Article Analysis Form for Hock: Forty Studies that Changed Psychology
... The hypothesis was supported. Results indicated that the brains of the enriched rats were indeed different from those of the impoverished rats in many ways. The cerebral cortex of the enriched rats was significantly heavier and thicker. There was greater activity of the nervous system enzyme a ...
... The hypothesis was supported. Results indicated that the brains of the enriched rats were indeed different from those of the impoverished rats in many ways. The cerebral cortex of the enriched rats was significantly heavier and thicker. There was greater activity of the nervous system enzyme a ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... • Used to diagnose and determine treatment ofr brain disorders • Electroencephalogram (EEG): electrodes plated on scalp to record brain’s electrical activity • Alpha waves: person is awake in quiet state ...
... • Used to diagnose and determine treatment ofr brain disorders • Electroencephalogram (EEG): electrodes plated on scalp to record brain’s electrical activity • Alpha waves: person is awake in quiet state ...
Side-note of Interest: Representation of Images
... to information that can be recalled independently of how it was learned. Since Tulving, educators focus on semantic memory. Several models of semantic long-term memory have been developed i.e. network models, feature comparison models, propositional models, parallel distributed processing (PDP) mode ...
... to information that can be recalled independently of how it was learned. Since Tulving, educators focus on semantic memory. Several models of semantic long-term memory have been developed i.e. network models, feature comparison models, propositional models, parallel distributed processing (PDP) mode ...
The Memory Process
... Why does is exist? One explanation is REPRESSION: • In Frued’s psychoanalytic theory, the process of moving anxiety producing memories to the unconscious mind. ...
... Why does is exist? One explanation is REPRESSION: • In Frued’s psychoanalytic theory, the process of moving anxiety producing memories to the unconscious mind. ...
Anatomy and Physiology brain
... Lobes: Several large grooves (fissures) separate each side of the brain into four distinct regions called lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital. Each hemisphere has one of each of these lobes, which generally control function on the opposite side of the body. The different portions of ea ...
... Lobes: Several large grooves (fissures) separate each side of the brain into four distinct regions called lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital. Each hemisphere has one of each of these lobes, which generally control function on the opposite side of the body. The different portions of ea ...
Syllabus P140C (68530) Cognitive Science
... – Even if some units do not work, information is still preserved – because information is distributed across a network, performance degrades gradually as function of damage – (aka: robustness, fault-tolerance, graceful degradation) ...
... – Even if some units do not work, information is still preserved – because information is distributed across a network, performance degrades gradually as function of damage – (aka: robustness, fault-tolerance, graceful degradation) ...
Mirror neurons – the missing link for consciousness?
... you are conscious. You’re conscious of these words, and perhaps even a feeling of interest in where this article is leading. How are these mental experiences produced? For years researchers ignored consciousness as being too subjective for scientific study, but more recently it has become one of the ...
... you are conscious. You’re conscious of these words, and perhaps even a feeling of interest in where this article is leading. How are these mental experiences produced? For years researchers ignored consciousness as being too subjective for scientific study, but more recently it has become one of the ...
Nervous System
... Muscular System- receptors in the muscles allow the brain to know the position and movement of the body. Endocrine System- hormones allow information to the brain for neural processing. Reproductive hormones affect the development of the nervous system. Lymphatic System- the brain can stimulate the ...
... Muscular System- receptors in the muscles allow the brain to know the position and movement of the body. Endocrine System- hormones allow information to the brain for neural processing. Reproductive hormones affect the development of the nervous system. Lymphatic System- the brain can stimulate the ...
The Central Nervous System (outline, introduction)
... Introduction The brain or the Encephalon is possibly the most complex organ to examine within the human body. Although only weighing approximately 1,300g in the average adult, all behaviours, actions, thoughts and feelings originate from billions of neural networks interacting to create what we reco ...
... Introduction The brain or the Encephalon is possibly the most complex organ to examine within the human body. Although only weighing approximately 1,300g in the average adult, all behaviours, actions, thoughts and feelings originate from billions of neural networks interacting to create what we reco ...
Inner music and brain connectivity
... Attention problems? Only if they are very weak, then object recognition in poor lighting conditions may be impaired. Otherwise: poor visual imagination, memory for visual features, inability to draw from memory, recall and describe faces and objects, notice changes, slow in making puzzles, difficult ...
... Attention problems? Only if they are very weak, then object recognition in poor lighting conditions may be impaired. Otherwise: poor visual imagination, memory for visual features, inability to draw from memory, recall and describe faces and objects, notice changes, slow in making puzzles, difficult ...
UNIT II File
... Surface water and groundwater quality remediation Floodplain studies Impact of land use and climate change Impact of agriculture (irrigation, drainage, nutrients and pesticides, etc.) ...
... Surface water and groundwater quality remediation Floodplain studies Impact of land use and climate change Impact of agriculture (irrigation, drainage, nutrients and pesticides, etc.) ...
