially lasts for enough generations to serve as a unit of natural selection”.(39) As such a gene is an inherited unit which is somewhere between a nucleotide and a chromosome. Systemic Concept: The gene is a combination of (one or more) nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) sequences, defined by the s ...
Mutations Website Assignment - Mercer Island School District
... 8. Being a carrier of the sickle cell anemia allele has a positive effect (which explains why this genetic disorder is most common among people who come from tropical areas have certain strains of mosquitoes.) Explain what this positive effect is. ...
... 8. Being a carrier of the sickle cell anemia allele has a positive effect (which explains why this genetic disorder is most common among people who come from tropical areas have certain strains of mosquitoes.) Explain what this positive effect is. ...
Document
... believed to involve alkylation of DNA. A series of adenosines and 2'-deoxyadenosine substituted at N6 by related ara1ky1s of differing carCinogenic potential has been prepared. We report here the crystal structure determinations of four of these compounds: N6_(anthracenyl-9-methyl)adenosine; N6_(10- ...
... believed to involve alkylation of DNA. A series of adenosines and 2'-deoxyadenosine substituted at N6 by related ara1ky1s of differing carCinogenic potential has been prepared. We report here the crystal structure determinations of four of these compounds: N6_(anthracenyl-9-methyl)adenosine; N6_(10- ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Translation Review
... 3. What type of bond holds the sugar and phosphate together? Is this bond strong or weak? What is the significance of this? They are joined by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages. These are strong bonds that are not meant to break. This helps to keep a strand of DNA or RNA intact. 4. What ...
... 3. What type of bond holds the sugar and phosphate together? Is this bond strong or weak? What is the significance of this? They are joined by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages. These are strong bonds that are not meant to break. This helps to keep a strand of DNA or RNA intact. 4. What ...
The microbial fuel cell could be a core
... spurred by demand for the grain-based fuel ethanol, have led to expensive tortillas.” ...
... spurred by demand for the grain-based fuel ethanol, have led to expensive tortillas.” ...
10.391
... spurred by demand for the grain-based fuel ethanol, have led to expensive tortillas.” ...
... spurred by demand for the grain-based fuel ethanol, have led to expensive tortillas.” ...
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to
... -Some of these transcription factors are activators (increase expression), while others are repressors (decrease expression). -The combination of transcription factors binding to the regulatory regions at any one time determines how much of the gene product will be produced. ...
... -Some of these transcription factors are activators (increase expression), while others are repressors (decrease expression). -The combination of transcription factors binding to the regulatory regions at any one time determines how much of the gene product will be produced. ...
1. a) 25% b)86% 2. For my opinion, I think the way to make
... It is used to determine the absorption light from a sample and it can be used as a detector of HPLC. The concentration of analyst in solution can be determined by measuring the absorbance of single wavelength and applying the Beer-Lambert Law. First, place the sample in the Uv-Vis beam and record th ...
... It is used to determine the absorption light from a sample and it can be used as a detector of HPLC. The concentration of analyst in solution can be determined by measuring the absorbance of single wavelength and applying the Beer-Lambert Law. First, place the sample in the Uv-Vis beam and record th ...
structure and function of genome
... The number of human genes seems to be less than a factor of two greater than that of many much simpler organisms, such as the roundworm and the fruit fly. human cells make extensive use of alternative splicing to produce several different proteins from a single gene, and the human proteome is though ...
... The number of human genes seems to be less than a factor of two greater than that of many much simpler organisms, such as the roundworm and the fruit fly. human cells make extensive use of alternative splicing to produce several different proteins from a single gene, and the human proteome is though ...
Bioinformatics
... • Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the ...
... • Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein • Genes provide the instructions for making specific proteins. • The bridge between DNA and protein synthesis is RNA. • RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes the ...
Terminator
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
Parallel Data Mining of microarray biological data
... There are mainly two technologies that have been developed in order to fix nucleotides chains on microarrays: one has been developed by Affymetrix (Santa Clara, California) and the other has been developed at the Stanford University. Affymetrix chips are made using photolitographic techniques to syn ...
