Structural and functional brain network correlates of depressive
... et al., 2014]. It is characterized by cognitive, motor and neuropsychiatric impairment. Depression can precede the onset of motor symptoms by many years [Tabrizi et al., 2009] and has a significant impact on morbidity [Beglinger et al., 2010] with a lifetime prevalence of 20% in the pre-symptomatic ...
... et al., 2014]. It is characterized by cognitive, motor and neuropsychiatric impairment. Depression can precede the onset of motor symptoms by many years [Tabrizi et al., 2009] and has a significant impact on morbidity [Beglinger et al., 2010] with a lifetime prevalence of 20% in the pre-symptomatic ...
The Cognitive Neuroscience of Human Memory Since H.M.
... 46%, n = 1 (Mayes et al. 2002)]. Neurohistological data from two of these patients (L.M. and W.H.) suggest an explanation for this striking consistency. As described above, these two patients had extensive cell loss in the hippocampus as well as in the dentate gyrus. Accordingly, a reduction in hipp ...
... 46%, n = 1 (Mayes et al. 2002)]. Neurohistological data from two of these patients (L.M. and W.H.) suggest an explanation for this striking consistency. As described above, these two patients had extensive cell loss in the hippocampus as well as in the dentate gyrus. Accordingly, a reduction in hipp ...
Synaptogenesis in the human cortex occurs between - UvA-DARE
... process. This had been shown by Huizen et al. (1985, 1987, see figure 2), where the bioelectrical activity of rat cerebral cortex cultures was blocked by tetrodotoxin (TTX). This prevented the large scale elimination of synapses. Furthermore, when the cultures grown in TTX-supplemented medium were s ...
... process. This had been shown by Huizen et al. (1985, 1987, see figure 2), where the bioelectrical activity of rat cerebral cortex cultures was blocked by tetrodotoxin (TTX). This prevented the large scale elimination of synapses. Furthermore, when the cultures grown in TTX-supplemented medium were s ...
Interactions between frontal cortex and basal ganglia in working
... the gate is closed, stimulus information does not strongly influence working memory, thereby allowing robust maintenance in the face of ongoing processing. The computational power of such a gating mechanism has been demonstrated in the LSTM model of Hochreiter and Schmidhuber (1997), which is based ...
... the gate is closed, stimulus information does not strongly influence working memory, thereby allowing robust maintenance in the face of ongoing processing. The computational power of such a gating mechanism has been demonstrated in the LSTM model of Hochreiter and Schmidhuber (1997), which is based ...
The impact of iconic gestures on foreign language word learning
... ment effect depends on the specific type of gesture, only iconic or symbolic gestures should lead to an enhancement of memory for words. Iconic gestures are not mere physical movements but are actions being defined by goal and expectancy [Rizzolatti et al., 2000]. They may draw a precise kinematic ima ...
... ment effect depends on the specific type of gesture, only iconic or symbolic gestures should lead to an enhancement of memory for words. Iconic gestures are not mere physical movements but are actions being defined by goal and expectancy [Rizzolatti et al., 2000]. They may draw a precise kinematic ima ...
Nancy A. O`Rourke Nicholas C. Weiler Kristina D
... identified 60 highly enriched proteins, some of which were not seen in heterogenous synapse purifications and may be specific to this synapse type 12. Future studies such as this will greatly contribute to a better understanding of synaptic diversity. Multiple lines of evidence from genomic, immunoh ...
... identified 60 highly enriched proteins, some of which were not seen in heterogenous synapse purifications and may be specific to this synapse type 12. Future studies such as this will greatly contribute to a better understanding of synaptic diversity. Multiple lines of evidence from genomic, immunoh ...
Neurons with Two Sites of Synaptic Integration Learn Invariant
... described by two main variables, corresponding to the two sites of integration (see Figure 1F): A is referred to as the activity of the neuron, and D represents the average potential at the apical dendrite. We simulate a rate coding neural network where a unit’s output is a real number representing ...
... described by two main variables, corresponding to the two sites of integration (see Figure 1F): A is referred to as the activity of the neuron, and D represents the average potential at the apical dendrite. We simulate a rate coding neural network where a unit’s output is a real number representing ...
