elastin - MBBS Students Club
... has the same amino acid sequence as the normal protein; that is, their primary structures are identical but its secondary structure is dominated by beta conformation is insoluble in all but the strongest solvents is highly resistant to digestion by proteases ...
... has the same amino acid sequence as the normal protein; that is, their primary structures are identical but its secondary structure is dominated by beta conformation is insoluble in all but the strongest solvents is highly resistant to digestion by proteases ...
ELASTIN - Rihs.com.pk
... has the same amino acid sequence as the normal protein; that is, their primary structures are identical but its secondary structure is dominated by beta conformation is insoluble in all but the strongest solvents is highly resistant to digestion by proteases ...
... has the same amino acid sequence as the normal protein; that is, their primary structures are identical but its secondary structure is dominated by beta conformation is insoluble in all but the strongest solvents is highly resistant to digestion by proteases ...
hw1009-aminoacids-proteins
... In this video, we see molecules hooking together to form macromolecules. The molecule is an amino acid or peptide, joining together to form a poplypeptide or protein. Please answer these questions: ...
... In this video, we see molecules hooking together to form macromolecules. The molecule is an amino acid or peptide, joining together to form a poplypeptide or protein. Please answer these questions: ...
Relationship between amino acids sequences and protein structures
... (http://binfs.umdnj.edu/sssdb/). The second goal of this study was to evaluate the hypothesis that proteins from different families and with very low sequence similarities but with an identical SSS have a common sequence pattern. To find common sequence regularities a new algorithm of the multiple s ...
... (http://binfs.umdnj.edu/sssdb/). The second goal of this study was to evaluate the hypothesis that proteins from different families and with very low sequence similarities but with an identical SSS have a common sequence pattern. To find common sequence regularities a new algorithm of the multiple s ...
Supplementary data 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9 include N, Total (ProtScore)
... The definitions of the table fields are described as follows: N is the rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Total (ProtScore) a measure of the total amount of evidence for a detected protein. The Total ProtScore is calculated using all of the ...
... The definitions of the table fields are described as follows: N is the rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Total (ProtScore) a measure of the total amount of evidence for a detected protein. The Total ProtScore is calculated using all of the ...
Measurement of Protein Molecular Weight using MALDI MS
... determined by the number of ionizable residues (basic residues such as arginine, lysine, and histidine in positive ion mode or acidic residues such as aspartic and glutamic acid in negative ion mode). For most proteins, the predominant ion signals are observed between m/z 500 and m/z 2000, independe ...
... determined by the number of ionizable residues (basic residues such as arginine, lysine, and histidine in positive ion mode or acidic residues such as aspartic and glutamic acid in negative ion mode). For most proteins, the predominant ion signals are observed between m/z 500 and m/z 2000, independe ...
Protein Folding Questions only
... Folding a 15 amino acid protein 1. Predictions: From your experience with oil and water, which sidechains might position themselves on the interior of a protein, where they are shielded from water? Why? - Which sidechains might be attracted to each other? Why? - Would the final shape of a protein be ...
... Folding a 15 amino acid protein 1. Predictions: From your experience with oil and water, which sidechains might position themselves on the interior of a protein, where they are shielded from water? Why? - Which sidechains might be attracted to each other? Why? - Would the final shape of a protein be ...
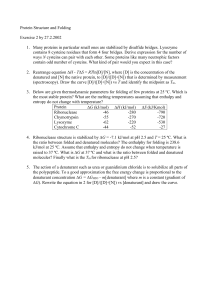
Protein Structure and Folding
... contains 8 cysteine residues that form 4 four bridges. Derive expression for the number of ways N cysteins can pair with each other. Some proteins like many neutrophic factors contain odd number of cysteins. What kind of pair would you expect in this case? 2. Rearrange equation H - TS = RTln[D]/[N ...
... contains 8 cysteine residues that form 4 four bridges. Derive expression for the number of ways N cysteins can pair with each other. Some proteins like many neutrophic factors contain odd number of cysteins. What kind of pair would you expect in this case? 2. Rearrange equation H - TS = RTln[D]/[N ...
Template to create a scientific poster
... calorimetry revealed that the I480N mutant differs significantly in its affinity for ADP, ATP, and peptide substrate. This mutant also displayed significant different reaction entropy as compared to the WT HSPA1A (N=4; bars= S.D.; p values are the results of a student’s t-test). The S16Y mutant diff ...
... calorimetry revealed that the I480N mutant differs significantly in its affinity for ADP, ATP, and peptide substrate. This mutant also displayed significant different reaction entropy as compared to the WT HSPA1A (N=4; bars= S.D.; p values are the results of a student’s t-test). The S16Y mutant diff ...
Slide 1
... Alzheimers’s, Parkinson’s and mad cow disease coincide with the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the form of amyloids. • no consensus on how the amyloids and the disease itself is linked but it is becoming clear that a misfolded protein can be used as a template to cause more misfolded proteins ...
... Alzheimers’s, Parkinson’s and mad cow disease coincide with the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the form of amyloids. • no consensus on how the amyloids and the disease itself is linked but it is becoming clear that a misfolded protein can be used as a template to cause more misfolded proteins ...
Progressive resistance exercise training decreases ribosomal
... training (RT) or sedentary (SED) group. RT animals were trained to climb a ladder apparatus with progressively heavier loads over a 10 week period. SED animals were not given any exercise training. Following this period, the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) muscle was excised and analyzed for protein le ...
... training (RT) or sedentary (SED) group. RT animals were trained to climb a ladder apparatus with progressively heavier loads over a 10 week period. SED animals were not given any exercise training. Following this period, the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) muscle was excised and analyzed for protein le ...
