university of oslo faculty of mathematics and natural sciences
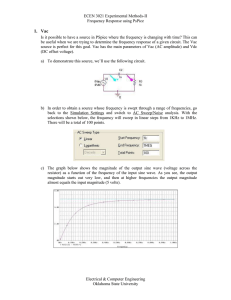
... where the output signal is in-phase with the input signal. Draw the circuit and assign component values. Also, write the mathematical expression for the gain of this type of amplifier. What can you say about the input impedance of such an amplifier? 2b) The operation amplifier has a Gain Bandwidth P ...
... where the output signal is in-phase with the input signal. Draw the circuit and assign component values. Also, write the mathematical expression for the gain of this type of amplifier. What can you say about the input impedance of such an amplifier? 2b) The operation amplifier has a Gain Bandwidth P ...
Frequency response of feedback amplifiers
... Applications of Analog Filters • Analog filters can be found in almost every electronic circuit. • Audio systems use them for pre-amplification, equalization, and tone control. • In communication systems, filters are used for tuning in specific frequencies and eliminating others (for example, to fi ...
... Applications of Analog Filters • Analog filters can be found in almost every electronic circuit. • Audio systems use them for pre-amplification, equalization, and tone control. • In communication systems, filters are used for tuning in specific frequencies and eliminating others (for example, to fi ...
SIMPLE LOW PASS AND HIGH PASS FILTER
... The frequencies 1 and 2 at which the output power drops to one half of its values at the resonant frequency are called the half-power frequencies. At these frequencies also known as cutoff frequencies or corner frequencies, the output voltage is | Vo ( c ) | 0.707 | Vo ( o ) | . This circuit w ...
... The frequencies 1 and 2 at which the output power drops to one half of its values at the resonant frequency are called the half-power frequencies. At these frequencies also known as cutoff frequencies or corner frequencies, the output voltage is | Vo ( c ) | 0.707 | Vo ( o ) | . This circuit w ...
User Manual - Quasar Electronic Kits
... The telephone pickup is really a magnetic field fluctuation detector. It picks up the oscillating magnetic field from the receiver of your telephone when someone is speaking to you. But it will also collect any other oscillating magnetic fields which happen to be floating around in the air. For exam ...
... The telephone pickup is really a magnetic field fluctuation detector. It picks up the oscillating magnetic field from the receiver of your telephone when someone is speaking to you. But it will also collect any other oscillating magnetic fields which happen to be floating around in the air. For exam ...
Coupling Capacitors (Updated 5-15
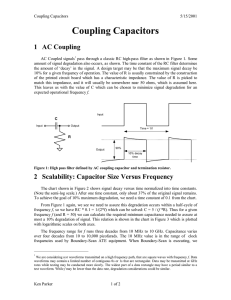
... From Figure 1 again, we see we need to assure this degradation occurs within a half-cycle of frequency f, so we have RC * 0.1 = 1/(2*f) which can be solved: C = 5 / (f *R). Thus for a given frequency f (and R = 50) we can calculate the required minimum capacitance needed to assure at most a 10% degr ...
... From Figure 1 again, we see we need to assure this degradation occurs within a half-cycle of frequency f, so we have RC * 0.1 = 1/(2*f) which can be solved: C = 5 / (f *R). Thus for a given frequency f (and R = 50) we can calculate the required minimum capacitance needed to assure at most a 10% degr ...
RiverbeckConfPaper160516
... from 15 dB – 45 dB, see Figure 5. On the main integrated circuit is a homodyne receiver with 1GHz complex IF bandwidth, programmable gain stages and continuous time channel filters followed by a homodyne transmitter. By mixing down the signal to baseband and up converting to the output frequency the ...
... from 15 dB – 45 dB, see Figure 5. On the main integrated circuit is a homodyne receiver with 1GHz complex IF bandwidth, programmable gain stages and continuous time channel filters followed by a homodyne transmitter. By mixing down the signal to baseband and up converting to the output frequency the ...