... There are mainly two technologies that have been developed in order to fix nucleotides chains on microarrays: one has been developed by Affymetrix (Santa Clara, California) and the other has been developed at the Stanford University. Affymetrix chips are made using photolitographic techniques to syn ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Power Point
... 1. DNA molecule unzip where the desired gene is located 2. Free floating RNA nucleotides pair with the DNA strand forming m-RNA (Transcription) 3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome 4. A specific t-RNA delivers a specific amino acid to the ribosome (Translation) 5. The m-RNA codon m ...
... 1. DNA molecule unzip where the desired gene is located 2. Free floating RNA nucleotides pair with the DNA strand forming m-RNA (Transcription) 3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome 4. A specific t-RNA delivers a specific amino acid to the ribosome (Translation) 5. The m-RNA codon m ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS What is a gene?
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
... • The segment of DNA that contains the gene for a specific protein or RNA that the cell wants to produce will unwind and the complementary RNA strand will be made by incorporation the RNA nucleotides ...
Design-Your-Own-Baby : The Techniques, Feasibility, and Ethics of Human Genetic Enhancement
... initially due to limitations on embryonic stem cell and human cloning research •However, when treatment for genetic disorders will be approved, it will open doors for other types of “therapy” •The first genetic enhancements that come before the FDA will be cloaked in ...
... initially due to limitations on embryonic stem cell and human cloning research •However, when treatment for genetic disorders will be approved, it will open doors for other types of “therapy” •The first genetic enhancements that come before the FDA will be cloaked in ...
Chapter 1
... foods and chemicals, is centuries old. • Genetic engineering is a new technique for biotechnology. Through genetic engineering, bacteria and fungi can produce a variety of proteins including vaccines and enzymes. • Missing or defective genes in human cells can be replaced in gene therapy. • Genetica ...
... foods and chemicals, is centuries old. • Genetic engineering is a new technique for biotechnology. Through genetic engineering, bacteria and fungi can produce a variety of proteins including vaccines and enzymes. • Missing or defective genes in human cells can be replaced in gene therapy. • Genetica ...
You Light Up My Life
... Smallest unit of an element that still retains the element’s properties. Electrons, protons, and neutrons are its building blocks. This hydrogen atom’s electron zips around a proton in a spherical volume of space Fig. 1-1a, p.2 ...
... Smallest unit of an element that still retains the element’s properties. Electrons, protons, and neutrons are its building blocks. This hydrogen atom’s electron zips around a proton in a spherical volume of space Fig. 1-1a, p.2 ...
level two biology: gene expression
... translation by stating the result of each process and why each process is necessary for protein synthesis. I can differentiate between transcription and translation by explaining which occurs first and why and where each process occurs in a cell. I can show that I know the difference between mRNA, t ...
... translation by stating the result of each process and why each process is necessary for protein synthesis. I can differentiate between transcription and translation by explaining which occurs first and why and where each process occurs in a cell. I can show that I know the difference between mRNA, t ...
Click here to - Kendriya Vidyalaya Sabarmati
... a)Explain the experiment conducted by Griffith on Streptococcus pneumonia. What did he conclude? b) Name three scientists who followed up Griffith’s experiment. c)What did they conclude and how? ...
... a)Explain the experiment conducted by Griffith on Streptococcus pneumonia. What did he conclude? b) Name three scientists who followed up Griffith’s experiment. c)What did they conclude and how? ...
S05 Biotechnology Gene Therapy 1
... A key advantage of physical methods: direct gene delivery • Diffusion of plasmid is slow (size dependent) • Internalization is higher than successful transfection • Cytoplasmic degradation is possible • Electroporation: entry to nucleus is achieved • Laser irradiation: nuclear envelope is perforated ...
... A key advantage of physical methods: direct gene delivery • Diffusion of plasmid is slow (size dependent) • Internalization is higher than successful transfection • Cytoplasmic degradation is possible • Electroporation: entry to nucleus is achieved • Laser irradiation: nuclear envelope is perforated ...
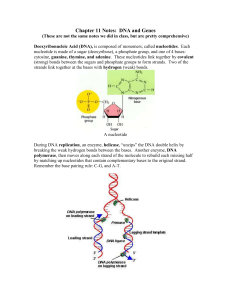
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the pro ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is also single stranded, like mRNA, but it is held together in a “hairpin” or “T” shape by hydrogen bonds. It carries a specific amino acid on one end based on a series of three bases on the other end called an anti-codon. There are only 20 amino acids that make up all of the pro ...