Clp proteins in photosynthetic organisms: An essential family of
... survival. My group has been studying the Clp family of molecular chaperones and proteases for many years in several different model photosynthetic organisms, ranging from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus to the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Work has also begun on Clp proteins that r ...
... survival. My group has been studying the Clp family of molecular chaperones and proteases for many years in several different model photosynthetic organisms, ranging from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus to the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Work has also begun on Clp proteins that r ...
FCS-FS-8. Students will discuss why proteins are important in food
... coiled structure. Creating a looser, less compact structure. ...
... coiled structure. Creating a looser, less compact structure. ...
Amino acids
... globular proteins assume as a consequence of the noncovalent interactions between the side chains in their primary structure) • quarternary (Many proteins are composed of several polypeptide chains = subunits) ...
... globular proteins assume as a consequence of the noncovalent interactions between the side chains in their primary structure) • quarternary (Many proteins are composed of several polypeptide chains = subunits) ...
Computational protein design
... discrete set of all allowed conformers of each side-chain, called rotamers. Residues that form the boundary between the core and surface require a combination of the core and the surface scoring functions. The algorithm considers both hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids at boundary positions, wh ...
... discrete set of all allowed conformers of each side-chain, called rotamers. Residues that form the boundary between the core and surface require a combination of the core and the surface scoring functions. The algorithm considers both hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids at boundary positions, wh ...
Protein Study Guide
... oxygen, but protein is the only macronutrient that contains nitrogen. There are an infinite number of proteins in any living organism. Most of the proteins in our body come from 20 amino acids. Of those 20 , 9 are essential amino acids which means the body does not produce or produce enough to meet ...
... oxygen, but protein is the only macronutrient that contains nitrogen. There are an infinite number of proteins in any living organism. Most of the proteins in our body come from 20 amino acids. Of those 20 , 9 are essential amino acids which means the body does not produce or produce enough to meet ...
The macromolecular sites of action through which drugs
... The macromolecular sites of action through which drugs mediate their effects are usually proteins. An understanding of what forces are responsible for the binding of drugs to proteins may be obtained by first considering what forces drive protein folding since these 2 processes share many common cha ...
... The macromolecular sites of action through which drugs mediate their effects are usually proteins. An understanding of what forces are responsible for the binding of drugs to proteins may be obtained by first considering what forces drive protein folding since these 2 processes share many common cha ...
protein
... Pure proteins are required to study enzyme function. Pure proteins can be used to determine what other proteins or molecules they might interact with. Pure proteins are needed for studies of protein function (e.g. Are there regulatory subunits? Is it phosphorylated? Is the protein regulated by its i ...
... Pure proteins are required to study enzyme function. Pure proteins can be used to determine what other proteins or molecules they might interact with. Pure proteins are needed for studies of protein function (e.g. Are there regulatory subunits? Is it phosphorylated? Is the protein regulated by its i ...
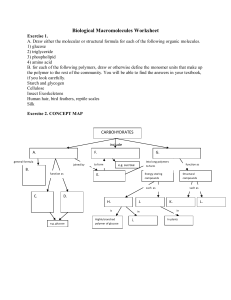
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... a. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in DNA b. the number _____ of different chemical classes of amino acids c. the number _____ of chains of nucleotides in a DNA molecule d. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in RNA e. the number _____ of different amino acids found in pr ...
... a. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in DNA b. the number _____ of different chemical classes of amino acids c. the number _____ of chains of nucleotides in a DNA molecule d. the number _____ of different nitrogenous bases in RNA e. the number _____ of different amino acids found in pr ...
Kay Hofmann - Tresch Group
... Spectra contain data of fewer proteins. But: more spectra have to be measured ...
... Spectra contain data of fewer proteins. But: more spectra have to be measured ...
Protein Electrophoresis
... •Transfer (blot) proteins onto membrane (nylon , nitrocellulose) •Probe the membrane with 1o antibody (recognizes your protein) •Add 2o antibody (this antibody is linked to an enzyme) •Substrate is added ...
... •Transfer (blot) proteins onto membrane (nylon , nitrocellulose) •Probe the membrane with 1o antibody (recognizes your protein) •Add 2o antibody (this antibody is linked to an enzyme) •Substrate is added ...
the protein (or proteins)
... Figure 2. Protein Interaction Network for Huntington’s Disease Comprehensive PPI network for htt [huntingtin protein] Y2H interactors [35 bait and 51 prey proteins & verified in pull down assays], red diamonds; previously published interactors, blue squares; interactors identified from databases HRP ...
... Figure 2. Protein Interaction Network for Huntington’s Disease Comprehensive PPI network for htt [huntingtin protein] Y2H interactors [35 bait and 51 prey proteins & verified in pull down assays], red diamonds; previously published interactors, blue squares; interactors identified from databases HRP ...
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation

Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (also known as BiFC) is a technology typically used to validate protein interactions. It is based on the association of fluorescent protein fragments that are attached to components of the same macromolecular complex. Proteins that are postulated to interact are fused to unfolded complementary fragments of a fluorescent reporter protein and expressed in live cells. Interaction of these proteins will bring the fluorescent fragments within proximity, allowing the reporter protein to reform in its native three-dimensional structure and emit its fluorescent signal. This fluorescent signal can be detected and located within the cell using an inverted fluorescence microscope that allows imaging of fluorescence in cells. In addition, the intensity of the fluorescence emitted is proportional to the strength of the interaction, with stronger levels of fluorescence indicating close or direct interactions and lower fluorescence levels suggesting interaction within a complex. Therefore, through the visualisation and analysis of the intensity and distribution of fluorescence in these cells, one can identify both the location and interaction partners of proteins of interest.