
Directed Reading B
... Directed Reading B Section: How DNA Works Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. ...
... Directed Reading B Section: How DNA Works Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. ...
Molecular-aided identification of woody plants in a tropical forest of
... In addition to blastclust, we also tested FastgroupII, a software used for clustering 16S ...
... In addition to blastclust, we also tested FastgroupII, a software used for clustering 16S ...
Sir Alec Jeffreys minisatellites
... Examples - DNA fingerprints. Tandemly repeated but often in dispersed clusters. Also called VNTR’s (variable number tandem repeats). Human λ33.1 minisatellite (62 bp) AAGGGTGGGCAGGAAGTGGAGTGTGTGCCTG CTTCCCTTCCCTGTCTTGTCCTGGAAACTCA Human λ33.5 minisatellite (17 bp) YGGGCAGGAGGGGGAGG ...
... Examples - DNA fingerprints. Tandemly repeated but often in dispersed clusters. Also called VNTR’s (variable number tandem repeats). Human λ33.1 minisatellite (62 bp) AAGGGTGGGCAGGAAGTGGAGTGTGTGCCTG CTTCCCTTCCCTGTCTTGTCCTGGAAACTCA Human λ33.5 minisatellite (17 bp) YGGGCAGGAGGGGGAGG ...
Molecular Genetics
... that allow the transport and break down of lactose. But these proteins are not needed unless lactose is present. – Operator – Like a light switch that turns transcription on and off. In lac operon, O region where repressor proteins are present. These are present, transcription cannot occur. These pr ...
... that allow the transport and break down of lactose. But these proteins are not needed unless lactose is present. – Operator – Like a light switch that turns transcription on and off. In lac operon, O region where repressor proteins are present. These are present, transcription cannot occur. These pr ...
CH 23 Part 2 Modern Genetics
... The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) copies a sequence of DNA. (a) A strand of DNA is mixed in solution with DNA precursors (nucleotides), a primer that targets a specific piece of DNA, and an enzyme (polymerase) that helps to assemble DNA. The mix is heated to 200°F to separate DNA strands. ...
... The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) copies a sequence of DNA. (a) A strand of DNA is mixed in solution with DNA precursors (nucleotides), a primer that targets a specific piece of DNA, and an enzyme (polymerase) that helps to assemble DNA. The mix is heated to 200°F to separate DNA strands. ...
Molecular Biology -
... (e.g. normal hemoglobin vs. sickle cell hemoglobin) person's characteristics or traits (e.g. normal health vs. sickle cell anemia) 2. The double helix structure of DNA, transcription and translation all depend on base-pairing rules that match each type of nucleotide in DNA or RNA with another nucl ...
... (e.g. normal hemoglobin vs. sickle cell hemoglobin) person's characteristics or traits (e.g. normal health vs. sickle cell anemia) 2. The double helix structure of DNA, transcription and translation all depend on base-pairing rules that match each type of nucleotide in DNA or RNA with another nucl ...
Manipulation DNA
... Many researchers are also applying the techniques of biotechnology to find new treatments for genetic diseases. In this activity, you will use paper models to stimulate the cutting of DNA; you will also model gel electrophoresis to analyze the DNA fragments produced. You will learn how these techniq ...
... Many researchers are also applying the techniques of biotechnology to find new treatments for genetic diseases. In this activity, you will use paper models to stimulate the cutting of DNA; you will also model gel electrophoresis to analyze the DNA fragments produced. You will learn how these techniq ...
Biology 12 Daily Notes - Mrs. Kennedy`s Biology 12 Site!
... Scientists have discovered a way to incorporate a gene that caused cancer into a mouse’s genes. This allowed the scientists to have a living model to use to study chemicals which cause cancer and apply it to humans ...
... Scientists have discovered a way to incorporate a gene that caused cancer into a mouse’s genes. This allowed the scientists to have a living model to use to study chemicals which cause cancer and apply it to humans ...
Title, arial 30pt Bold, all caps
... • Consists of multiple primer sets within a single PCR mixture to produce amplicons (amplified DNA fragments which correspond to the bands on the gel) of varying sizes that are specific to different DNA sequences. In this Biplex PCR reaction, a primer set for the internal control corn gene Inverta ...
... • Consists of multiple primer sets within a single PCR mixture to produce amplicons (amplified DNA fragments which correspond to the bands on the gel) of varying sizes that are specific to different DNA sequences. In this Biplex PCR reaction, a primer set for the internal control corn gene Inverta ...
Study Guide
... PolC so that the fusion protein PolC-GFP would be made instead of the normal PolC. Can you guess how they did this? Paragraphs 2 and 3 • What is the central question of this study? • An interesting difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes is mentioned here: prokaryotic chromosomes g ...
... PolC so that the fusion protein PolC-GFP would be made instead of the normal PolC. Can you guess how they did this? Paragraphs 2 and 3 • What is the central question of this study? • An interesting difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes is mentioned here: prokaryotic chromosomes g ...
PPT File
... Add methyl group5’-cytosine pyrimidine ring A result of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) activity Typically occurring in a CpG dinucleotide ...
... Add methyl group5’-cytosine pyrimidine ring A result of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) activity Typically occurring in a CpG dinucleotide ...
Genetic Mutations & Genetic Engineering
... Transformation: A cell takes in DNA from outside the cell Plasmid: Foreign DNA formed into a small circular DNA molecule. Used to incorporate foreign DNA into bacteria that will replicate allow it to be replicated Genetic Marker: Gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry plasmid ...
