4.2.2 – Passive RC Filters
... We can now see the shape of the graph much more clearly, but the response is not exactly as we discussed in the ‘ideal’ case. This is because we are dealing with real component values and a real circuit. The reactance of the capacitor is changing all the time as frequency changes, it doesn’t suddenl ...
... We can now see the shape of the graph much more clearly, but the response is not exactly as we discussed in the ‘ideal’ case. This is because we are dealing with real component values and a real circuit. The reactance of the capacitor is changing all the time as frequency changes, it doesn’t suddenl ...
A receiver architecture for devices in wireless body area networks
... scenarios the power consumption and sensitivity of the wakeup receiver may be even more important to the system performance than that of the main transceiver. The targeted total power consumption is 1 mW in active mode, when either receiver or transmitter is operated. To avoid interference they will ...
... scenarios the power consumption and sensitivity of the wakeup receiver may be even more important to the system performance than that of the main transceiver. The targeted total power consumption is 1 mW in active mode, when either receiver or transmitter is operated. To avoid interference they will ...
Filtering Noise Frequencies Using Notch Filters
... each circuit. This confirmation was necessary because the expected value of noise from the ambient light was different from what was expected (120 Hz versus 60 Hz). The filters actually did not notch at 120 Hz, but closer to 100 Hz: this was due in part to the percent error associated with the equat ...
... each circuit. This confirmation was necessary because the expected value of noise from the ambient light was different from what was expected (120 Hz versus 60 Hz). The filters actually did not notch at 120 Hz, but closer to 100 Hz: this was due in part to the percent error associated with the equat ...
Delivering Clean and Pure Power
... well in useful applications to overcome distribution system problems. Power electronics has three faces in power distribution: one that introduces valuable industrial and domestic equipment; a second one that creates problems; and, finally, a third one that helps to solve those problems. On one hand ...
... well in useful applications to overcome distribution system problems. Power electronics has three faces in power distribution: one that introduces valuable industrial and domestic equipment; a second one that creates problems; and, finally, a third one that helps to solve those problems. On one hand ...
Power Quality Improvement by Shunt Active Performance Filters
... shunt active performance filters with intension to compensate higher harmonic currents of non-linear load. The authors of this article deal with usage of a combination of fuzzy system techniques and artificial intelligence, which is also known as Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interference Systems- ANFIS for ...
... shunt active performance filters with intension to compensate higher harmonic currents of non-linear load. The authors of this article deal with usage of a combination of fuzzy system techniques and artificial intelligence, which is also known as Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interference Systems- ANFIS for ...
An electrical machine with integrated drive LCL filter components
... components into a single package. This approach is important for applications such as traction motors, aerospace, electric vehicles and cars where space, mass or volume constraints are high. Incorporation of electromagnetic components, such as line filters, into electric machines can be achieved by ...
... components into a single package. This approach is important for applications such as traction motors, aerospace, electric vehicles and cars where space, mass or volume constraints are high. Incorporation of electromagnetic components, such as line filters, into electric machines can be achieved by ...
Harmonic Distortion
... transformers. This “extra” current is not real (it will not produce work) but nevertheless due to this current, transformers and wires must be overdimensioned to prevent over-heating effects. Distortion of the input voltage wave. That could implicate important effects: It could affect to the corre ...
... transformers. This “extra” current is not real (it will not produce work) but nevertheless due to this current, transformers and wires must be overdimensioned to prevent over-heating effects. Distortion of the input voltage wave. That could implicate important effects: It could affect to the corre ...
Introduction - Simple Media Networks, Inc
... user can choose the circuit design to produce a desired gain level and frequency response. Pad placement for many components have been provided so that different filters in the Sallen-Key topology can be realized on this board. All of the resistor pads (prefix R) are of 0603 size, while the pads for ...
... user can choose the circuit design to produce a desired gain level and frequency response. Pad placement for many components have been provided so that different filters in the Sallen-Key topology can be realized on this board. All of the resistor pads (prefix R) are of 0603 size, while the pads for ...
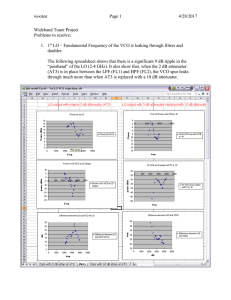
Problems to resolve:
... Since the chip can be pre-programmed, my thought is that we could replace the DDS on the 2nd LO board by 2 separate PLLs, one for the 2063.2 MHz LO and the other for the 1726.4 MHz part (which gets divided down to 863.2 MHz). For the 2063.2, we would synthesize a frequency instead of 2062.5 MHz, whi ...
... Since the chip can be pre-programmed, my thought is that we could replace the DDS on the 2nd LO board by 2 separate PLLs, one for the 2063.2 MHz LO and the other for the 1726.4 MHz part (which gets divided down to 863.2 MHz). For the 2063.2, we would synthesize a frequency instead of 2062.5 MHz, whi ...