SECTION 5-5: FREQUENCY TRANSFORMATIONS
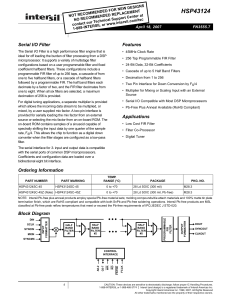
... two step process where it is determined what is to be built (the filter transfer function) and then how to build it (the topology used for the circuit). In general, filters are built out of one-pole sections for real poles, and two-pole sections for pole pairs. While you can build a filter out of th ...
... two step process where it is determined what is to be built (the filter transfer function) and then how to build it (the topology used for the circuit). In general, filters are built out of one-pole sections for real poles, and two-pole sections for pole pairs. While you can build a filter out of th ...
MTI TN113: The Series to Parallel Impedance Transformation
... Recall, that Q (the “quality factor”), is a measure of how much energy is not lost in a reactive element. The higher the Q, the less energy is lost. In the circuit world, we model the loss as a simple resistor. Note that the Q for series (Qs) and parallel (Qp) circuits is numerically the same at ...
... Recall, that Q (the “quality factor”), is a measure of how much energy is not lost in a reactive element. The higher the Q, the less energy is lost. In the circuit world, we model the loss as a simple resistor. Note that the Q for series (Qs) and parallel (Qp) circuits is numerically the same at ...
Cutler-Hammer - Performance Power Solutions
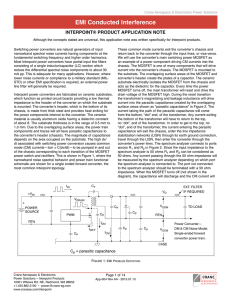
... The Point of Common Coupling (PCC) with the consumer/utility interface is the closest point on the utility side of the customer's service where another utility customer is or could be supplied. The ownership of any apparatus such as a transformer that the utility might provide in the customers syste ...
... The Point of Common Coupling (PCC) with the consumer/utility interface is the closest point on the utility side of the customer's service where another utility customer is or could be supplied. The ownership of any apparatus such as a transformer that the utility might provide in the customers syste ...
High-accuracy charge-redistribution SC video bandpass filter in
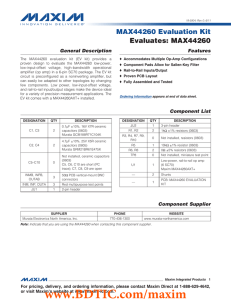
... filter coefficients. The main purpose of the filter to be described is to produce a particular nonlinear phase characteristic in a video channel as well as the creation of selectivity. This filter is intended as part of an integrated multistandard TV color decoder in an embedded application. When us ...
... filter coefficients. The main purpose of the filter to be described is to produce a particular nonlinear phase characteristic in a video channel as well as the creation of selectivity. This filter is intended as part of an integrated multistandard TV color decoder in an embedded application. When us ...
Introduction
... As carbon reduction policies gather pace in the Asian steel mill industry, many existing plants are expected to invest in process and equipment upgrades to meet new environment regulations. Key to the success of these upgrades will be new gas filtering and waste water recycling systems. In addition, ...
... As carbon reduction policies gather pace in the Asian steel mill industry, many existing plants are expected to invest in process and equipment upgrades to meet new environment regulations. Key to the success of these upgrades will be new gas filtering and waste water recycling systems. In addition, ...
LMF100 High Performance Dual Switched Capacitor Filter
... of the other bandpass filter section. The crosstalk is the ratio between the output of the grounded filter section and the 1 VRMS input signal of the other section. Note 7: The short circuit source current is measured by forcing the output that is being tested to its maximum positive voltage swing a ...
... of the other bandpass filter section. The crosstalk is the ratio between the output of the grounded filter section and the 1 VRMS input signal of the other section. Note 7: The short circuit source current is measured by forcing the output that is being tested to its maximum positive voltage swing a ...
harmonic reduction in power system - Sacramento
... The term harmonics referred to Power quality in ideal world would mean how pure the voltage is, how pure the current waveform is in its sinusoidal form. Power quality is very important to commercial and industrial power system designs. Ideally, the electrical supply should be a perfect sinusoidal wa ...
... The term harmonics referred to Power quality in ideal world would mean how pure the voltage is, how pure the current waveform is in its sinusoidal form. Power quality is very important to commercial and industrial power system designs. Ideally, the electrical supply should be a perfect sinusoidal wa ...