Fundamentals of protein structure
... •Counting from the N-terminal end, the C=O group of each amino acid residue is hydrogen bonded to the N-H group of the amino acid four residues away from it in the covalently bonded sequence. •(each C ) of one a.a. is hydrogen bonded to the (-NH) of the next fourth amino acid in the chain (1 →4). •T ...
... •Counting from the N-terminal end, the C=O group of each amino acid residue is hydrogen bonded to the N-H group of the amino acid four residues away from it in the covalently bonded sequence. •(each C ) of one a.a. is hydrogen bonded to the (-NH) of the next fourth amino acid in the chain (1 →4). •T ...
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC)
... by testing mutants of the interactors with deleted binding domains, or by experiments using a known competitor for one of the two interactors that can be added as a third element. Moreover a protein known not to interact with the one or other interactor can be used for complementation. If this is no ...
... by testing mutants of the interactors with deleted binding domains, or by experiments using a known competitor for one of the two interactors that can be added as a third element. Moreover a protein known not to interact with the one or other interactor can be used for complementation. If this is no ...
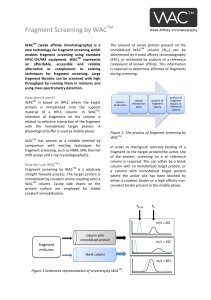
Fragment Screening by WAC - Transientic Interactions
... new technology for fragment screening which enables fragment screening using standard HPLC-‐UV/MS equipment. WACTM represents an affordable, accessible and reliable alternative or complement to existing t ...
... new technology for fragment screening which enables fragment screening using standard HPLC-‐UV/MS equipment. WACTM represents an affordable, accessible and reliable alternative or complement to existing t ...
Developing a Novel Means of Observing the
... transcription of cDNA clones from such plasmids are translated just as efficiently as native mRNAs in injected embryos. Thus, the study of a laboratory-manipulated endogenous protein is possible due the vector’s capability of producing protein expression in intact embryos comparable to proteins left ...
... transcription of cDNA clones from such plasmids are translated just as efficiently as native mRNAs in injected embryos. Thus, the study of a laboratory-manipulated endogenous protein is possible due the vector’s capability of producing protein expression in intact embryos comparable to proteins left ...
Bacterial Bioreactors for High Yield Production of Recombinant Protein
... Eotaxin synthesis rates from pColdI(SP-4) gradually increased from day 1 to 3, peaked between days 3 and 4, and were sustained at that level through the final 7-day time point. In contrast, eotaxin expression levels from pColdI(SP-2) were relatively modest initially, increased only marginally, peake ...
... Eotaxin synthesis rates from pColdI(SP-4) gradually increased from day 1 to 3, peaked between days 3 and 4, and were sustained at that level through the final 7-day time point. In contrast, eotaxin expression levels from pColdI(SP-2) were relatively modest initially, increased only marginally, peake ...
Protein Physics by Computer. Step by Step: Protein Visualization
... Green Fluorescent Protein originates from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria. Unlike to other chromoproteins, that use separate cofactors, the chromophore in GFP is produced from three adjacend amino acids by an cyclization and oxidation step, and the only nececcity to do so is the presence of oxygen. ...
... Green Fluorescent Protein originates from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria. Unlike to other chromoproteins, that use separate cofactors, the chromophore in GFP is produced from three adjacend amino acids by an cyclization and oxidation step, and the only nececcity to do so is the presence of oxygen. ...
Mean-field minimization methods for biological macromolecules
... MFT applications to protein sequence design In inverted protein design, one seeks protein sequences that arc compatible with a known three-dimensional structure. Two main issues have to be addressed in this procedure. Firstly, the combinatorial problem of testing all possible sequences on the struct ...
... MFT applications to protein sequence design In inverted protein design, one seeks protein sequences that arc compatible with a known three-dimensional structure. Two main issues have to be addressed in this procedure. Firstly, the combinatorial problem of testing all possible sequences on the struct ...
Amino acids in proteins
... Peptides and proteins • contain 2 or more AAs bound by peptide bond(s) ...
... Peptides and proteins • contain 2 or more AAs bound by peptide bond(s) ...
Prior Art - Cabic.com
... of protein P was known in the art. The description explains that the activity of protein P was previously known to result in lowering blood pressure. The inventors assert they have newly produced a stable crystalline form of protein P. Protein P in crystalline form is inactive. The descripti ...
... of protein P was known in the art. The description explains that the activity of protein P was previously known to result in lowering blood pressure. The inventors assert they have newly produced a stable crystalline form of protein P. Protein P in crystalline form is inactive. The descripti ...
Equilibrium and Free Energy of Protein Denaturation
... The denaturation of some proteins can be described by a two-state transition model in which the protein exists in either the native (N) or completely unfolded, denatured (D) conformation. In large and more complex proteins, there may be multiple unfolding intermediates where only part of the protein ...
... The denaturation of some proteins can be described by a two-state transition model in which the protein exists in either the native (N) or completely unfolded, denatured (D) conformation. In large and more complex proteins, there may be multiple unfolding intermediates where only part of the protein ...
NTSAD Monthly Research Review What is Pyrimethamine? 21st
... People with rare diseases often have difficulty being reimbursed for the care they receive because that care is "off-label" and may not be covered by health insurance. This financial burden can be an enormous strain on patients and families, especially when the cost of off-label treatments runs very ...
... People with rare diseases often have difficulty being reimbursed for the care they receive because that care is "off-label" and may not be covered by health insurance. This financial burden can be an enormous strain on patients and families, especially when the cost of off-label treatments runs very ...
