Digital Circuit I (EEI 101)
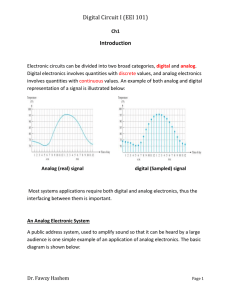
... Most waveforms encountered in digital systems are composed of series of pulses, sometimes called pulse trains, and can be classified as either periodic or nonperiodic. A periodic pulse waveform is one that repeats itself at a fixed interval, called a period (T). The frequency (f) is the rate at whic ...
... Most waveforms encountered in digital systems are composed of series of pulses, sometimes called pulse trains, and can be classified as either periodic or nonperiodic. A periodic pulse waveform is one that repeats itself at a fixed interval, called a period (T). The frequency (f) is the rate at whic ...
Chapter 5 – Series Circuits
... voltage across a resistor in a series circuit is equal to the value of the resistor times the total impressed voltage across the series elements divided by the total resistance of the series elements. The rule can be extended to voltage across two or more series elements if the resistance includes ...
... voltage across a resistor in a series circuit is equal to the value of the resistor times the total impressed voltage across the series elements divided by the total resistance of the series elements. The rule can be extended to voltage across two or more series elements if the resistance includes ...
ONET8531T 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... AGC AND RSSI The voltage drop across the internal photodiode supply-filter resistor is monitored by the bias and RSSI control circuit block, in the situation where a PIN diode is biased using the FILTER pins. If the DC input current exceeds a specified level then it is partially cancelled by means o ...
... AGC AND RSSI The voltage drop across the internal photodiode supply-filter resistor is monitored by the bias and RSSI control circuit block, in the situation where a PIN diode is biased using the FILTER pins. If the DC input current exceeds a specified level then it is partially cancelled by means o ...
LT6558 - 550MHz, 2200V/µs Gain of 1, Single Supply Triple Video Amplifier with Input Bias Control
... The LT®6558 is a high speed triple video amplifier with an internal fixed gain of 1 and a programmable DC input bias voltage. This amplifier features a 400MHz 2VP-P signal bandwidth, 2200V/µs slew rate and a unique ability to drive heavy output loads to 0.8V of the supply rails, making the LT6558 ideal ...
... The LT®6558 is a high speed triple video amplifier with an internal fixed gain of 1 and a programmable DC input bias voltage. This amplifier features a 400MHz 2VP-P signal bandwidth, 2200V/µs slew rate and a unique ability to drive heavy output loads to 0.8V of the supply rails, making the LT6558 ideal ...
PTH04070W: 3-A 3.3/5.5-V Input Adjustable
... The input voltage range of the PTH04070W is from 3 V to 5.5 V, allowing operation from either a 3.3-V or 5-V input bus. Using state-of-the-art switched-mode power-conversion technology, the PTH04070W can step down to voltages as low as 0.9 V from a 5-V input bus, with typically less than 1 W of powe ...
... The input voltage range of the PTH04070W is from 3 V to 5.5 V, allowing operation from either a 3.3-V or 5-V input bus. Using state-of-the-art switched-mode power-conversion technology, the PTH04070W can step down to voltages as low as 0.9 V from a 5-V input bus, with typically less than 1 W of powe ...
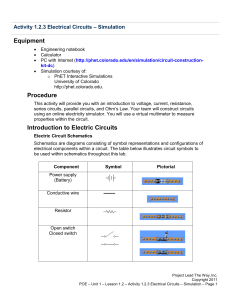
Activity 1.2.3 Electrical Circuits – Simulation
... Your team will construct a series and parallel circuit using the steps provided below. Creating a Circuit 4. Launch Circuit Construction Kit from University of Colorado at Boulder: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc 5. Drag a battery from the circuit palate on the rig ...
... Your team will construct a series and parallel circuit using the steps provided below. Creating a Circuit 4. Launch Circuit Construction Kit from University of Colorado at Boulder: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/circuit-construction-kit-dc 5. Drag a battery from the circuit palate on the rig ...
AD584 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... circuits. If R2 is zero, adjusting R1 to its lower limit will result in a loss of control over the output voltage. If precision voltages are required to be set at levels other than the standard outputs, the 20% absolute tolerance in the internal resistor ladder must be accounted for. Alternatively, ...
... circuits. If R2 is zero, adjusting R1 to its lower limit will result in a loss of control over the output voltage. If precision voltages are required to be set at levels other than the standard outputs, the 20% absolute tolerance in the internal resistor ladder must be accounted for. Alternatively, ...
