DNA Replication
... would be based on its structure • They said if you peeled apart DNA down the middle it would be easy to copy • This is because all of the unpaired bases must be paired with a specific base ...
... would be based on its structure • They said if you peeled apart DNA down the middle it would be easy to copy • This is because all of the unpaired bases must be paired with a specific base ...
Presentation 1 Guidelines
... together, a phosphate on one nucleotide forms a covalent bond with a hydroxyl group at the 3 position on another nucleotide. C7. The bases conform to the AT/GC rule of complementarity. There are two hydrogen bonds between A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C. The planar rings of the bas ...
... together, a phosphate on one nucleotide forms a covalent bond with a hydroxyl group at the 3 position on another nucleotide. C7. The bases conform to the AT/GC rule of complementarity. There are two hydrogen bonds between A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C. The planar rings of the bas ...
View/print full test page
... genes in the panel plus ten bases into the introns and untranslated regions (5' and 3'). Sanger sequencing is performed to confirm variants suspected or confirmed to be pathogenic. o Deletion/duplication analysis is performed using a high resolution, custom microarray platform designed to target the ...
... genes in the panel plus ten bases into the introns and untranslated regions (5' and 3'). Sanger sequencing is performed to confirm variants suspected or confirmed to be pathogenic. o Deletion/duplication analysis is performed using a high resolution, custom microarray platform designed to target the ...
biotechnology
... Polymorphism in chromosomal DNA can arise from the presence of a variable number of tandem repeats. These are short sequences of DNA at scattered locations in the genome, repeated in tandem (like freight cars of a train). • The number of these repeat units varies from person to person, but is unique ...
... Polymorphism in chromosomal DNA can arise from the presence of a variable number of tandem repeats. These are short sequences of DNA at scattered locations in the genome, repeated in tandem (like freight cars of a train). • The number of these repeat units varies from person to person, but is unique ...
High-throughput cloning of eukaryotic open reading frames (ORFs
... S-tag (for visualization) and a 6XHIS-tag (for purification). pVP16-GW has an 8XHIS tag (for purification) and both have the MBP (maltose-binding protein, for solubilization) fused to the N-terminal of the target protein. When required, the entire fusion is cleavable from the protein target by TEV p ...
... S-tag (for visualization) and a 6XHIS-tag (for purification). pVP16-GW has an 8XHIS tag (for purification) and both have the MBP (maltose-binding protein, for solubilization) fused to the N-terminal of the target protein. When required, the entire fusion is cleavable from the protein target by TEV p ...
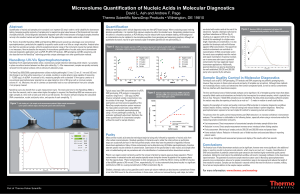
Microvolume Quantification of Nucleic Acids in Molecular Diagnostics
... Molecular techniques used in clinical diagnostics today are often qPCR based assays. When conducting assays involving absolute quantification, it is important that unknown samples lie within the standard curve. Extrapolating standard curves for outliers is a hazardous practice, as PCR efficiency may ...
... Molecular techniques used in clinical diagnostics today are often qPCR based assays. When conducting assays involving absolute quantification, it is important that unknown samples lie within the standard curve. Extrapolating standard curves for outliers is a hazardous practice, as PCR efficiency may ...
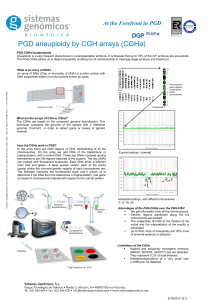
At the Forefront in PGD
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
... Fundamentals of combined chromosomal PGD Couples with one member carrying a balanced chromosomal rearrangement (translocation or inversion) have an increased risk of generating abnormal embryos as a result of segregation of the balanced abnormality. This causes, recurrent abortions and, in many case ...
DNA Mutation
... Gene mutations occur in two ways: they can be inherited from a parent ( hereditary mutations or germline mutations) or acquired during a person’s lifetime and occur in the DNA of individual cells (acquired or sporadic mutations). These changes can be caused by environmental factors such as ultraviol ...
... Gene mutations occur in two ways: they can be inherited from a parent ( hereditary mutations or germline mutations) or acquired during a person’s lifetime and occur in the DNA of individual cells (acquired or sporadic mutations). These changes can be caused by environmental factors such as ultraviol ...
Cloning a Paper Plasmid
... These are needed to transcribe the gene properly when it is read. In addition, the HindIII & EcoR1 restriction enzyme cutting sites (sequences of bases) are marked in bold on the Jellyfish Glo gene DNA. The two restriction enzymes and their respective restriction sites are listed below. These enzyme ...
... These are needed to transcribe the gene properly when it is read. In addition, the HindIII & EcoR1 restriction enzyme cutting sites (sequences of bases) are marked in bold on the Jellyfish Glo gene DNA. The two restriction enzymes and their respective restriction sites are listed below. These enzyme ...
Molecular_genetics_revision_checklist
... promoter, operator, structural gene. The role of the inhibitor in blocking the pathway of RNA polymerase needs to be explained. In eukaryotes - control of metabolic pathways by gene expression includes enhancers and transcription factors. Students should understand the role of control elements, inc ...
... promoter, operator, structural gene. The role of the inhibitor in blocking the pathway of RNA polymerase needs to be explained. In eukaryotes - control of metabolic pathways by gene expression includes enhancers and transcription factors. Students should understand the role of control elements, inc ...