... Transformation: A cell takes in DNA from outside the cell Plasmid: Foreign DNA formed into a small circular DNA molecule. Used to incorporate foreign DNA into bacteria that will replicate allow it to be replicated Genetic Marker: Gene that makes it possible to distinguish bacteria that carry plasmid ...
DNA PROFILING
... pattern of the DNA profile is then compared with those of the victim and the suspect. If the profile matches the suspect it provides strong evidence that the suspect was present at the crime scene (it does not prove they committed the crime). If the profile doesn’t match the suspect then that su ...
... pattern of the DNA profile is then compared with those of the victim and the suspect. If the profile matches the suspect it provides strong evidence that the suspect was present at the crime scene (it does not prove they committed the crime). If the profile doesn’t match the suspect then that su ...
supplementary materials and methods
... Analysis of the LMNB1 duplication by quantitative real-time PCR. Amplification was performed in a total of 20 µl containing 10 µl of Taqman Universal PCR Master mix (P/N 4324018, Applied Biosystems), 1 µl of RNase P kit (20X, VIC dye, P/N 4316844), 2 µl of forward (5’-gccaaaaaacagttagcagatgaa) and r ...
... Analysis of the LMNB1 duplication by quantitative real-time PCR. Amplification was performed in a total of 20 µl containing 10 µl of Taqman Universal PCR Master mix (P/N 4324018, Applied Biosystems), 1 µl of RNase P kit (20X, VIC dye, P/N 4316844), 2 µl of forward (5’-gccaaaaaacagttagcagatgaa) and r ...
Biotechnology - The Bio Edge
... B. Somatic cells are much tougher than gametes and can certainly reduce their exposure to environmental agents that might cause mutations to occur. C. Somatic cells are in the various organs of organisms and are shielded from the harmful agents that might cause mutations. D. Somatic cells are not pa ...
... B. Somatic cells are much tougher than gametes and can certainly reduce their exposure to environmental agents that might cause mutations to occur. C. Somatic cells are in the various organs of organisms and are shielded from the harmful agents that might cause mutations. D. Somatic cells are not pa ...
BIOD19H3 Epigenetics in Health and Disease Professor: Winter 2015
... Professor: Patrick McGowan; TA: Wilfred de Vega ...
... Professor: Patrick McGowan; TA: Wilfred de Vega ...
NA stabilization
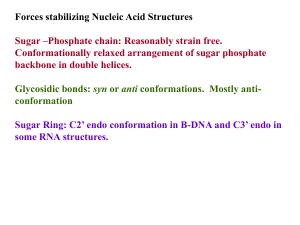
... Standard Watson Crick base Pairind is most preferred. Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. ...
... Standard Watson Crick base Pairind is most preferred. Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. ...
DOC-fFORTE [Frauen in Forschung und Technologie]
... from a donor to a recipient cell via direct contact. This way of gene transfer is commonly used by bacteria for exchanging genetic information, such as for example antibiotic resistance genes. It represents an important driving force for their evolution, but this also means that conjugative DNA tran ...
... from a donor to a recipient cell via direct contact. This way of gene transfer is commonly used by bacteria for exchanging genetic information, such as for example antibiotic resistance genes. It represents an important driving force for their evolution, but this also means that conjugative DNA tran ...
DNA Replication and DNA Repair Study Guide Focus on the
... i. Beginning point of replication ii. Prokaryotes (bacteria)- 1 origin of replication iii. Eukaryotes- 1 to 2000 origins of replication per chromosome b. Direction- two forks proceed in opposite directions c. Forks i. Replication sites ii. Proceed in one direction (one for each direction) iii. Repli ...
... i. Beginning point of replication ii. Prokaryotes (bacteria)- 1 origin of replication iii. Eukaryotes- 1 to 2000 origins of replication per chromosome b. Direction- two forks proceed in opposite directions c. Forks i. Replication sites ii. Proceed in one direction (one for each direction) iii. Repli ...
procedure - DNA Interactive
... replicating faithfully as cells divided and organisms developed. Observations made by Barbara McClintock at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory told a radically different story. McClintock observed that regions of DNA could jump, or "transpose". This observation challenged the simplistic view of how a gen ...
... replicating faithfully as cells divided and organisms developed. Observations made by Barbara McClintock at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory told a radically different story. McClintock observed that regions of DNA could jump, or "transpose". This observation challenged the simplistic view of how a gen ...
UNIT 7 TEST DNA TEST BLUEPRINT
... UNIT 7 DNA TEST A 1. When the __ for insulin is inserted into bacteria, they can be used to mass-produce insulin. a) chromosome b) gene c) fragment d) base 2. Who discovered the structure of DNA and made a model of it? a) Mendel b) Hershey and Chase c) Watson and Crick d) Wilkins and Franklin 3. Whi ...
... UNIT 7 DNA TEST A 1. When the __ for insulin is inserted into bacteria, they can be used to mass-produce insulin. a) chromosome b) gene c) fragment d) base 2. Who discovered the structure of DNA and made a model of it? a) Mendel b) Hershey and Chase c) Watson and Crick d) Wilkins and Franklin 3. Whi ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).


















![DOC-fFORTE [Frauen in Forschung und Technologie]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015302276_1-4cc97339477b912d48a10971c4bcea0b-300x300.png)



