Impedance Matching Networks Applied to RF Power Transistors
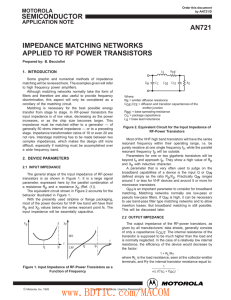
... to be realized by a lumped element. A transmission line can be used instead (Fig. 7). R1 ...
... to be realized by a lumped element. A transmission line can be used instead (Fig. 7). R1 ...
Chapter 8: Analog Filters
... dependent change in the input/output transfer function that is defined as the frequency response. Filters have many practical applications. A simple, single-pole, low-pass filter (the integrator) is often used to stabilize amplifiers by rolling off the gain at higher frequencies where excessive phas ...
... dependent change in the input/output transfer function that is defined as the frequency response. Filters have many practical applications. A simple, single-pole, low-pass filter (the integrator) is often used to stabilize amplifiers by rolling off the gain at higher frequencies where excessive phas ...
Harmonic Filtering
... ECOsineTM – Passive Harmonic Filters Schaffner ECOsineTM passive harmonic filters represent an economical solution to the challenge of load-applied harmonic mitigation in three-phase power systems. With features including more compact dimensions to comparable products, quick installation and easily ...
... ECOsineTM – Passive Harmonic Filters Schaffner ECOsineTM passive harmonic filters represent an economical solution to the challenge of load-applied harmonic mitigation in three-phase power systems. With features including more compact dimensions to comparable products, quick installation and easily ...
A Guide to the Design of Laminate PCBs at Microwave
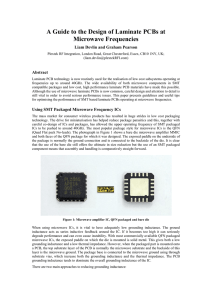
... presence of the Nickel can cause significant losses. One alternative is a silver finish but this may eventually tarnish which could be an issue. PCBs usually include a solder resist layer to define the apertures for the solder paste for SMT components. Solder resist is often omitted from the RF trac ...
... presence of the Nickel can cause significant losses. One alternative is a silver finish but this may eventually tarnish which could be an issue. PCBs usually include a solder resist layer to define the apertures for the solder paste for SMT components. Solder resist is often omitted from the RF trac ...
i ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First and foremost, I would like to thank
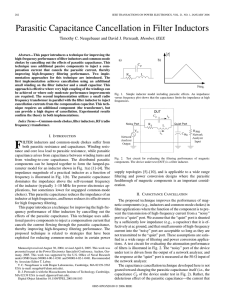
... present day. One of the most critical issues in practical filter applications is the RC time constant variation (inversely proportional to the –3dB frequency) due to variations in process, temperature, etc. The corner frequency of a switched capacitor filter is dependent on the product of the clock ...
... present day. One of the most critical issues in practical filter applications is the RC time constant variation (inversely proportional to the –3dB frequency) due to variations in process, temperature, etc. The corner frequency of a switched capacitor filter is dependent on the product of the clock ...
Improving the Active Power Filter Performance with a Prediction
... N recent years active power filters (APFs) have been widely studied and several methods to control them have been proposed, e.g. [1] – [4]. In harmonic filtering the active filter current reference generation plays an important role: if the reference is poor, a good filtering result cannot be achiev ...
... N recent years active power filters (APFs) have been widely studied and several methods to control them have been proposed, e.g. [1] – [4]. In harmonic filtering the active filter current reference generation plays an important role: if the reference is poor, a good filtering result cannot be achiev ...
Pipelining and Parallel Processing
... Parallel processing for Low power (1) Parallel processing, like pipelining, can reduce the power consumption of a system by allowing the supply voltage to be reduced. supply voltage can be reduced to ...
... Parallel processing for Low power (1) Parallel processing, like pipelining, can reduce the power consumption of a system by allowing the supply voltage to be reduced. supply voltage can be reduced to ...
power quality: harmonics in power systems
... based on the harmonic characteristics of the loads where the power is applied. According to the nature of the single tuned filter, the filtering needs to start at the lowest harmonic frequency generated by the load. In this design that is the fifth harmonics. The filter will be tuned little below th ...
... based on the harmonic characteristics of the loads where the power is applied. According to the nature of the single tuned filter, the filtering needs to start at the lowest harmonic frequency generated by the load. In this design that is the fifth harmonics. The filter will be tuned little below th ...
Improvement of the Electric Power Quality Using Series Active and
... harmonics are eliminated. By this means, it is possible to improve the passive filter compensation characteristics without depending on the system impedance, since the set load-filter would present resistive behavior. It also avoids the danger that the passive filter behaves as a harmonic drain of c ...
... harmonics are eliminated. By this means, it is possible to improve the passive filter compensation characteristics without depending on the system impedance, since the set load-filter would present resistive behavior. It also avoids the danger that the passive filter behaves as a harmonic drain of c ...
X-Band Portable System PM6.5 - Ham
... GHz, etc.). The sideband signal is reversed also meaning USB at X-Band = LSB at 2-meters. ...
... GHz, etc.). The sideband signal is reversed also meaning USB at X-Band = LSB at 2-meters. ...
Harmonics Filter Design
... In recent years, harmonics are considered as one of the most essential problems in the industrial power distribution networks. The problem of harmonics is increasing due to the use of the variable speed drives (VSDs), the uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and the solid-state devices. Harmonics c ...
... In recent years, harmonics are considered as one of the most essential problems in the industrial power distribution networks. The problem of harmonics is increasing due to the use of the variable speed drives (VSDs), the uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and the solid-state devices. Harmonics c ...
Harmonic reduction methods
... load on a single AFD decreases, the individual distortion contribution percentage decreases, resulting in less of a need for cancellation. It is possible for a facility with a large number of AFDs to feed two halves of the distribution from phase-shifted transformers, yielding a large reduction in h ...
... load on a single AFD decreases, the individual distortion contribution percentage decreases, resulting in less of a need for cancellation. It is possible for a facility with a large number of AFDs to feed two halves of the distribution from phase-shifted transformers, yielding a large reduction in h ...