FAN2315 TinyBuck™ 15 A Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator FAN2315 — TinyBuck™
... benefits include excellent line and load transient response, cycle-by-cycle current limiting, and no loop compensation required. ...
... benefits include excellent line and load transient response, cycle-by-cycle current limiting, and no loop compensation required. ...
OPA3832
... provides an output swing to within 30mV of ground and 60mV of the positive supply. The high output drive current and low differential gain and phase errors also make it ideal for single-supply consumer video products. Low distortion operation is ensured by high bandwidth (80MHz) and slew rate (350V/ ...
... provides an output swing to within 30mV of ground and 60mV of the positive supply. The high output drive current and low differential gain and phase errors also make it ideal for single-supply consumer video products. Low distortion operation is ensured by high bandwidth (80MHz) and slew rate (350V/ ...
Full-Bridge DMOS PWM Motor Driver A4950
... Allegro MicroSystems, LLC reserves the right to make, from time to time, such departures from the detail specifications as may be required to permit improvements in the performance, reliability, or manufacturability of its products. Before placing an order, the user is cautioned to verify that the i ...
... Allegro MicroSystems, LLC reserves the right to make, from time to time, such departures from the detail specifications as may be required to permit improvements in the performance, reliability, or manufacturability of its products. Before placing an order, the user is cautioned to verify that the i ...
Precision Adjustable Current-Limited Power
... The TPS2556/57 is a current-limited, power-distribution switch using N-channel MOSFETs for applications where short circuits or heavy capacitive loads will be encountered. This device allows the user to program the current-limit threshold between 500 mA and 5.0 A (typ) via an external resistor. This ...
... The TPS2556/57 is a current-limited, power-distribution switch using N-channel MOSFETs for applications where short circuits or heavy capacitive loads will be encountered. This device allows the user to program the current-limit threshold between 500 mA and 5.0 A (typ) via an external resistor. This ...
Electric_currents[1].
... hurtle around continuously. They collide with ions but because their movement is random there is no net energy transfer. ...
... hurtle around continuously. They collide with ions but because their movement is random there is no net energy transfer. ...
Measurements in electric circuits and Ohms Law (1st Common Lab)
... 7. Repeat steps 3-6 using the green resistor instead of the lamp. Note: because of the high current the resistor may burn when connected to 12V if left on too long – do not keep the power on any longer than is necessary to take your measurements. 8. Turn the power off and implement the circuit B bel ...
... 7. Repeat steps 3-6 using the green resistor instead of the lamp. Note: because of the high current the resistor may burn when connected to 12V if left on too long – do not keep the power on any longer than is necessary to take your measurements. 8. Turn the power off and implement the circuit B bel ...
SC4508A Buck or Buck-Boost (Inverting) Current Mode Controller POWER MANAGEMENT
... as a switch using current mode, programmable switching frequency architecture. During steady state operation, the switch is turned on each cycle and turned off when the voltage across current sense resistor exceeds the voltage level at COMP pin set by voltage loop error amplifier. A fixed 0.5V artif ...
... as a switch using current mode, programmable switching frequency architecture. During steady state operation, the switch is turned on each cycle and turned off when the voltage across current sense resistor exceeds the voltage level at COMP pin set by voltage loop error amplifier. A fixed 0.5V artif ...
Some Useful Electrical Circuit Information
... Power = Voltage x Current (applies generally) Power = V2/R = I2R (only applies to resistances) ...
... Power = Voltage x Current (applies generally) Power = V2/R = I2R (only applies to resistances) ...
Thevenin, Norton and Tellegen Theorems - GATE Study
... Example 2: Find the Thevenin voltage and Thevenin resistance of the given circuit ...
... Example 2: Find the Thevenin voltage and Thevenin resistance of the given circuit ...
Building Electrical System - CUNY Building Performance Lab
... • Work with a partner • Let people know where you are working ...
... • Work with a partner • Let people know where you are working ...
Understanding and Applying Current-Mode Control Theory
... For the buck regulator, this is equivalent to a ramp whose slope is VIN · Ri / L. Up-slope = (VIN - VO) · Ri / L Down-slope = VO · Ri / L For the boost regulator, this is equivalent to a ramp whose slope is VO · Ri / L. Up-slope = VIN · Ri / L Down-slope = (VO - VIN) · Ri / L For the buck-boost regu ...
... For the buck regulator, this is equivalent to a ramp whose slope is VIN · Ri / L. Up-slope = (VIN - VO) · Ri / L Down-slope = VO · Ri / L For the boost regulator, this is equivalent to a ramp whose slope is VO · Ri / L. Up-slope = VIN · Ri / L Down-slope = (VO - VIN) · Ri / L For the buck-boost regu ...
electric current - fwiatrowskimbhs
... • First, the conductivity of the material the wire is made of. If electrons can move through the material better, then there will be less resistance. • Second, it depends on the thickness of the wire. The thicker the wire, the more paths it offers for flow of charge; therefore, the less resistance i ...
... • First, the conductivity of the material the wire is made of. If electrons can move through the material better, then there will be less resistance. • Second, it depends on the thickness of the wire. The thicker the wire, the more paths it offers for flow of charge; therefore, the less resistance i ...
Direct Current Circuits - NUS Physics Department
... energy provided by the power supply is absorbed by the resistors. In a multi-loop circuit, the values of the resistors and the power supplies are known. It is necessary to determine how many independent currents are in the circuit, to label them and then to assign a direction to each current. Applic ...
... energy provided by the power supply is absorbed by the resistors. In a multi-loop circuit, the values of the resistors and the power supplies are known. It is necessary to determine how many independent currents are in the circuit, to label them and then to assign a direction to each current. Applic ...
APPLIED ELECTRONICS Outcome 1
... AMPLIFICATION and BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS Input transducers rarely produce sufficient voltage to operate output transducers, (motors, bulbs, etc.) directly. To overcome this problem, we need to AMPLIFY their output voltage or current. Amplifying devices are said to be active components as oppos ...
... AMPLIFICATION and BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS Input transducers rarely produce sufficient voltage to operate output transducers, (motors, bulbs, etc.) directly. To overcome this problem, we need to AMPLIFY their output voltage or current. Amplifying devices are said to be active components as oppos ...
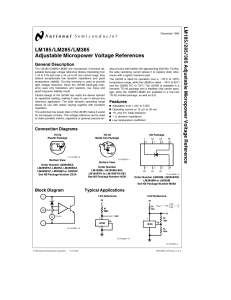
LM185 LM285 LM385 Adjustable Micropower Voltage References
... feature exceptionally low dynamic impedance and good temperature stability. On-chip trimming is used to provide tight voltage tolerance. Since the LM185 band-gap reference uses only transistors and resistors, low noise and good long-term stability result. Careful design of the LM185 has made the dev ...
... feature exceptionally low dynamic impedance and good temperature stability. On-chip trimming is used to provide tight voltage tolerance. Since the LM185 band-gap reference uses only transistors and resistors, low noise and good long-term stability result. Careful design of the LM185 has made the dev ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).




![Electric_currents[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012360684_1-64c8520b323976fcd197d28cbb535e82-300x300.png)