Chapter 20-21 Test Review Chapter Summary 20.1. Current • Define
... • Calculate voltages, currents, or resistances with Ohm’s law. • Explain what an ohmic material is. • Describe a simple circuit. 20.3. Resistance and Resistivity • Explain the concept of resistivity. • Use resistivity to calculate the resistance of specified configurations of material. 20.4. Electri ...
... • Calculate voltages, currents, or resistances with Ohm’s law. • Explain what an ohmic material is. • Describe a simple circuit. 20.3. Resistance and Resistivity • Explain the concept of resistivity. • Use resistivity to calculate the resistance of specified configurations of material. 20.4. Electri ...
Diodes
... Input and Output waveforms are shown on the right. The half-wave rectifier with filter capacitor and resistive load is shown in Figure a) ...
... Input and Output waveforms are shown on the right. The half-wave rectifier with filter capacitor and resistive load is shown in Figure a) ...
14ELN15_Question Bank
... Ans- Zero signal values of IC and VCE 4). Improper biasing of a Transistor circuit leads to a). excessive heat production at collector terminal b). distortion in output signal c). Faulty location load line Ans- Distortion in output signal ...
... Ans- Zero signal values of IC and VCE 4). Improper biasing of a Transistor circuit leads to a). excessive heat production at collector terminal b). distortion in output signal c). Faulty location load line Ans- Distortion in output signal ...
RESISTANCE AND OHM`S LAW
... • A small portable stove operates from a 120V outlet. When it is in use, 6A flow through it. What is the resistance of the heating element on the stove? R = V/I = 120V/6A = 20 Ω ...
... • A small portable stove operates from a 120V outlet. When it is in use, 6A flow through it. What is the resistance of the heating element on the stove? R = V/I = 120V/6A = 20 Ω ...
Electricity Notes, Part I
... resistance of 60 Ω, the current will be 120V ÷ 60Ω = 2 Amperes (or “2 amps”) A battery acts as a “pump” for electrons, pushing them out one end (the negative terminal) and pulling them in the other end (the positive terminal). The amount that the battery pushes the electrons depends on its voltage. ...
... resistance of 60 Ω, the current will be 120V ÷ 60Ω = 2 Amperes (or “2 amps”) A battery acts as a “pump” for electrons, pushing them out one end (the negative terminal) and pulling them in the other end (the positive terminal). The amount that the battery pushes the electrons depends on its voltage. ...
Lecture Notes: Y F Chapter 26
... 13V = I 1 (3Ω ) + I 3 (5Ω ) Multiply top equation by 5 and add two equations: 65V = I 1 (10Ω ) − I 3 (5Ω ) 13V = I 1 (3Ω ) + I 3 (5Ω ) 78V = I 1 (13Ω ) I1 = 6 A ...
... 13V = I 1 (3Ω ) + I 3 (5Ω ) Multiply top equation by 5 and add two equations: 65V = I 1 (10Ω ) − I 3 (5Ω ) 13V = I 1 (3Ω ) + I 3 (5Ω ) 78V = I 1 (13Ω ) I1 = 6 A ...
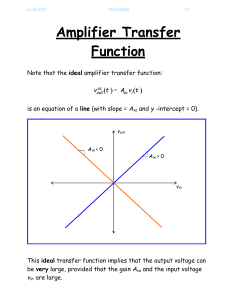
Amplifier Transfer F..
... For example, the output limits of an amplifier might be L+ = 15 V and L- = -15 V. However, we find that these limits are also often asymmetric (e.g., L+ = +15 V and L- = +5 V). ...
... For example, the output limits of an amplifier might be L+ = 15 V and L- = -15 V. However, we find that these limits are also often asymmetric (e.g., L+ = +15 V and L- = +5 V). ...
3-500ZG - RF Parts Company
... Note: TYPICAL OPERATION data arc obtained by calculation ftom published characteristic curves or actual measurcmcnt. Adjustmed ofthe rfgdd voltage to obtain the specified plate cunent at the specified bias and plale voltages is assumcd. Ifthis procedure is followcd, there will be little variation in ...
... Note: TYPICAL OPERATION data arc obtained by calculation ftom published characteristic curves or actual measurcmcnt. Adjustmed ofthe rfgdd voltage to obtain the specified plate cunent at the specified bias and plale voltages is assumcd. Ifthis procedure is followcd, there will be little variation in ...
Diodes
... Input and Output waveforms are shown on the right. The half-wave rectifier with filter capacitor and resistive load is shown in Figure 6 with the input and output waveforms in Figure 5. ...
... Input and Output waveforms are shown on the right. The half-wave rectifier with filter capacitor and resistive load is shown in Figure 6 with the input and output waveforms in Figure 5. ...
TL082-N 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Note 5: These specifications apply for VS = ± 15V and 0˚C ≤TA ≤ +70˚C. VOS, IB and IOS are measured at VCM = 0. Note 6: The input bias currents are junction leakage currents which approximately double for every 10˚C increase in the junction temperature, Tj. Due to the limited production test time, t ...
... Note 5: These specifications apply for VS = ± 15V and 0˚C ≤TA ≤ +70˚C. VOS, IB and IOS are measured at VCM = 0. Note 6: The input bias currents are junction leakage currents which approximately double for every 10˚C increase in the junction temperature, Tj. Due to the limited production test time, t ...
NCP1207AADAPGEVB Implementing NCP1207 in QR 24 W AC-DC Converter with Synchronous Rectifier
... within the secondary current loop. Resistor R6 loads the secondary winding of the current transformer. The resistor R6 converts the current into a voltage. That voltage is filtered and limited by capacitor C6 and diode D3. It then goes to the gate driver, which consists in transistors Q2, Q3 and Q4 ...
... within the secondary current loop. Resistor R6 loads the secondary winding of the current transformer. The resistor R6 converts the current into a voltage. That voltage is filtered and limited by capacitor C6 and diode D3. It then goes to the gate driver, which consists in transistors Q2, Q3 and Q4 ...
Experiment 3 The Wheatstone Bridge
... the left, and equal to the battery voltage if it is all the way to the right. Therefore the voltage divider can be used to provide any voltage between zero and the power supply voltage. In this experiment you will use a type of voltage divider called a rheostat. ...
... the left, and equal to the battery voltage if it is all the way to the right. Therefore the voltage divider can be used to provide any voltage between zero and the power supply voltage. In this experiment you will use a type of voltage divider called a rheostat. ...
Chapter 17 Alternating Currents
... (b) non-useful - car-vibration at particular engine speed, unwanted oscillations in amplifiers at high frequencies (stray C’s), oscillations in suspended bridges due to wind/marching across etc. ...
... (b) non-useful - car-vibration at particular engine speed, unwanted oscillations in amplifiers at high frequencies (stray C’s), oscillations in suspended bridges due to wind/marching across etc. ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).