
FOD2742A, FOD2742B, FOD2742C Optically Isolated Error Amplifier FOD2742A,
... obtain the most recent revision. Package specifications do not expand the terms of Fairchild’s worldwide terms and conditions, specifically the warranty therein, which covers Fairchild products. Always visit Fairchild Semiconductor’s online packaging area for the most recent package drawings: ...
... obtain the most recent revision. Package specifications do not expand the terms of Fairchild’s worldwide terms and conditions, specifically the warranty therein, which covers Fairchild products. Always visit Fairchild Semiconductor’s online packaging area for the most recent package drawings: ...
SGA-4386(Z)
... responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change comp ...
... responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change comp ...
Lab 3
... Connect the Hall effect sensor to one of the DC voltage sources on the lab power supply. Set the voltage to approximately 11 V. (The exact value of supply voltage is not critical since a voltage regulator has been built into the equipment to supply a bias of exactly 5 V to the sensor). Connect the ...
... Connect the Hall effect sensor to one of the DC voltage sources on the lab power supply. Set the voltage to approximately 11 V. (The exact value of supply voltage is not critical since a voltage regulator has been built into the equipment to supply a bias of exactly 5 V to the sensor). Connect the ...
Chap 8 First Order Circuits
... below each of these circuits. These equations merely came from applying KVL (to the circuit with the capacitor) and KCL (to the circuit with the inductor). How do we solve these equations? Note that they all have the same mathematical form! The form is a homogeneous, (i.e. one variable), linear, (i. ...
... below each of these circuits. These equations merely came from applying KVL (to the circuit with the capacitor) and KCL (to the circuit with the inductor). How do we solve these equations? Note that they all have the same mathematical form! The form is a homogeneous, (i.e. one variable), linear, (i. ...
MAX16963 Dual 2.2MHz, Low-Voltage Step-Down DC-DC Converter General Description
... losses at heavy loads and reduce critical/parasitic inductance, making the layout a much simpler task with respect to discrete solutions. Following a simple layout and footprint ensures first-pass success in new designs. The device is offered in a factory-preset output voltage or adjustable output-v ...
... losses at heavy loads and reduce critical/parasitic inductance, making the layout a much simpler task with respect to discrete solutions. Following a simple layout and footprint ensures first-pass success in new designs. The device is offered in a factory-preset output voltage or adjustable output-v ...
OPA691 Wideband, Current Feedback OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER With Disable FEATURES
... +5V to +12V Single-Supply ±2.5V to ±6V Dual-Supply ● UNITY-GAIN STABLE: 280MHz (G = 1) ● HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT: 190mA ● OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING: ±4.0V ● HIGH SLEW RATE: 2100V/µs ● LOW dG/dφ: 0.07% /0.02° ● LOW SUPPLY CURRENT: 5.1mA ● LOW DISABLED CURRENT: 150µA ● WIDEBAND +5V OPERATION: 190MHz (G = +2) ...
... +5V to +12V Single-Supply ±2.5V to ±6V Dual-Supply ● UNITY-GAIN STABLE: 280MHz (G = 1) ● HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT: 190mA ● OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING: ±4.0V ● HIGH SLEW RATE: 2100V/µs ● LOW dG/dφ: 0.07% /0.02° ● LOW SUPPLY CURRENT: 5.1mA ● LOW DISABLED CURRENT: 150µA ● WIDEBAND +5V OPERATION: 190MHz (G = +2) ...
Word Pro - Common Board Configuration Parallel Circuits
... Kirchoff’s current law states that the total current entering a junction or parallel circuits is equal to the current leaving that junction or parallel circuit. The total circuit current value in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the individual current values. The total circuit resistance is ...
... Kirchoff’s current law states that the total current entering a junction or parallel circuits is equal to the current leaving that junction or parallel circuit. The total circuit current value in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the individual current values. The total circuit resistance is ...
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
... pointing in the same direction, we assume that this component contributes a positive voltage If we encounter a source of emf pointing in the opposite direction, we consider that component to contribute a negative voltage Thus we will get the same information from the analysis of a simple circuit ...
... pointing in the same direction, we assume that this component contributes a positive voltage If we encounter a source of emf pointing in the opposite direction, we consider that component to contribute a negative voltage Thus we will get the same information from the analysis of a simple circuit ...
L25.ppt
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
L25.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
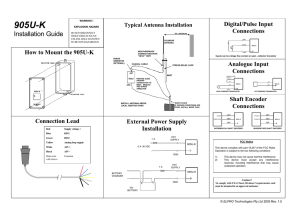
TLP7920(F) - Toshiba America Electronic Components
... Note 2: When either VIN+ or VIN- or both are equal to or greater than VDD1 - 2 V (e.g., if VDD1 = 5 V, when VIN+ and/or VIN- are equal to or greater than 5 V - 2 V = 3 V), isolation amplifiers go into one of the test modes. Do not raise either VIN+ or VIN- above this voltage to keep the device in fu ...
... Note 2: When either VIN+ or VIN- or both are equal to or greater than VDD1 - 2 V (e.g., if VDD1 = 5 V, when VIN+ and/or VIN- are equal to or greater than 5 V - 2 V = 3 V), isolation amplifiers go into one of the test modes. Do not raise either VIN+ or VIN- above this voltage to keep the device in fu ...
Hooke`s Law
... loads hinder the motion of the charge, and this hindrance is called the electrical resistance, R. Resistance is given in ohms (Ω, a capital Greek omega), where an ohm is a volt/amp. Inside a material that has electrical resistance, the kinetic energy of the moving charges is transformed into heat en ...
... loads hinder the motion of the charge, and this hindrance is called the electrical resistance, R. Resistance is given in ohms (Ω, a capital Greek omega), where an ohm is a volt/amp. Inside a material that has electrical resistance, the kinetic energy of the moving charges is transformed into heat en ...
RLC Series Circuit Lab
... 6) Take the other end of the PASCO patch cords used in step 5 above and connect one set of them across the resistor, one set across the inductor and one set across the capacitor. These will measure the voltage across each component. MAKE certain that the red leads are placed at a higher electric pot ...
... 6) Take the other end of the PASCO patch cords used in step 5 above and connect one set of them across the resistor, one set across the inductor and one set across the capacitor. These will measure the voltage across each component. MAKE certain that the red leads are placed at a higher electric pot ...
Proportion of Voltage to Resistance in a Series Circuit
... The total resistance, RTotal, of a series circuit is found by adding up the resistance values of the individual resistors. A single voltage, Vs, can be measured across each resistor. There exists a very important relationship between voltage and resistance: In a series electrical circuit with multip ...
... The total resistance, RTotal, of a series circuit is found by adding up the resistance values of the individual resistors. A single voltage, Vs, can be measured across each resistor. There exists a very important relationship between voltage and resistance: In a series electrical circuit with multip ...
posted
... IDENTIFY: The capacitor discharges exponentially through the voltmeter. Since the potential difference across the capacitor is directly proportional to the charge on the plates, the voltage across the plates decreases exponentially with the same time constant as the charge. SET UP: The reading of th ...
... IDENTIFY: The capacitor discharges exponentially through the voltmeter. Since the potential difference across the capacitor is directly proportional to the charge on the plates, the voltage across the plates decreases exponentially with the same time constant as the charge. SET UP: The reading of th ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).















![L 25 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Electric current (symbol I](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007903713_1-7c777a1a37e6fccaeb2ed3a9724ccb92-300x300.png)