Weekly Report 4
... outcome. It attempts to minimize error by adjusting the input into the system. Filters For Quadcoptor balance during flying, it is required to implement digital control methods. MPU6050 provides accel and gyro, total 6 axis data. Accel data shows orientation which responds slowly, kind of like a low ...
... outcome. It attempts to minimize error by adjusting the input into the system. Filters For Quadcoptor balance during flying, it is required to implement digital control methods. MPU6050 provides accel and gyro, total 6 axis data. Accel data shows orientation which responds slowly, kind of like a low ...
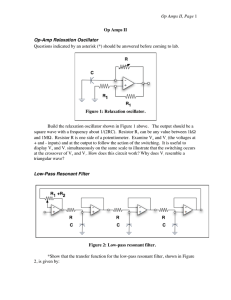
Op Amps II, Page
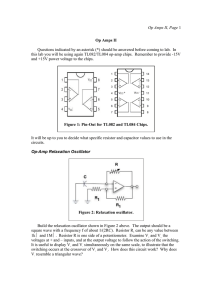
... + and - inputs) and at the output to follow the action of the switching. It is useful to display V+ and V- simultaneously on the same scale to illustrate that the switching occurs at the crossover of V+ and V-. How does this circuit work? Why does V- resemble a triangular wave? Low-Pass Resonant Fil ...
... + and - inputs) and at the output to follow the action of the switching. It is useful to display V+ and V- simultaneously on the same scale to illustrate that the switching occurs at the crossover of V+ and V-. How does this circuit work? Why does V- resemble a triangular wave? Low-Pass Resonant Fil ...
What is Sound
... will probably become more familiar with variations on these from working with the processing tools in Soundforge. These are: Lowpass filters, which let through unchanged all frequencies below a certain point and attenuate all the rest (see Figure 2). The diagram below is known as an amplitudeversus- ...
... will probably become more familiar with variations on these from working with the processing tools in Soundforge. These are: Lowpass filters, which let through unchanged all frequencies below a certain point and attenuate all the rest (see Figure 2). The diagram below is known as an amplitudeversus- ...
Equalization (audio)

Equalization (British: equalisation) is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization is called an equalizer. These devices strengthen (boost) or weaken (cut) the energy of specific frequency bands.In sound recording and reproduction, equalization is the process commonly used to alter the frequency response of an audio system using linear filters. Most hi-fi equipment uses relatively simple filters to make bass and treble adjustments. Graphic and parametric equalizers have much more flexibility in tailoring the frequency content of an audio signal. An equalizer is the circuit or equipment used to achieve equalization. Since equalizers, ""adjust the amplitude of audio signals at particular frequencies,"" they are, ""in other words, frequency-specific volume knobs.""In the field of audio electronics, the term ""equalization"" has come to include the adjustment of frequency responses for practical or aesthetic reasons, often resulting in a net response that is not truly equalized. The term EQ specifically refers to this variant of the term. Stereos typically have adjustable equalizers which boost or cut bass or treble frequencies. Broadcast and recording studios use sophisticated equalizers capable of much more detailed adjustments, such as eliminating unwanted sounds or making certain instruments or voices more prominent.Equalizers are used in recording studios, radio studios and production control rooms, and live sound reinforcement to correct the response of microphones, instrument pick-ups, loudspeakers, and hall acoustics. Equalization may also be used to eliminate unwanted sounds, make certain instruments or voices more prominent, enhance particular aspects of an instrument's tone, or combat feedback (howling) in a public address system. Equalizers are also used in music production to adjust the timbre of individual instruments by adjusting their frequency content and to fit individual instruments within the overall frequency spectrum of the mix.The most common equalizers in music production are parametric, semi-parametric, graphic, peak, and program equalizers. Graphic equalizers are often included in consumer audio equipment and software which plays music on home computers. Parametric equalizers require more expertise than graphic equalizers, and they can provide more specific compensation or alteration around a chosen frequency. This may be used in order to remove (or to create) a resonance, for instance.