Product Specification
... (9) The register setting values are rewritten by the influence of static electricity, a noise, etc. to unsuitable value, incorrect operating may occur. It is suggested that the SPI interface will setup as frequently as possible. ...
... (9) The register setting values are rewritten by the influence of static electricity, a noise, etc. to unsuitable value, incorrect operating may occur. It is suggested that the SPI interface will setup as frequently as possible. ...
LTC1734L-4.2
... and through the internal 0.06Ω current sense resistor. This current is close in magnitude, but slightly more than the collector current since it includes the base current. Amplifier A3, along with the P-channel FET, will force the same voltage that appears across the 0.06Ω resistor to appear across ...
... and through the internal 0.06Ω current sense resistor. This current is close in magnitude, but slightly more than the collector current since it includes the base current. Amplifier A3, along with the P-channel FET, will force the same voltage that appears across the 0.06Ω resistor to appear across ...
Chapter 4: RF/IF Circuits
... used at the input, hence, can provide further gain. By combining both output currents (typically, using a transformer) this voltage gain can be doubled. Finally, it will be apparent that the isolation between the various ports, in particular, from the LO port to the RF port, is inherently much lower ...
... used at the input, hence, can provide further gain. By combining both output currents (typically, using a transformer) this voltage gain can be doubled. Finally, it will be apparent that the isolation between the various ports, in particular, from the LO port to the RF port, is inherently much lower ...
P4M644YL, P8M648YL SDRAM MODULE 4M, 8M x 64 DIMM
... OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE, IOUT =3mA INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT, VIN = GND to Vcc OUTPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT, VOUT = GND to Vcc STANDBY CURRENT SCL=SDA=Vcc -0.3V, All other inputs = GND or 3.3V +10% ...
... OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE, IOUT =3mA INPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT, VIN = GND to Vcc OUTPUT LEAKAGE CURRENT, VOUT = GND to Vcc STANDBY CURRENT SCL=SDA=Vcc -0.3V, All other inputs = GND or 3.3V +10% ...
(DAQ) Block Optimized for Ultra Low Power
... Figure 11: Buffer driving the input In order to drive a differential input signal, a dual op-amp is used in a modified buffer configuration. It is critical that the op-amp has low power consumption such as OPA333, OPA336, OPA313 etc. The typical operating current for these is below 100 uA. A simple ...
... Figure 11: Buffer driving the input In order to drive a differential input signal, a dual op-amp is used in a modified buffer configuration. It is critical that the op-amp has low power consumption such as OPA333, OPA336, OPA313 etc. The typical operating current for these is below 100 uA. A simple ...
Word
... 1. Use the DVM probe wires to measure and record VLED and VR1 VLED = ____________ volts VR1 = ____________ volts 2. Is VLED + VR1 = VT? (YES/NO) 3. Using Ohm’s law, calculate the Current, I = ...
... 1. Use the DVM probe wires to measure and record VLED and VR1 VLED = ____________ volts VR1 = ____________ volts 2. Is VLED + VR1 = VT? (YES/NO) 3. Using Ohm’s law, calculate the Current, I = ...
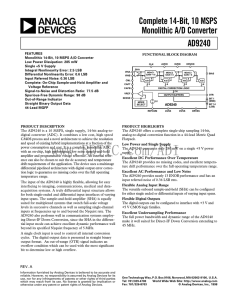
AD9240 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... levels in successive channels as well as sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. The AD9240 also performs well in communication systems employing Direct-IF Down Conversion, since the SHA in the differential input mode can achieve excellent dynamic performance ...
... levels in successive channels as well as sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. The AD9240 also performs well in communication systems employing Direct-IF Down Conversion, since the SHA in the differential input mode can achieve excellent dynamic performance ...
Vac = 120 V rms
... (cycles per second). In North America, AC system frequency is standardized at 60 Hertz. Much of the remaining world has chosen a 50 Hz standard. Alternating voltages also reverse polarity in a periodic manner with continually changing amplitude. The shape of the voltage waveform is dependent upon th ...
... (cycles per second). In North America, AC system frequency is standardized at 60 Hertz. Much of the remaining world has chosen a 50 Hz standard. Alternating voltages also reverse polarity in a periodic manner with continually changing amplitude. The shape of the voltage waveform is dependent upon th ...
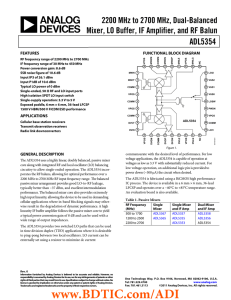
ADL5354 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Center Tap for Diversity Channel Input Balun. Bypass to ground using low inductance capacitor. RF Input for Diversity Channel. Internally matched to 50 Ω. Must be ac-coupled. Diversity Amplifier Bias Setting. Connect a 1.3 kΩ resistor to ground for typical operation. Diversity Channel Differential O ...
... Center Tap for Diversity Channel Input Balun. Bypass to ground using low inductance capacitor. RF Input for Diversity Channel. Internally matched to 50 Ω. Must be ac-coupled. Diversity Amplifier Bias Setting. Connect a 1.3 kΩ resistor to ground for typical operation. Diversity Channel Differential O ...
Behavioral Modeling
... ◦ Operating temperature ◦ Marginal supply voltage ◦ Output load capacitance ...
... ◦ Operating temperature ◦ Marginal supply voltage ◦ Output load capacitance ...
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB
... meter under test is high. The driving system of the meter consists of current coil connected in series with load and shunt coil connected in parallel to the supply. The moving system consists of a non-magnetic material and light material i.e aluminum disc. This disc is positioned in the air gap betw ...
... meter under test is high. The driving system of the meter consists of current coil connected in series with load and shunt coil connected in parallel to the supply. The moving system consists of a non-magnetic material and light material i.e aluminum disc. This disc is positioned in the air gap betw ...
AN4731, Understanding Injection Current on NXP ® Automotive
... Generally, automotive systems have voltages that are typically higher than the operating voltages of the MCU. As CMOS transistor geometries get smaller and smaller, safe operating voltages on the internal transistors get lower. Therefore, inputs and outputs of the devices must use larger geometry tr ...
... Generally, automotive systems have voltages that are typically higher than the operating voltages of the MCU. As CMOS transistor geometries get smaller and smaller, safe operating voltages on the internal transistors get lower. Therefore, inputs and outputs of the devices must use larger geometry tr ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).