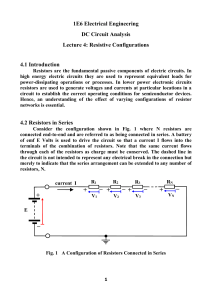
MAX15090/MAX15090A 2.7V to 18V, 12A, Hot-Swap Solution with Current Report Output General Description
... VCC Default UndervoltageLockout Hysteresis ...
... VCC Default UndervoltageLockout Hysteresis ...
Lect17
... keep current flowing: emf = L dI/dt (can be much larger than e) • However, now there’s no place for the current to go charges build up on switch contacts high voltage across switch gap •If the electric field exceeds the “dielectric strength” (~30 kV/cm in air) breakdown SPARK! This phenomeno ...
... keep current flowing: emf = L dI/dt (can be much larger than e) • However, now there’s no place for the current to go charges build up on switch contacts high voltage across switch gap •If the electric field exceeds the “dielectric strength” (~30 kV/cm in air) breakdown SPARK! This phenomeno ...
PAM99700 Description Pin Assignments
... LED current control without the need for high side current sensing or the design of any closed loop controllers. The IC uses very few external components and enables both Linear and PWM dimming of the LED current. A resistor connected to the RT pin programs the frequency of operation (or the off-tim ...
... LED current control without the need for high side current sensing or the design of any closed loop controllers. The IC uses very few external components and enables both Linear and PWM dimming of the LED current. A resistor connected to the RT pin programs the frequency of operation (or the off-tim ...
ESCC 2134000 (Resistors and Thermistors)
... (a) For high values of resistance, the limiting element voltage may prevent the rated dissipation being attained. (b) For the dissipation at temperatures other than +70°C, reference should be made to the rating graphs for variable resistors or the relevant Detail Specification. (c) For situations wh ...
... (a) For high values of resistance, the limiting element voltage may prevent the rated dissipation being attained. (b) For the dissipation at temperatures other than +70°C, reference should be made to the rating graphs for variable resistors or the relevant Detail Specification. (c) For situations wh ...
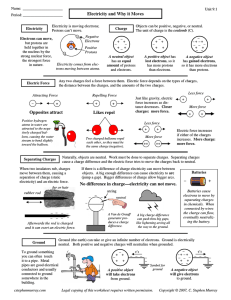
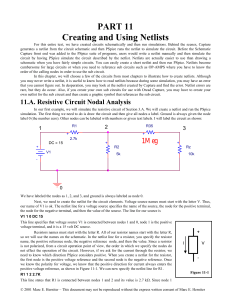
Electricity and Why it Moves
... Voltage (V), Current (I), or Resistance (R)? A _____ If you increase resistance what decreases? B. ____ If you increases voltage what increases? C. ____ If the current decreased what increased? D. _____ If current increased what increased? E. _____ If current increased what decreased? F. _____ If re ...
... Voltage (V), Current (I), or Resistance (R)? A _____ If you increase resistance what decreases? B. ____ If you increases voltage what increases? C. ____ If the current decreased what increased? D. _____ If current increased what increased? E. _____ If current increased what decreased? F. _____ If re ...
cop SMATV def FR int
... This unit conforms to standard EN60065 and is manufactured in die cast housing with F connectors and direct connection to the mains. Shielding factor to standard EN50083-2. It is possible to equalise cable losses from 0 to 20dB. Mains voltage 220-240V~ , 50-60Hz. Power consumption 3.5W. ...
... This unit conforms to standard EN60065 and is manufactured in die cast housing with F connectors and direct connection to the mains. Shielding factor to standard EN50083-2. It is possible to equalise cable losses from 0 to 20dB. Mains voltage 220-240V~ , 50-60Hz. Power consumption 3.5W. ...
dc/ac converters using silicon controlled rectifiers for fluorescent
... In lighting practice today there is a general trend towards higher levels of illumination. The lighting in public transport vehicles, such as railway carriages and buses, is no exception. The power in these vehicles is usually obtained from a dynamo oflimitedcapacity, togetherwith a buffer battery. ...
... In lighting practice today there is a general trend towards higher levels of illumination. The lighting in public transport vehicles, such as railway carriages and buses, is no exception. The power in these vehicles is usually obtained from a dynamo oflimitedcapacity, togetherwith a buffer battery. ...
LTC4075
... charging and there is insufficient power at DCIN, the USBPWR pin is high impedance. In all other cases, this pin is pulled low by an internal N-channel MOSFET, provided that there is power present at the DCIN, USBIN, or BAT inputs. This output is capable of sinking up to 1mA, making it suitable for d ...
... charging and there is insufficient power at DCIN, the USBPWR pin is high impedance. In all other cases, this pin is pulled low by an internal N-channel MOSFET, provided that there is power present at the DCIN, USBIN, or BAT inputs. This output is capable of sinking up to 1mA, making it suitable for d ...
Chip tantalum capacitors with open-function built
... of 3Ω or less at a temperature of 85±2°C, leave the sample at room temperature/humidity for 1 to 2h and measure the value. As per 4.35 JIS C 5101-1 As per 4.9 JIS C 5101-3 A force is applied to the terminal until it bends to 1mm and by a prescribed tool maintain the condition for 5s. (See the figure ...
... of 3Ω or less at a temperature of 85±2°C, leave the sample at room temperature/humidity for 1 to 2h and measure the value. As per 4.35 JIS C 5101-1 As per 4.9 JIS C 5101-3 A force is applied to the terminal until it bends to 1mm and by a prescribed tool maintain the condition for 5s. (See the figure ...
Application Note Driving IGBTs with unipolar gate voltage
... In applications with screw terminal power connections it is often possible to use a Rogowski coil for measurements. In most cases, however, it is not possible to measure directly in one arm. In smaller modules the load current is often brought to the PCB via solder pins. Here it is recommended to me ...
... In applications with screw terminal power connections it is often possible to use a Rogowski coil for measurements. In most cases, however, it is not possible to measure directly in one arm. In smaller modules the load current is often brought to the PCB via solder pins. Here it is recommended to me ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).