`What` and `where` in the human brain
... selectivity has also been reported for parietal neurons, these neurons demonstrate even more complex spatial properties 127,281. Thus, much of the neural mechanism for both object vision and spatial vision can be viewed as a ‘bottom-up’ process subserved by feedforward projections between successive ...
... selectivity has also been reported for parietal neurons, these neurons demonstrate even more complex spatial properties 127,281. Thus, much of the neural mechanism for both object vision and spatial vision can be viewed as a ‘bottom-up’ process subserved by feedforward projections between successive ...
Grid Cell Firing May Arise From Interference of Theta Frequency
... DERIVATION OF BURGESS MODEL FROM EXPERIMENTAL CONSTANT H This section demonstrates how Eq. (1), determined entirely from experimental data, can be used to derive the model of grid cells presented by Burgess et al. (2005, 2007). This derivation demonstrates that the model is not just an ad hoc accoun ...
... DERIVATION OF BURGESS MODEL FROM EXPERIMENTAL CONSTANT H This section demonstrates how Eq. (1), determined entirely from experimental data, can be used to derive the model of grid cells presented by Burgess et al. (2005, 2007). This derivation demonstrates that the model is not just an ad hoc accoun ...
Reconsolidation of human memory
... for instance, often show a memory bias toward threat-related information (2). Moreover, drug addiction has been interpreted as an usurpation of systems of associative memory underlying reward-related learning (3). Altering such dysfunctional memories is a crucial step in the successful treatment of ...
... for instance, often show a memory bias toward threat-related information (2). Moreover, drug addiction has been interpreted as an usurpation of systems of associative memory underlying reward-related learning (3). Altering such dysfunctional memories is a crucial step in the successful treatment of ...
An fMRI Investigation of Emotional Engagement in Moral Judgement
... 1. During contemplation of dilemmas such as the footbridge dilemma, brain areas associated with emotion would be more active as compared to contemplation of dilemmas such as the trolley dilemma. 2. “A pattern of behavioral interference similar to that observed in cognitive tasks in which automatic p ...
... 1. During contemplation of dilemmas such as the footbridge dilemma, brain areas associated with emotion would be more active as compared to contemplation of dilemmas such as the trolley dilemma. 2. “A pattern of behavioral interference similar to that observed in cognitive tasks in which automatic p ...
spinal cord
... • Modern brain-imaging techniques suggest that consciousness is an emergent property of the brain based on activity in many areas of the cortex ...
... • Modern brain-imaging techniques suggest that consciousness is an emergent property of the brain based on activity in many areas of the cortex ...
Neurons of human nucleus accumbens
... with the obvious cytoarchitectural differences and lower impregnation quality of some parts of septal region, may be Golgi-dependent characteristics observed in these regions. It is well-known that the Golgi method is neural and highly selective. On the other hand, this technique provides useful inf ...
... with the obvious cytoarchitectural differences and lower impregnation quality of some parts of septal region, may be Golgi-dependent characteristics observed in these regions. It is well-known that the Golgi method is neural and highly selective. On the other hand, this technique provides useful inf ...
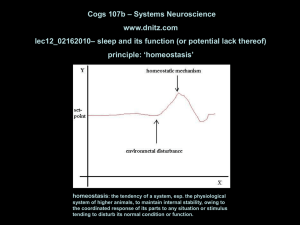
REM-off
... potentials may differ depending on the properties of other types of ion channels. The properties of those other ion channels may vary dynamically across time. In this sense, the ‘connection’, in terms of its influence on the postsynaptic neuron, varies across time, The ‘anatomy’ varies as a ‘functio ...
... potentials may differ depending on the properties of other types of ion channels. The properties of those other ion channels may vary dynamically across time. In this sense, the ‘connection’, in terms of its influence on the postsynaptic neuron, varies across time, The ‘anatomy’ varies as a ‘functio ...
Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light
... on the number of neurons that can be imaged at the same time and the total brain size of the animal under study. Thus, interactions between neurons in different brain areas are easily missed, and functionally related ensembles of neurons are undetectable if their activity is not tightly locked to a ...