4 TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS
... positive and negative polarity) is applied across the terminals of E-B so that VBE will reach the cut-in voltage (0.6V for silicon and 0.2V for germanium), a forward current IB will be generated between E-B. As shown in Fig. 4.2 b), if a reverse bias (P and N are respectively connected to negative a ...
... positive and negative polarity) is applied across the terminals of E-B so that VBE will reach the cut-in voltage (0.6V for silicon and 0.2V for germanium), a forward current IB will be generated between E-B. As shown in Fig. 4.2 b), if a reverse bias (P and N are respectively connected to negative a ...
MAX2202 RMS Power Detector General Description Features
... The MAX2202 generally requires a terminating resistor and series capacitor between the directional coupler’s output and detector RF input. As shown in the Typical Operating Characteristics, an S11 of less than -9dB is possible when a terminating resistor of 50Ω and series capacitor of 220pF are used ...
... The MAX2202 generally requires a terminating resistor and series capacitor between the directional coupler’s output and detector RF input. As shown in the Typical Operating Characteristics, an S11 of less than -9dB is possible when a terminating resistor of 50Ω and series capacitor of 220pF are used ...
UC3827-1 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The timing capacitor (CCT) is linearly charged with the charge current forcing the OSC pin to charge to a 3.4 V threshold. After exceeding this threshold, the RS flip-flop is set driving CLKSYN high and RDEAD low which discharges CCT. CT continues to discharge until it reaches a 0.5 V threshold and ...
... The timing capacitor (CCT) is linearly charged with the charge current forcing the OSC pin to charge to a 3.4 V threshold. After exceeding this threshold, the RS flip-flop is set driving CLKSYN high and RDEAD low which discharges CCT. CT continues to discharge until it reaches a 0.5 V threshold and ...
a High Accuracy Ultralow I , 200 mA, SOT-23, anyCAP
... The amplifier is constructed in such a way that at equilibrium it produces a large, temperature-proportional input “offset voltage” that is repeatable and very well controlled. The temperatureproportional offset voltage is combined with the complementary diode voltage to form a “virtual bandgap” vol ...
... The amplifier is constructed in such a way that at equilibrium it produces a large, temperature-proportional input “offset voltage” that is repeatable and very well controlled. The temperatureproportional offset voltage is combined with the complementary diode voltage to form a “virtual bandgap” vol ...
High Speed, ESD-Protected, Full-Duplex, ADM2490E i
... logic side of the interface. Therefore, the part has two main sections: a digital isolation section and a transceiver section (see Figure 21). The driver input signal, which is applied to the TxD pin and referenced to logic ground (GND1), is coupled across an isolation barrier to appear at the trans ...
... logic side of the interface. Therefore, the part has two main sections: a digital isolation section and a transceiver section (see Figure 21). The driver input signal, which is applied to the TxD pin and referenced to logic ground (GND1), is coupled across an isolation barrier to appear at the trans ...
document
... 4. The electrons carry energy from the cell to the lamp. 5. The electrons then return to the cell to get more energy. 6. The electrons are NOT used by the lamp. 7. Voltage measures the amount of energy each coulomb receives or gives. 8. Physics is the most important subject Science subject! ...
... 4. The electrons carry energy from the cell to the lamp. 5. The electrons then return to the cell to get more energy. 6. The electrons are NOT used by the lamp. 7. Voltage measures the amount of energy each coulomb receives or gives. 8. Physics is the most important subject Science subject! ...
2201_Homework_08
... 2. For the circuit shown, find the Thévenin equivalent circuit with respect to terminals a and b. Draw the Thévenin equivalent circuit. On the drawing, clearly show the terminals a and b, the value of the circuit elements, and the reference voltage for the Thévenin voltage source. iS1= 10iX ...
... 2. For the circuit shown, find the Thévenin equivalent circuit with respect to terminals a and b. Draw the Thévenin equivalent circuit. On the drawing, clearly show the terminals a and b, the value of the circuit elements, and the reference voltage for the Thévenin voltage source. iS1= 10iX ...
Supplementary Information
... The green curve is the 50 Hz original sine signal, the yellow curve is the signal after 180° phase-shift circuit. The pink curve is the output signal from the two-input adder. The phase-shift filter is an effective method to separate weak Nernstian potential signal from relatively strong interferenc ...
... The green curve is the 50 Hz original sine signal, the yellow curve is the signal after 180° phase-shift circuit. The pink curve is the output signal from the two-input adder. The phase-shift filter is an effective method to separate weak Nernstian potential signal from relatively strong interferenc ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).