IN HUMAN EVOLUTION
... that his visit was of “no value to the people mately managed to create a composite geancient populations migrated and mixed of Czechoslovakia.” In Rome, thieves stole nome from three female Neandertals and across the globe. “The whole field is explodthe modern human skull. compare it with modern hum ...
... that his visit was of “no value to the people mately managed to create a composite geancient populations migrated and mixed of Czechoslovakia.” In Rome, thieves stole nome from three female Neandertals and across the globe. “The whole field is explodthe modern human skull. compare it with modern hum ...
Amplification and partial sequencing of Ixodes Scapularis Shaker
... The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has begun funding the DNA sequencing of the deer tick genome in hopes of understanding the role ticks play in passing pathogens to humans that cause lyme disease, rocky mountain spotted fever and tularemia (9). The research project undertaken ...
... The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has begun funding the DNA sequencing of the deer tick genome in hopes of understanding the role ticks play in passing pathogens to humans that cause lyme disease, rocky mountain spotted fever and tularemia (9). The research project undertaken ...
2014
... Indicate the tRNA anticodon sequences (correctly labeling 5' and 3' ends) that would recognize each of the six codons for this minimal number of tRNA molecules: Anticodon sequence (label polarity) 3'-GCI-5' or 3'-GCG-5' ...
... Indicate the tRNA anticodon sequences (correctly labeling 5' and 3' ends) that would recognize each of the six codons for this minimal number of tRNA molecules: Anticodon sequence (label polarity) 3'-GCI-5' or 3'-GCG-5' ...
Can pseudocomplementary peptide nucleic acid nucleases
... is a priori determined by Watson-Crick base pairings between the pcPNA strands and the DNA substrate. Thus, pcPNAN for aimed cleavage of genomes can be straightforwardly designed and synthesized without any selection procedure. The site specificity is high enough to cut one site in human genome, bec ...
... is a priori determined by Watson-Crick base pairings between the pcPNA strands and the DNA substrate. Thus, pcPNAN for aimed cleavage of genomes can be straightforwardly designed and synthesized without any selection procedure. The site specificity is high enough to cut one site in human genome, bec ...
Slide ()
... The transcription cycle. The transcription cycle can be described in six steps: (1) Template binding and closed RNA polymerase-promoter complex formation: RNAP binds to DNA and then locates a promoter (P), (2) Open promoter complex formation: once bound to the promoter, RNAP melts the two DNA strand ...
... The transcription cycle. The transcription cycle can be described in six steps: (1) Template binding and closed RNA polymerase-promoter complex formation: RNAP binds to DNA and then locates a promoter (P), (2) Open promoter complex formation: once bound to the promoter, RNAP melts the two DNA strand ...
STATION 1: Nucleic acids
... (C) inducible synthesis of -galactosidase (D) synthesis of inactive -galactosidase (E) synthesis of -galactosidase only in the absence of lactose 11) In humans, the Barr body is an (A) active X chromosome in females (B) active X chromosome in males (C) inactive Y chromosome in males (D) inactive ...
... (C) inducible synthesis of -galactosidase (D) synthesis of inactive -galactosidase (E) synthesis of -galactosidase only in the absence of lactose 11) In humans, the Barr body is an (A) active X chromosome in females (B) active X chromosome in males (C) inactive Y chromosome in males (D) inactive ...
(2) Excision Repair
... • Recent research in bacteria, yeast and mammalian cells • most of the mutations arise by transletion bypass • when highly processive semiconservative DNA replication is arrested at DNA lesions • translesion synthesis (TLS) polymerases allows them to insert nucleotides opposite DNA lesions, but at t ...
... • Recent research in bacteria, yeast and mammalian cells • most of the mutations arise by transletion bypass • when highly processive semiconservative DNA replication is arrested at DNA lesions • translesion synthesis (TLS) polymerases allows them to insert nucleotides opposite DNA lesions, but at t ...
Chapter 4 Sequencing DNA and Databases
... which Oswald Avery had previously shown to be the genetic material. The next question was to determine how this genetic information coded for the proteins that carry out cellular functions. Scientists therefore wanted to examine the sequences of the DNA they were working with. The first DNA sequence ...
... which Oswald Avery had previously shown to be the genetic material. The next question was to determine how this genetic information coded for the proteins that carry out cellular functions. Scientists therefore wanted to examine the sequences of the DNA they were working with. The first DNA sequence ...
DNA Structure: Gumdrop Modeling Student Version
... 4. Now have a partner take the second piece of string and wrap it 2 times around the tape ring on one finger making sure to wrap up the first (hair color) gene. Then take the other end and wrap it 2 times around the other finger making sure to keep the second (eye color) gene in the middle exposed ...
... 4. Now have a partner take the second piece of string and wrap it 2 times around the tape ring on one finger making sure to wrap up the first (hair color) gene. Then take the other end and wrap it 2 times around the other finger making sure to keep the second (eye color) gene in the middle exposed ...
sample exam 2010
... 88. Briefly define or describe the technique of population sampling known as "quadrat sampling." (2 marks) 89. Energy calculations suggest that raising animals for food is not an efficient use of land, and that more people can be fed on a plant-based diet. Describe situations in which an animal-base ...
... 88. Briefly define or describe the technique of population sampling known as "quadrat sampling." (2 marks) 89. Energy calculations suggest that raising animals for food is not an efficient use of land, and that more people can be fed on a plant-based diet. Describe situations in which an animal-base ...
Lecture3- Molecular Biology-1(2013).
... The chromosomes of many bacteria and viruses contain circular DNA which is supercoiled ...
... The chromosomes of many bacteria and viruses contain circular DNA which is supercoiled ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).