... on the number of neurons that can be imaged at the same time and the total brain size of the animal under study. Thus, interactions between neurons in different brain areas are easily missed, and functionally related ensembles of neurons are undetectable if their activity is not tightly locked to a ...
Imaging Brain Slices
... Whole-cell patch clamp is commonly used to study electrophysiological properties of neurons in brain slices (Edwards et al., 1989). Using electrodes filled with fluorescent dyes, the whole-cell configuration of patch clamp injects the dyes into neurons by diffusion through the pipette tip into the n ...
... Whole-cell patch clamp is commonly used to study electrophysiological properties of neurons in brain slices (Edwards et al., 1989). Using electrodes filled with fluorescent dyes, the whole-cell configuration of patch clamp injects the dyes into neurons by diffusion through the pipette tip into the n ...
Effects of Misleading and Weapons 1 Running head
... originally present when tested ten minutes after witnessing an event. The misinformation effect strengthens with time: participants respond with significant inaccuracy when tested one week after exposure to the event and MPI (Loftus, E., 1975). The introduction of written MPI also increases the misi ...
... originally present when tested ten minutes after witnessing an event. The misinformation effect strengthens with time: participants respond with significant inaccuracy when tested one week after exposure to the event and MPI (Loftus, E., 1975). The introduction of written MPI also increases the misi ...
Full-Text PDF
... of each WM tract, and then statistical analysis performed on a voxel-by-voxel basis to test for group differences (see Figure 1e,f). Due to the requirement that corrections are performed for multiple comparisons across the many hundreds of voxels that constitute the WM skeleton in each subject, TBSS ...
... of each WM tract, and then statistical analysis performed on a voxel-by-voxel basis to test for group differences (see Figure 1e,f). Due to the requirement that corrections are performed for multiple comparisons across the many hundreds of voxels that constitute the WM skeleton in each subject, TBSS ...
Use of T2-weighted susceptibility contrast MRI for mapping the
... Rats were anesthetized with a mixture of halothane and air (0.8 ml/min flow rate). Halothane concentration was 4% to establish the anesthesia, 2% during installation of the rat in the NMR probe, 1% for normal rats, and 0.4–0.8% for rats bearing a glioma during MRI experiment. The body temperature of ...
... Rats were anesthetized with a mixture of halothane and air (0.8 ml/min flow rate). Halothane concentration was 4% to establish the anesthesia, 2% during installation of the rat in the NMR probe, 1% for normal rats, and 0.4–0.8% for rats bearing a glioma during MRI experiment. The body temperature of ...
Time constants
... constants. The stimulus is a voltage step (dotted line), and the membrane potential changes like an RC circuit, with a time constant given by τ = RC. Typical membrane time constants, measured in this way or in similar ways, are about 15 ms for neocortical pyramidal cells and 20-50 ms for other CNS n ...
... constants. The stimulus is a voltage step (dotted line), and the membrane potential changes like an RC circuit, with a time constant given by τ = RC. Typical membrane time constants, measured in this way or in similar ways, are about 15 ms for neocortical pyramidal cells and 20-50 ms for other CNS n ...
Visual Memory and Visual Perception Recruit
... (A) Modality-specific processing regions, demarcated in black, include visual, auditory, motor, and olfactory. It should be noted that the ventral visual pathway traverses the inferior occipital and temporal cortex (see text) but is shown in the lateral view for illustrative purposes. Unless otherwi ...
... (A) Modality-specific processing regions, demarcated in black, include visual, auditory, motor, and olfactory. It should be noted that the ventral visual pathway traverses the inferior occipital and temporal cortex (see text) but is shown in the lateral view for illustrative purposes. Unless otherwi ...
Signaling in large-scale neural networks
... Introduction The neuronal coding problem It seems that behavioral diversity and flexibility scale with the number of interconnected neurons in nervous systems. For this reason alone, the relation between behavior and the properties and activity of individual neurons becomes increasingly intractable ...
... Introduction The neuronal coding problem It seems that behavioral diversity and flexibility scale with the number of interconnected neurons in nervous systems. For this reason alone, the relation between behavior and the properties and activity of individual neurons becomes increasingly intractable ...