Physics Equation List :Form 5 - One
... The current flow into a resistor = the current flow inside the resistor = the current flows out from the The current flow into a parallel circuit is equal to the resistor sum of the current in each branches of the circuit. IA = IB = IC I = I1 + I2 Example ...
... The current flow into a resistor = the current flow inside the resistor = the current flows out from the The current flow into a parallel circuit is equal to the resistor sum of the current in each branches of the circuit. IA = IB = IC I = I1 + I2 Example ...
Transistor Devices Inc.
... The linearity of the external program is set to be within 2% above lA. The transient response of the dynaload is determined by the feedback loop characteristics of the constant current 1·egulator to achieve precision ...
... The linearity of the external program is set to be within 2% above lA. The transient response of the dynaload is determined by the feedback loop characteristics of the constant current 1·egulator to achieve precision ...
Lecture Notes
... The SAME amount of current I passes through three different resistors. • R2 has twice the cross-sectional area and the same length as R1, • R3 is three times as long as R1 but has same cross-sectional area as R1. ...
... The SAME amount of current I passes through three different resistors. • R2 has twice the cross-sectional area and the same length as R1, • R3 is three times as long as R1 but has same cross-sectional area as R1. ...
2W Constant Output Power Class-D Audio Amplifier with Adaptive
... 9 Parameter Measurement Information All parameters are measured according to the conditions described in the Specifications section. Many audio analyzers will not give the correct readings on a Class-D amplifier without additional filtering, even if they have an internal low-pass filter. A RC 30kHz ...
... 9 Parameter Measurement Information All parameters are measured according to the conditions described in the Specifications section. Many audio analyzers will not give the correct readings on a Class-D amplifier without additional filtering, even if they have an internal low-pass filter. A RC 30kHz ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not supported. ...
... Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not supported. ...
Moving coil meters for DC measurements
... Frequency is the number of cycles per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz), but frequencies tend to be high so kilohertz (kHz) and megahertz (MHz) are often used. 1kHz = 1000Hz and 1MHz = 1000000Hz. ...
... Frequency is the number of cycles per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz), but frequencies tend to be high so kilohertz (kHz) and megahertz (MHz) are often used. 1kHz = 1000Hz and 1MHz = 1000000Hz. ...
PHY 124 Lab 3
... equivalent resistance of R and the ammeter is close to resistance of R because if Rammeter «R then R + Rammeter R. This is only approximately true for the ammeter you will use in the lab. Because of this, the most significant source of error in this lab will come from the current measurements. Note ...
... equivalent resistance of R and the ammeter is close to resistance of R because if Rammeter «R then R + Rammeter R. This is only approximately true for the ammeter you will use in the lab. Because of this, the most significant source of error in this lab will come from the current measurements. Note ...
Blackbird Vacuum Tube Preamp
... clipping distortion, which is rich in both even and odd order harmonics for a saturated, sustaining distortion. In this mode the Blackbird can effortlessly climb the gain curve to produce a huge spectrum of powerful heavy metal sounds. The response always remains focused and tight for excellent stri ...
... clipping distortion, which is rich in both even and odd order harmonics for a saturated, sustaining distortion. In this mode the Blackbird can effortlessly climb the gain curve to produce a huge spectrum of powerful heavy metal sounds. The response always remains focused and tight for excellent stri ...
High PSR Low Drop-out Voltage Regulator (LDO)
... As discussed previously in section II-B the performance of the error amplifier is directly correlated with the PSSR of the LDO system. The intuitive mode analysis of P SRR helps in the definition of error amplifier specifications. Since the PSRR specifications of the LDO system are −70dB@1kHz, the e ...
... As discussed previously in section II-B the performance of the error amplifier is directly correlated with the PSSR of the LDO system. The intuitive mode analysis of P SRR helps in the definition of error amplifier specifications. Since the PSRR specifications of the LDO system are −70dB@1kHz, the e ...
Thevenin`s Theorem
... terminals, we would see VTH, the Open Circuit Voltage. This can be seen in the schematic on the right. In the laboratory, we could place a voltmeter across terminals A and B and measure VTH. Since the circuit is open at terminals A and B, no current flows through R3. With no current through R3, ther ...
... terminals, we would see VTH, the Open Circuit Voltage. This can be seen in the schematic on the right. In the laboratory, we could place a voltmeter across terminals A and B and measure VTH. Since the circuit is open at terminals A and B, no current flows through R3. With no current through R3, ther ...
Alternating Current
... (Q.35) What is the inductive reactance of a coil if current through it is 800 mA and the voltage across it is 40 V? (Q.36) Which of the following quantities remain constant in a step-down transformer? (A) Current (B) Voltage (C) Power (D) None of these ...
... (Q.35) What is the inductive reactance of a coil if current through it is 800 mA and the voltage across it is 40 V? (Q.36) Which of the following quantities remain constant in a step-down transformer? (A) Current (B) Voltage (C) Power (D) None of these ...
Electric basics
... You are probably wondering the difference between voltage and current like most people do. I could explain in a complicated way....but instead I will explain in simple terms. Using a water example is good in my opinion. Say I have a fire truck connected to a fire hydrant. Let's say this fire truck h ...
... You are probably wondering the difference between voltage and current like most people do. I could explain in a complicated way....but instead I will explain in simple terms. Using a water example is good in my opinion. Say I have a fire truck connected to a fire hydrant. Let's say this fire truck h ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws
... currents flowing in branches of the circuit. For example, in Fig. 2.1 the currents flowing in the four branches connected to the node have been defined as I1, I2, I3, I4 and Kirchhoff’s Current Law allows us to write down an equation relating these currents. Looking closely at Fig. 2.1, we see that ...
... currents flowing in branches of the circuit. For example, in Fig. 2.1 the currents flowing in the four branches connected to the node have been defined as I1, I2, I3, I4 and Kirchhoff’s Current Law allows us to write down an equation relating these currents. Looking closely at Fig. 2.1, we see that ...
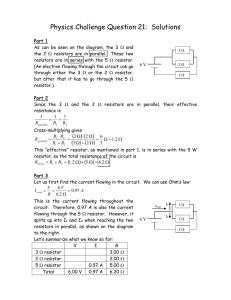
Physics Challenge Question 1: Solutions
... Adding many resistors in parallel makes it easier for the current to flow. If I keep adding resistors in parallel, it eventually becomes “infinitely easy” for the current to flow. (It has more ways to go, which lowers the resistance.) This can also be seen from the equation: ...
... Adding many resistors in parallel makes it easier for the current to flow. If I keep adding resistors in parallel, it eventually becomes “infinitely easy” for the current to flow. (It has more ways to go, which lowers the resistance.) This can also be seen from the equation: ...
Sensor Signal Conditioning for Biomedical Instrumentation
... to minimize its introduction in the first place (Webster, 1998). Appropriate shielding, sensor design, wiring, and grounding practice has very significant impact in terms of reducing noise onto the sensor reading, while judicial use of basic filtering and amplification can subsequently improve the S ...
... to minimize its introduction in the first place (Webster, 1998). Appropriate shielding, sensor design, wiring, and grounding practice has very significant impact in terms of reducing noise onto the sensor reading, while judicial use of basic filtering and amplification can subsequently improve the S ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).