Maple Syrup Urine Disease – Clinical Management Pathway
... MSUD Anamix infant oral or NG as tolerated, or MSUD Aid III if fluid restricted, to provide at least 3g/kg/day protein equivalent Give Isoleucine & Valine supplements, 100-200mg each, to maintain target levels (see below) If feeds poorly tolerated IV 10% dextrose + added electrolytes (+/- insulin ...
... MSUD Anamix infant oral or NG as tolerated, or MSUD Aid III if fluid restricted, to provide at least 3g/kg/day protein equivalent Give Isoleucine & Valine supplements, 100-200mg each, to maintain target levels (see below) If feeds poorly tolerated IV 10% dextrose + added electrolytes (+/- insulin ...
,C. Notes:
... lead to the production of temperature-sensitive proteins. Therefore, some of the temperaturesensitive revertants may be second-site revertants. Approximately 40 wild-type revertants were isolated a+ 25°C and 4 of One of these tempemture-sensitive stmins was the strrrin desired; i.e., it had a these ...
... lead to the production of temperature-sensitive proteins. Therefore, some of the temperaturesensitive revertants may be second-site revertants. Approximately 40 wild-type revertants were isolated a+ 25°C and 4 of One of these tempemture-sensitive stmins was the strrrin desired; i.e., it had a these ...
Myosin (light chain)
... repeating structures, such as β-pleated sheets and α-helices • Tertiary structure = 3-dimensional shape of a folded polypeptide, maintained by disulfide bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic effects • Quarternaty structure = several polypeptide chains associated together to form a functiona ...
... repeating structures, such as β-pleated sheets and α-helices • Tertiary structure = 3-dimensional shape of a folded polypeptide, maintained by disulfide bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic effects • Quarternaty structure = several polypeptide chains associated together to form a functiona ...
Egg Protein in Sports Nutrition
... times more protein synthesis than with free amino acids or a fast absorbing protein such as whey protein alone.2 This can be an optimal approach for allowing lean muscle growth. Slowly absorbed amino acids, such as those in egg protein promote leucine balance, better than a fast absorbing protein or ...
... times more protein synthesis than with free amino acids or a fast absorbing protein such as whey protein alone.2 This can be an optimal approach for allowing lean muscle growth. Slowly absorbed amino acids, such as those in egg protein promote leucine balance, better than a fast absorbing protein or ...
No Slide Title
... • PROSITE provides consensus patterns for a lot of PTM sites, however in most cases these patterns are very short and the true modifications occur based on the structural or environmental context in the protein fold • Because of this reason, methods based on reg expressions or local alignment method ...
... • PROSITE provides consensus patterns for a lot of PTM sites, however in most cases these patterns are very short and the true modifications occur based on the structural or environmental context in the protein fold • Because of this reason, methods based on reg expressions or local alignment method ...
Chapter 3
... Many experiments have shown that proteins can spontaneously fold from an unfolded state to their folded native state. This proves that the amino acid sequence contains enough information to specify tertiary structure. Bonds within the peptide backbone seek out different possible conformations as the ...
... Many experiments have shown that proteins can spontaneously fold from an unfolded state to their folded native state. This proves that the amino acid sequence contains enough information to specify tertiary structure. Bonds within the peptide backbone seek out different possible conformations as the ...
1 Corporation obtaining approval, the name of its representative
... for the modified CP4 EPSPS protein was transferred (NK603). It has been determined that the respective Bt proteins (the modified Cry1F, Cry1Ab and modified Cry3Aa2 proteins) derived from the genes transferred to this stacked line do not interact with one another to change the specificity of the inse ...
... for the modified CP4 EPSPS protein was transferred (NK603). It has been determined that the respective Bt proteins (the modified Cry1F, Cry1Ab and modified Cry3Aa2 proteins) derived from the genes transferred to this stacked line do not interact with one another to change the specificity of the inse ...
Imaging cellular acylation Rami N. Hannoush Genentech, Inc
... Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, USA ...
... Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, USA ...
TONE UP. GET LEAN. BE STRONG.
... The body is able to make non-essential amino acids from other amino acids in the body. The body, however, is not able to make essential amino acids; the only way to get them is through diet. One of the best ways to ensure you are meeting your needs is by eating highquality protein foods. Protein sou ...
... The body is able to make non-essential amino acids from other amino acids in the body. The body, however, is not able to make essential amino acids; the only way to get them is through diet. One of the best ways to ensure you are meeting your needs is by eating highquality protein foods. Protein sou ...
Structural Bioinformatics In this presentation……
... Template library of fragments • The process of protein modeling becomes extremely easier if all the common fragments or side-chains are developed and stored as molecule template library • This technique reduces the time consumed greatly as well as speeds up the visualization • Until date, about 180 ...
... Template library of fragments • The process of protein modeling becomes extremely easier if all the common fragments or side-chains are developed and stored as molecule template library • This technique reduces the time consumed greatly as well as speeds up the visualization • Until date, about 180 ...
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation

Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (also known as BiFC) is a technology typically used to validate protein interactions. It is based on the association of fluorescent protein fragments that are attached to components of the same macromolecular complex. Proteins that are postulated to interact are fused to unfolded complementary fragments of a fluorescent reporter protein and expressed in live cells. Interaction of these proteins will bring the fluorescent fragments within proximity, allowing the reporter protein to reform in its native three-dimensional structure and emit its fluorescent signal. This fluorescent signal can be detected and located within the cell using an inverted fluorescence microscope that allows imaging of fluorescence in cells. In addition, the intensity of the fluorescence emitted is proportional to the strength of the interaction, with stronger levels of fluorescence indicating close or direct interactions and lower fluorescence levels suggesting interaction within a complex. Therefore, through the visualisation and analysis of the intensity and distribution of fluorescence in these cells, one can identify both the location and interaction partners of proteins of interest.