Memory Capacity of a Hebbian Learning Model with Inhibition
... can vary with N as f ∼ log N/N, then the capacity can be raised to O(1/f ) = O(N/ log N). If transition robability can also vary with N, the capacity can reach O(N 2 / log2 N). However, these conclusions were made by assuming all stimuli are of a single coding level and by ignoring the covariances b ...
... can vary with N as f ∼ log N/N, then the capacity can be raised to O(1/f ) = O(N/ log N). If transition robability can also vary with N, the capacity can reach O(N 2 / log2 N). However, these conclusions were made by assuming all stimuli are of a single coding level and by ignoring the covariances b ...
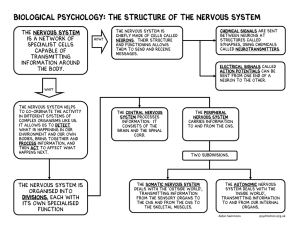
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... to co-ordinate the activity in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
... to co-ordinate the activity in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
The Sensorimotor Stage
... • Gap between dendrites of different neurons across which neurotransmitters travel to relay information from one neuron to another ...
... • Gap between dendrites of different neurons across which neurotransmitters travel to relay information from one neuron to another ...
Neurons & Transmission of Information
... impulses (sends messages) through the nervous system •contains 3 major parts--cell body, dendrites, & an axon –Cell body = contains the nucleus & carries out the metabolic (life-sustaining) functions of the neuron –dendrites = receivers of signals from other neurons (look like tree branches) –axon = ...
... impulses (sends messages) through the nervous system •contains 3 major parts--cell body, dendrites, & an axon –Cell body = contains the nucleus & carries out the metabolic (life-sustaining) functions of the neuron –dendrites = receivers of signals from other neurons (look like tree branches) –axon = ...
Memory - School District #83
... room, or does the TV or radio have to be on, etc…). You will be marked out of 5 for the quality of your response and the evidence of thought and effort put into your answer. ...
... room, or does the TV or radio have to be on, etc…). You will be marked out of 5 for the quality of your response and the evidence of thought and effort put into your answer. ...
Nervous System
... Sensory neurons carry signals from sense receptors in the CNS Motor neurons carry signals from the CNS to muscles or glands Interneurons form all the electrical connections within the CNS itself Unlike other cells, neurons cannot replace themselves. If the cell body of neuron is damaged or deg ...
... Sensory neurons carry signals from sense receptors in the CNS Motor neurons carry signals from the CNS to muscles or glands Interneurons form all the electrical connections within the CNS itself Unlike other cells, neurons cannot replace themselves. If the cell body of neuron is damaged or deg ...
Maximum entropy modeling of multi-neuron firing patterns in V1
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... Neurons are composed of dendrites that receive signals, a cell body with a nucleus, and an axon that conducts a nerve impulse away. Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take informatio ...
... Neurons are composed of dendrites that receive signals, a cell body with a nucleus, and an axon that conducts a nerve impulse away. Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take informatio ...
Teaching with the Brain-Based Natural Human Learning FACES
... As a learner goes through the stages of this natural learning process, the learner’s brain constructs its neural networks from the lowest twig up. ...
... As a learner goes through the stages of this natural learning process, the learner’s brain constructs its neural networks from the lowest twig up. ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... • Cell Body: Contains a large, centrally located nucleus and a large nucleolus. The cytoplasm contains many mitochondria and lysosomes. It also contains Golgi bodies and rough endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... • Cell Body: Contains a large, centrally located nucleus and a large nucleolus. The cytoplasm contains many mitochondria and lysosomes. It also contains Golgi bodies and rough endoplasmic reticulum. ...
Memory - teacherver.com
... Storage is the process in which information is retained over time and how it is represented in memory. The quality of memory is not only based in encoding but memory also needs to be stored properly after encoding. - memory storage involves three separate systems: sensory memory, short-term memory, ...
... Storage is the process in which information is retained over time and how it is represented in memory. The quality of memory is not only based in encoding but memory also needs to be stored properly after encoding. - memory storage involves three separate systems: sensory memory, short-term memory, ...
Brain Anatomy PPT
... In the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex neurons are distributed according to the part of the body that generates sensory input or receives motor input Frontal lobe ...
... In the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex neurons are distributed according to the part of the body that generates sensory input or receives motor input Frontal lobe ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
A Case for Computer Brain Interfaces
... predecessors, as they outsource their information filtration to computer systems. In comparison with Hoffman, Bawden acknowledges the limitations of the human neural processing capacity, however his analysis alludes to a possible solution: It may be argued that information overload is the natural an ...
... predecessors, as they outsource their information filtration to computer systems. In comparison with Hoffman, Bawden acknowledges the limitations of the human neural processing capacity, however his analysis alludes to a possible solution: It may be argued that information overload is the natural an ...