LTC6403-1 - 200MHz, Low Noise, Low Power Fully Differential Input
... voltage offset. Common mode power supply rejection (PSRRCM) is defined as the ratio of the change in supply voltage to the change in the common mode offset, VOUTCM – VOCM. Note 10: Output swings are measured as differences between the output and the respective power supply rail. Note 11: Extended ope ...
... voltage offset. Common mode power supply rejection (PSRRCM) is defined as the ratio of the change in supply voltage to the change in the common mode offset, VOUTCM – VOCM. Note 10: Output swings are measured as differences between the output and the respective power supply rail. Note 11: Extended ope ...
BD239/ A/B/ C NPN Epitaxial Silicon Transistor
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
... 2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. ...
Design of CMOS Crystal Oscillator with Low Power
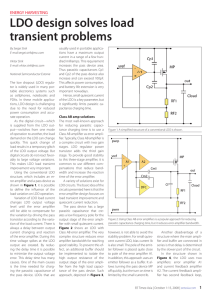
... combined with C1 and C2 to form a feedback network that tends to stabilize the frequency and supply 180 degree phase shift to the feedback path because of the π network. These conditions conform with the Barkhausen criterion of oscillation that overall phase shifts is zero and a closed loop gain sho ...
... combined with C1 and C2 to form a feedback network that tends to stabilize the frequency and supply 180 degree phase shift to the feedback path because of the π network. These conditions conform with the Barkhausen criterion of oscillation that overall phase shifts is zero and a closed loop gain sho ...
CHAPTER 4 ELEC 2015 REVIEW key
... A speaker has a resistance of 8 Ω. If 2.85 A of current is delivered to the speaker by the amplifier, the speaker is dissipating __________. ANS: The best answer/response to the above question/statement is: a) 23 W b) 65 W c) 1.02 W d) 22.5 W ...
... A speaker has a resistance of 8 Ω. If 2.85 A of current is delivered to the speaker by the amplifier, the speaker is dissipating __________. ANS: The best answer/response to the above question/statement is: a) 23 W b) 65 W c) 1.02 W d) 22.5 W ...
INA301-Q1 36-V, Automotive, High-Speed, Zero
... INA301-Q1 36-V, Automotive, High-Speed, Zero-Drift, Voltage-Output Current-Shunt Monitor With High-Speed, Overcurrent Protection Comparator 1 Features ...
... INA301-Q1 36-V, Automotive, High-Speed, Zero-Drift, Voltage-Output Current-Shunt Monitor With High-Speed, Overcurrent Protection Comparator 1 Features ...
lesson 2: worksheet - Walden University ePortfolio for Mike Dillon
... 4) Use the simulator to create a circuit that meets the following requirements: a. A 48-V battery b. A switch c. A current of 2.0 A d. An equivalent resistance of 24 e. At least four resisters with at least two parallel branches. f. The voltage and resistances should be labeled on the schematic fo ...
... 4) Use the simulator to create a circuit that meets the following requirements: a. A 48-V battery b. A switch c. A current of 2.0 A d. An equivalent resistance of 24 e. At least four resisters with at least two parallel branches. f. The voltage and resistances should be labeled on the schematic fo ...
Testing the Pulse Width Modulator
... Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a common technique used for speed control. To help understand how PWM works, consider the following analogy of riding a bike. When you wish to accelerate, you start peddling at a comfortable cadence (your output is on). Once you reach your desired speed you quit peddl ...
... Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a common technique used for speed control. To help understand how PWM works, consider the following analogy of riding a bike. When you wish to accelerate, you start peddling at a comfortable cadence (your output is on). Once you reach your desired speed you quit peddl ...
CHAPTER 4 ELEC 2015 REVIEW
... A speaker has a resistance of 8 Ω. If 2.85 A of current is delivered to the speaker by the amplifier, the speaker is dissipating __________. ANS: The best answer/response to the above question/statement is: a) 23 W b) 65 W c) 1.02 W d) 22.5 W ...
... A speaker has a resistance of 8 Ω. If 2.85 A of current is delivered to the speaker by the amplifier, the speaker is dissipating __________. ANS: The best answer/response to the above question/statement is: a) 23 W b) 65 W c) 1.02 W d) 22.5 W ...
12-Bit, 80 MSPS CommsADC? Analog-to-Digital
... little or no difference in performance between the singleended and differential-input configurations. The common mode of the clock inputs is set internally to AVDD/2 using 5-kΩ resistors (Figure 20). The clock input should be either a sine wave or a square wave having a 50% duty cycle. When driven w ...
... little or no difference in performance between the singleended and differential-input configurations. The common mode of the clock inputs is set internally to AVDD/2 using 5-kΩ resistors (Figure 20). The clock input should be either a sine wave or a square wave having a 50% duty cycle. When driven w ...
