presentation source
... • Use of probes to identify specific nucleotide sequences • Probes can be radioactively labeled: when the nucleic acid sequence of the probe links with the DNA sequence of interest, a radioactive recombinant is formed that can be detected ...
... • Use of probes to identify specific nucleotide sequences • Probes can be radioactively labeled: when the nucleic acid sequence of the probe links with the DNA sequence of interest, a radioactive recombinant is formed that can be detected ...
12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
DNA Cloning - MrMsciences
... How it Works • Combine gene of interest and bacterial plasmid • Recombinant DNA • DNA from two or more different sources that have been joined together to form a single molecule • Amplification and identification ...
... How it Works • Combine gene of interest and bacterial plasmid • Recombinant DNA • DNA from two or more different sources that have been joined together to form a single molecule • Amplification and identification ...
ANSWER KEY Nucleic Acid and DNA Replication Outline Notes
... 3 SUGARS and PHOSPHATES bond between free nucleotides. Enzyme DNA polymerase binds the two strands together. ...
... 3 SUGARS and PHOSPHATES bond between free nucleotides. Enzyme DNA polymerase binds the two strands together. ...
Chapter 31: Epigenetic Effects Are Inherited
... • Xic includes the Xist gene, which codes for an RNA that is found only on inactive X chromosomes • The mechanism that is responsible for preventing Xist RNA from accumulating on the active chromosome is unknown. • Specific condensins are responsible for condensing inactive X chromosomes in C. elega ...
... • Xic includes the Xist gene, which codes for an RNA that is found only on inactive X chromosomes • The mechanism that is responsible for preventing Xist RNA from accumulating on the active chromosome is unknown. • Specific condensins are responsible for condensing inactive X chromosomes in C. elega ...
The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... did we find out that DNA was the molecule responsible for inheritance? ...
... did we find out that DNA was the molecule responsible for inheritance? ...
DNA polymerase I
... new strands in 5’ to 3’ direction. Primase makes RNA primer. Lagging strand DNA consists of Okazaki fragments. In E. coli, pol I fills in gaps in the lagging strand and removes RNA primer. Fragments are joined by DNA ...
... new strands in 5’ to 3’ direction. Primase makes RNA primer. Lagging strand DNA consists of Okazaki fragments. In E. coli, pol I fills in gaps in the lagging strand and removes RNA primer. Fragments are joined by DNA ...
Study_Guide
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
Introduction to Epigenetics - BITS Embryo
... • When a cell undergoes mitosis or meiosis, the epigenetic information is stably transmitted to the subsequent generation • Epigenetic controls add an ‘extra layer’ of transcriptional control ...
... • When a cell undergoes mitosis or meiosis, the epigenetic information is stably transmitted to the subsequent generation • Epigenetic controls add an ‘extra layer’ of transcriptional control ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
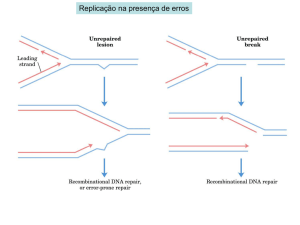
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Name:
... What are the full names of the four nitrogenous bases? 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? Draw a picture if it would help. (This is discussed in the paragraph prio ...
... What are the full names of the four nitrogenous bases? 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? Draw a picture if it would help. (This is discussed in the paragraph prio ...
UNIT 7 – MOLECULAR GENETICS Mon, 1/23 – Mon, 2/13 Unit
... Explain the importance of RNAi. Compare three natural process of gene transfer in bacteria. Describe the importance of plasmids. Explain the concept of an operon and the function of the operator, repressor and co-repressor. Explain the importance of regulatory genes. Compare and contrast inducible a ...
... Explain the importance of RNAi. Compare three natural process of gene transfer in bacteria. Describe the importance of plasmids. Explain the concept of an operon and the function of the operator, repressor and co-repressor. Explain the importance of regulatory genes. Compare and contrast inducible a ...
2015 Chaffey College Poster
... Fishes can be compared to other fish with the same DNA. The 16S ribosomal gene and cytochrome-‐oxidase subunit (COI) are two parts to fishes’ DNA that are specific for all species of fish. To begin, ...
... Fishes can be compared to other fish with the same DNA. The 16S ribosomal gene and cytochrome-‐oxidase subunit (COI) are two parts to fishes’ DNA that are specific for all species of fish. To begin, ...
replication (nucleus) transcription (nucleus) translation (cytoplasm
... Has the bases A, C, G and T ...
... Has the bases A, C, G and T ...
Lect2 Genetics
... DNA repair mechanisms Recombination can occur –cutting out and insertion of pieces of DNA These can all leads to changes in genetic material and thus changes in phenotype! ...
... DNA repair mechanisms Recombination can occur –cutting out and insertion of pieces of DNA These can all leads to changes in genetic material and thus changes in phenotype! ...
MolecularBiology1APLab6
... • Contain random DNA fragments that are collected or exchanged w/ other bacteria • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance ...
... • Contain random DNA fragments that are collected or exchanged w/ other bacteria • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance ...
PCR Lab Notes
... proteins are called exons. Both introns and exons are initially transcribed, then introns are spliced out of the RNA to create the messenger RNA (mRNA). ...
... proteins are called exons. Both introns and exons are initially transcribed, then introns are spliced out of the RNA to create the messenger RNA (mRNA). ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).