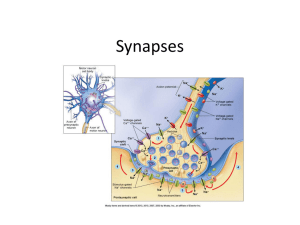
Nervous System
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... What types of automatic survival functions are controlled by the brainstem? ...
... What types of automatic survival functions are controlled by the brainstem? ...
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... • Neurotransmitters cause ion channels to open – Some channels let Na+ ions in depolarization – Other channels let K+ ions out and Cl- in hyperpolarization that inhibits action potential ...
... • Neurotransmitters cause ion channels to open – Some channels let Na+ ions in depolarization – Other channels let K+ ions out and Cl- in hyperpolarization that inhibits action potential ...
File
... Margie suffered damage to part of the surface of her brain after being struck by a golf club let loose by an irate golfer that had just sliced a key drive. As a result Margie has lost some sensory awareness of her left leg. Where is Margie’s brain damage (be specific). Your grandmother has begun to ...
... Margie suffered damage to part of the surface of her brain after being struck by a golf club let loose by an irate golfer that had just sliced a key drive. As a result Margie has lost some sensory awareness of her left leg. Where is Margie’s brain damage (be specific). Your grandmother has begun to ...
neurons
... Functions of the Cortex The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
... Functions of the Cortex The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... The limbic system, which includes the amygdala, the hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus, is not dedicated to a single function. Instead, structures within the limbic system have diverse functions, including emotion, motivation, olfaction, behavior, and memory. Furthermore, parts of the brain out ...
... The limbic system, which includes the amygdala, the hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus, is not dedicated to a single function. Instead, structures within the limbic system have diverse functions, including emotion, motivation, olfaction, behavior, and memory. Furthermore, parts of the brain out ...
Neuroscientists identify brain circuit necessary for memory formation
... Just one day after the fear-conditioning event, the were based on analyzing how damage to certain researchers found that memories of the event were brain areas affects memories. However, in 2012, being stored in engram cells in both the Tonegawa's lab developed a way to label cells hippocampus and t ...
... Just one day after the fear-conditioning event, the were based on analyzing how damage to certain researchers found that memories of the event were brain areas affects memories. However, in 2012, being stored in engram cells in both the Tonegawa's lab developed a way to label cells hippocampus and t ...
BOX 42.1 HOW DO WE LEARN ABOUT BRAIN EVOLUTION? There
... record can be studied. Because bones readily fossilize, whereas soft tissues seldom do, we know a lot about the bones of our ancestors, but much less about everything else. Of course one can infer much about some soft tissues, such as muscles, from their effects on bones, and this is true for brains ...
... record can be studied. Because bones readily fossilize, whereas soft tissues seldom do, we know a lot about the bones of our ancestors, but much less about everything else. Of course one can infer much about some soft tissues, such as muscles, from their effects on bones, and this is true for brains ...
Cerebral Palsy
... recurring and excessive discharge from neurons Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
... recurring and excessive discharge from neurons Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
Module 31: Studying and Building Memories
... Unconscious processing, thinking about a decision without realizing you are thinking about it; extremely helpful in evaluating evidence, making plans, and listening to ...
... Unconscious processing, thinking about a decision without realizing you are thinking about it; extremely helpful in evaluating evidence, making plans, and listening to ...
The Brain Game: Adopted from Rod Plotnik: Table created by Mary
... 15. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 16. The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates our natural biorhythms. 17. Michael J. Fox—the substantia nigra of the midbrain. 18. Gwen— ...
... 15. Grandma Mary—Broca’s Area—the part of the language system located in the frontal lobe (left hemisphere) is most important for producing speech. 16. The suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus regulates our natural biorhythms. 17. Michael J. Fox—the substantia nigra of the midbrain. 18. Gwen— ...
File
... ___________________ The long fiber that carries nerve impulses. ___________________ A bundle of axons. ___________________ The connection between adjacent neurons. ___________________ The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. ___________________ A rapid automatic response to a ...
... ___________________ The long fiber that carries nerve impulses. ___________________ A bundle of axons. ___________________ The connection between adjacent neurons. ___________________ The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. ___________________ A rapid automatic response to a ...
Ch. 11 Notes
... • Specializes in words, logic, analytical thinking, reading, and writing • Responsible for boundaries and knowing right from wrong • Knows and respects rules and deadlines Description of the Right-Hemisphere Functions • Alerts us to novelty; tells us when someone is lying or making a joke • Speciali ...
... • Specializes in words, logic, analytical thinking, reading, and writing • Responsible for boundaries and knowing right from wrong • Knows and respects rules and deadlines Description of the Right-Hemisphere Functions • Alerts us to novelty; tells us when someone is lying or making a joke • Speciali ...
Memory
... • He learned and recalled a list of nonsense syllables which had no meaning over several trials. • Forgetting was very rapaid over the first hour after learning which slowed down thereafter. ...
... • He learned and recalled a list of nonsense syllables which had no meaning over several trials. • Forgetting was very rapaid over the first hour after learning which slowed down thereafter. ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 8: Memory What Is Memory? LEARNING
... Forgetting is the inability to recall information that has previously been encoded. Initially, researchers believed that failure to access information regularly led to its loss from awareness, a theory known as decay theory. This theory is less popular now, and researchers instead emphasize other pr ...
... Forgetting is the inability to recall information that has previously been encoded. Initially, researchers believed that failure to access information regularly led to its loss from awareness, a theory known as decay theory. This theory is less popular now, and researchers instead emphasize other pr ...
3.E.2 Nervous System - kromko
... Axons conduct signals away from the cell body. Axons can be as long as many meters in large vertebrates. A “nerve” is a bundle of axons. ...
... Axons conduct signals away from the cell body. Axons can be as long as many meters in large vertebrates. A “nerve” is a bundle of axons. ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... unmyelinated axons. White matter is composed primarily of myelinated axons. During brain development, an outer, superficial region of gray matter forms from migrating peripheral neurons. External sheets of gray matter, called the cortex, cover the surface of most of the adult brain (the cerebrum and ...
... unmyelinated axons. White matter is composed primarily of myelinated axons. During brain development, an outer, superficial region of gray matter forms from migrating peripheral neurons. External sheets of gray matter, called the cortex, cover the surface of most of the adult brain (the cerebrum and ...
HERE - Covenant Cluster
... Memory Processes • Encoding the processing of information into the memory system • Storage the retention of encoded information over time • Retrieval the process of getting information out of memory ...
... Memory Processes • Encoding the processing of information into the memory system • Storage the retention of encoded information over time • Retrieval the process of getting information out of memory ...
TOC - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., ...