TOP Design Study - DCC - LIGO Document Control Center Portal
... The input signals are balanced about ground. The bias currents for the inputs to this circuit are supplied by the input signals, and each subsequent stage is biased by the previous one. The dc voltages to ground are therefore defined throughout the circuit. As the signals are not referred to any oth ...
... The input signals are balanced about ground. The bias currents for the inputs to this circuit are supplied by the input signals, and each subsequent stage is biased by the previous one. The dc voltages to ground are therefore defined throughout the circuit. As the signals are not referred to any oth ...
THS3201-EP
... The THS3201 is a wide-band, high-speed current-feedback amplifier, designed to operate over a wide supply range of ±3.3 V to ±7.5 V for today's high-performance applications. The wide supply range, combined with low distortion and high slew rate, makes the THS3201 ideally suited for arbitrary wavefo ...
... The THS3201 is a wide-band, high-speed current-feedback amplifier, designed to operate over a wide supply range of ±3.3 V to ±7.5 V for today's high-performance applications. The wide supply range, combined with low distortion and high slew rate, makes the THS3201 ideally suited for arbitrary wavefo ...
UCC2817A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... VCC: Connect to a stable source of at least 20 mA between 10 V and 17 V for normal operation. Bypass VCC directly to GND to absorb supply current spikes required to charge external MOSFET gate capacitances. To prevent inadequate gate drive signals, the output devices are inhibited unless VVCC exceed ...
... VCC: Connect to a stable source of at least 20 mA between 10 V and 17 V for normal operation. Bypass VCC directly to GND to absorb supply current spikes required to charge external MOSFET gate capacitances. To prevent inadequate gate drive signals, the output devices are inhibited unless VVCC exceed ...
MAX16975 28V, 1.2A Automotive Step-Down Converter with Low Operating Current General Description
... switch. The device operates with input voltages from 3.5V to 28V and tolerates input transients up to 42V. During undervoltage events, such as cold-crank conditions, the internal pass device maintains 94% duty cycle for a short time. An open-drain, active-low reset output helps to monitor the output ...
... switch. The device operates with input voltages from 3.5V to 28V and tolerates input transients up to 42V. During undervoltage events, such as cold-crank conditions, the internal pass device maintains 94% duty cycle for a short time. An open-drain, active-low reset output helps to monitor the output ...
Parallel Circuits
... will give the following readings: First set your meter to DC Volts If you place the positive lead (red) at point A, B, C or D and measure to points E, F, G, or H with the common lead (black) you will get the same reading of 15V ...
... will give the following readings: First set your meter to DC Volts If you place the positive lead (red) at point A, B, C or D and measure to points E, F, G, or H with the common lead (black) you will get the same reading of 15V ...
TRF2052 - uri=media.digikey
... channel for IF frequencies. The current-output charge pumps directly drive passive RC filter networks, to generate VCO control voltages. Fast main-channel frequency switching is achieved with a charge pump arrangement that increases the current drive and alters the loop-filter frequency response dur ...
... channel for IF frequencies. The current-output charge pumps directly drive passive RC filter networks, to generate VCO control voltages. Fast main-channel frequency switching is achieved with a charge pump arrangement that increases the current drive and alters the loop-filter frequency response dur ...
A 1.55 GHz to 2.45 GHz Center Frequency Continuous
... area of 2.2 mm2. A chip photograph is shown in Fig. 5. The measurement setup consists of a Rohde&Schwarz SMF100A for the generation of the clock signal, a SMU-200 for sinusoidal and modulated RF input signals and the spectrum analyzer FSQ-8. Measurements are automated with GPIB and read out with Mat ...
... area of 2.2 mm2. A chip photograph is shown in Fig. 5. The measurement setup consists of a Rohde&Schwarz SMF100A for the generation of the clock signal, a SMU-200 for sinusoidal and modulated RF input signals and the spectrum analyzer FSQ-8. Measurements are automated with GPIB and read out with Mat ...
Operational Amplifier Circuits Comparators and Positive Feedback
... Note that as Vin exceeds Vref, the voltage at the output of the comparator switches from VL to VH and the alarm is turned on. Notice that sometime after t1 the voltage Vin begins to decrease and at time t2 is crosses Vref . Now the output of the comparator switches back to VL and the alarm is turned ...
... Note that as Vin exceeds Vref, the voltage at the output of the comparator switches from VL to VH and the alarm is turned on. Notice that sometime after t1 the voltage Vin begins to decrease and at time t2 is crosses Vref . Now the output of the comparator switches back to VL and the alarm is turned ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).